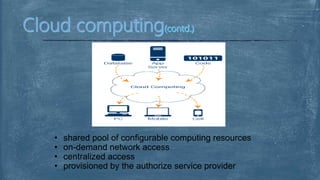
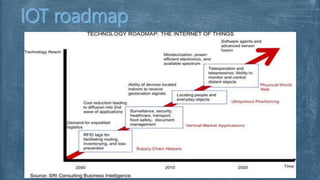
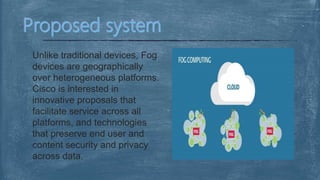
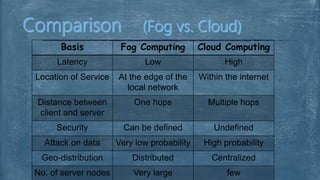
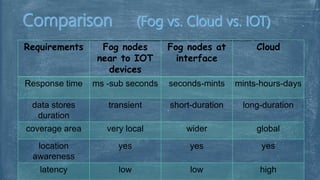
The document explores fog computing, a decentralized computing model that processes data at the network edge rather than exclusively in the cloud, enhancing efficiency and reducing latency. It compares fog computing with cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), detailing advantages, limitations, and applications in areas such as smart cities and real-time traffic management. Additionally, it describes the need for this model in the evolving IoT landscape and highlights the ongoing development efforts by Cisco's OpenFog Consortium.