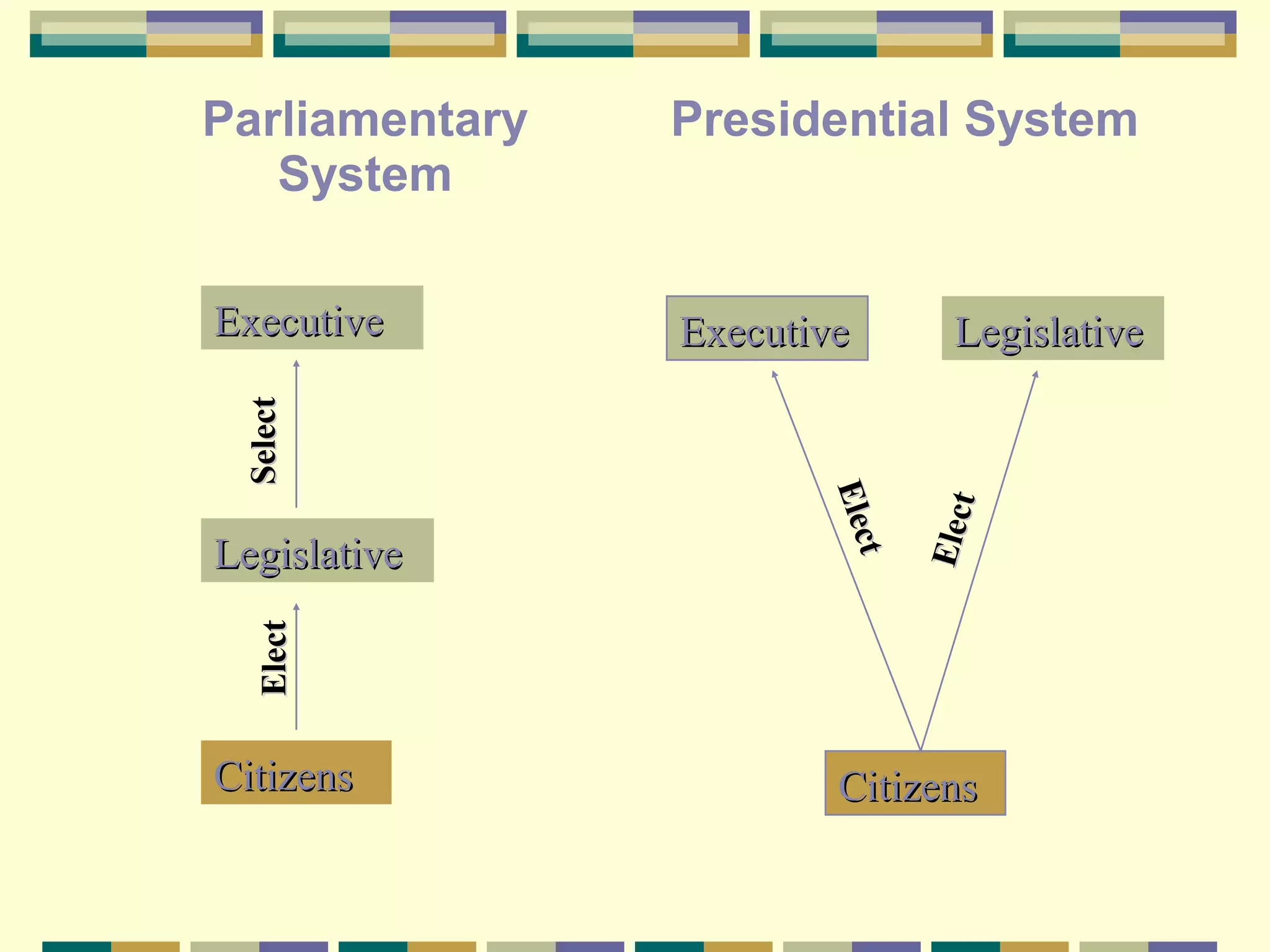
This document discusses different forms of government. It describes the three main types of government as autocracy, oligarchy, and democracy, based on who rules and citizen participation. It then examines specific forms of autocracy like dictatorship, absolute monarchy, and constitutional monarchy. Oligarchy is defined as rule by a small dominant group. Democracy is defined as rule by the people, with direct and representative forms. The two main systems of democratic government are also outlined as parliamentary and presidential.