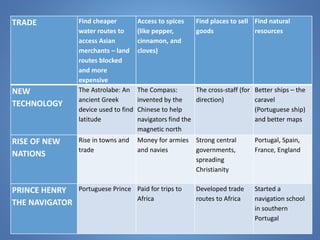
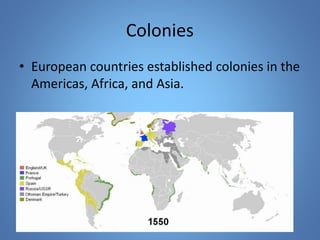
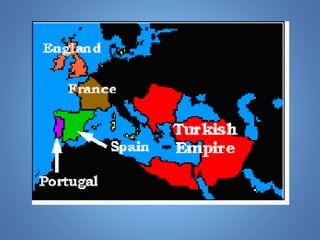
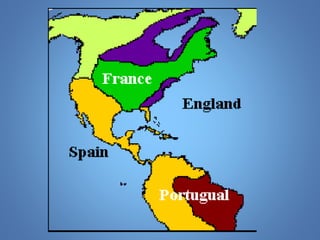
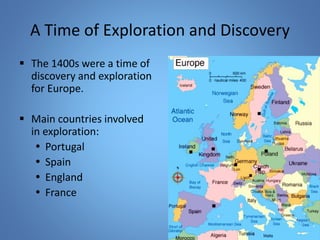
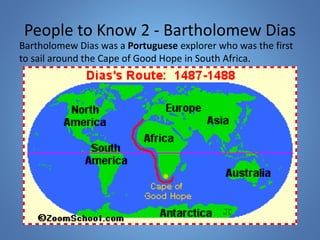
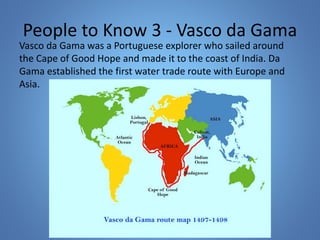
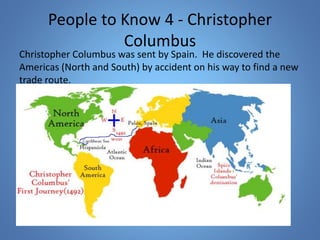
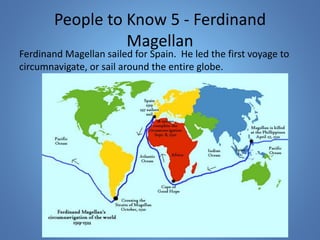
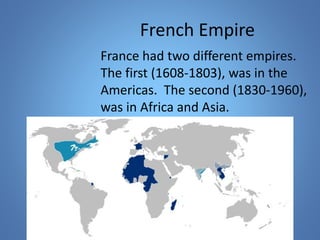
European exploration began in the 15th century as European powers sought new trade routes to Asia to access valuable spices and other goods. This document provides background on why Western European nations like Portugal, Spain, England, and France established overseas colonies starting in this era. It explores their motivations, including accessing Asian trade, spreading Christianity, finding natural resources, and gaining economic and geopolitical advantages over rivals. New technologies like the compass and caravel ships enabled explorers like da Gama, Columbus, and Magellan to discover new lands and establish European colonial empires across Africa, Asia, and the Americas.