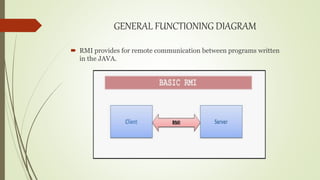
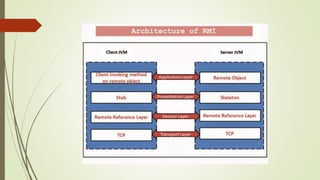
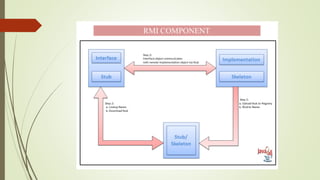
The document discusses Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI), which allows remote method calls between Java programs. RMI provides a thin client that maximizes hardware investments. It requires objects to be serializable and looked up from a registry. The RMI architecture has four layers - the application layer containing client and server logic, a proxy layer with stubs and skeletons, a transport layer managing connections, and a remote reference layer managing references. Key RMI components are the server containing remote objects, the client invoking methods, and the registry containing object references.