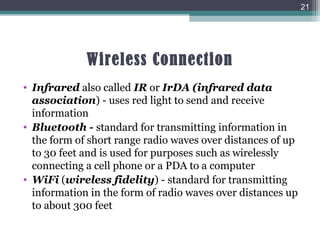
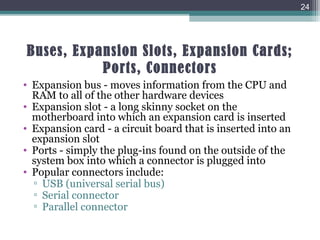
This document defines hardware and software, describes categories of each, and provides examples of common hardware and software components. It defines hardware as physical computer components like keyboards and monitors, and software as programs that operate computers. The document categorizes hardware into input, output, storage, processing, and connection devices. It describes two main types of software: application software for specific tasks, and system software like operating systems that support applications and hardware. Finally, it provides examples of common hardware components, like printers and disk drives, and software, like operating systems and web browsers.