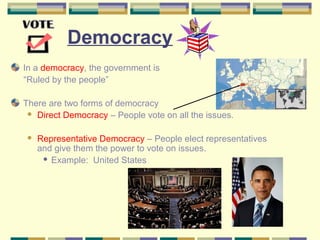
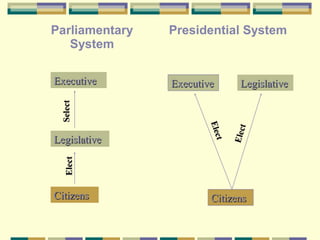
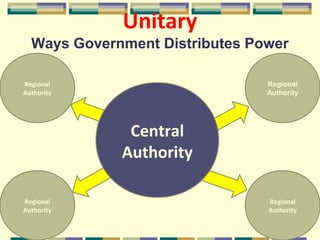
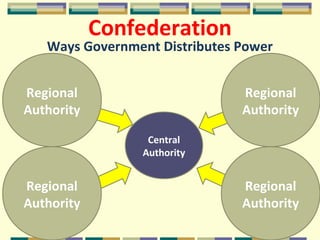
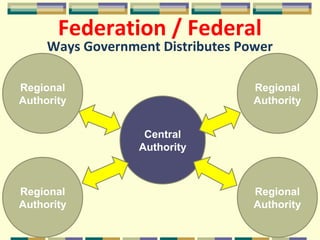
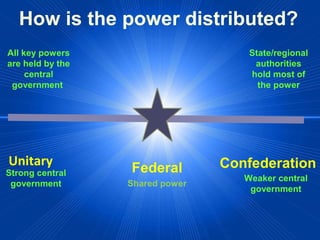
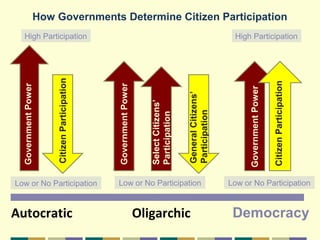
This document discusses different forms of government. It describes three main types - autocracy, oligarchy, and democracy - based on who rules and citizen participation. It also outlines three systems for distributing power - unitary, confederation, and federal. Unitary governments have all power centralized, while federal systems share power between central and regional authorities. The document provides examples like the UK and US to illustrate different combinations of type and system.