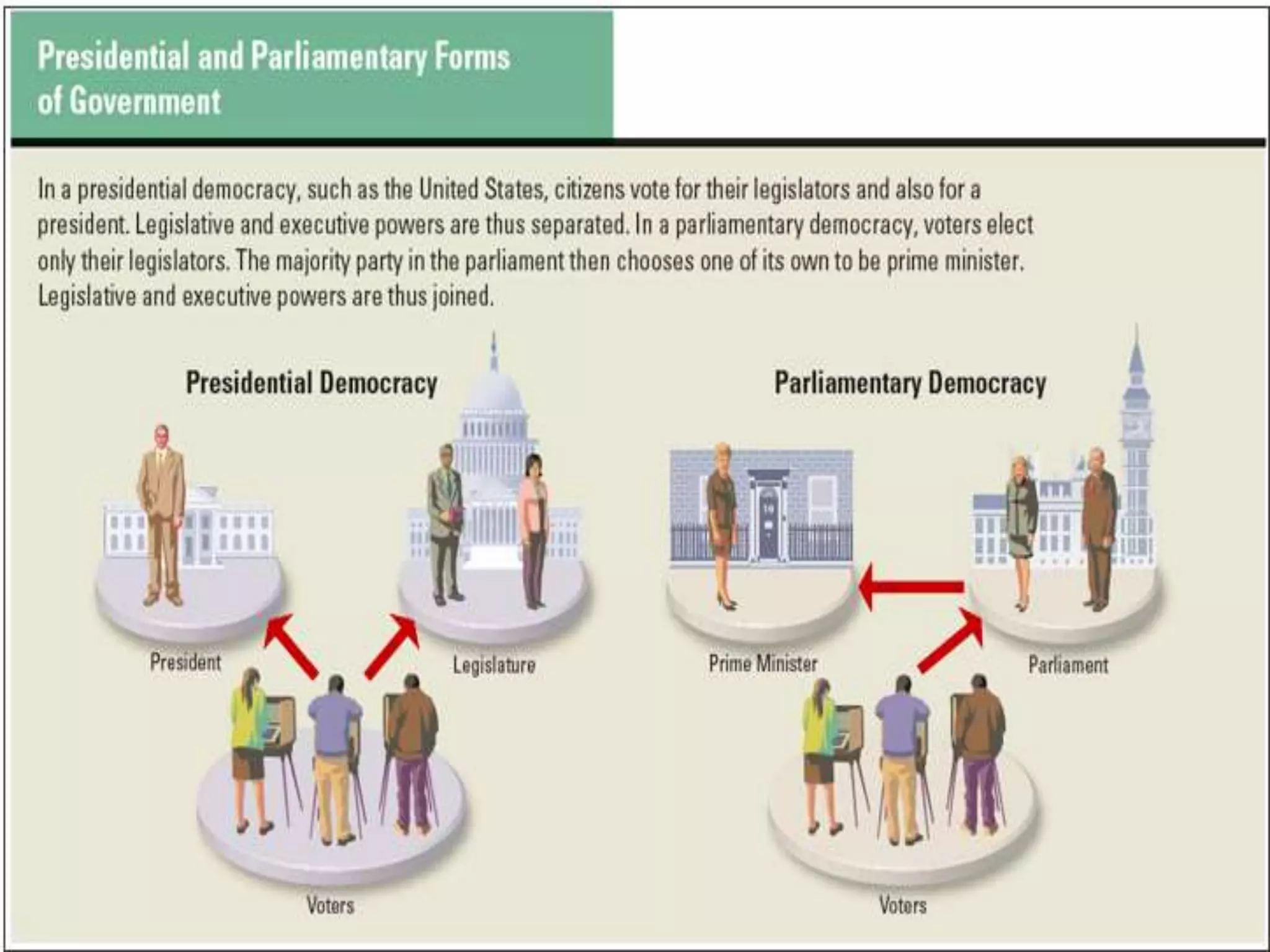
This document compares different forms of government around the world. It discusses monarchies, dictatorships, theocracies, single-party states, parliamentary democracies, and presidential democracies. For each system, it provides a definition and examples of modern countries that demonstrate that form of government. It notes that while most countries have some form of government, the main models that exist are rule by a single person, rule by an elite group, and rule by the broader population.