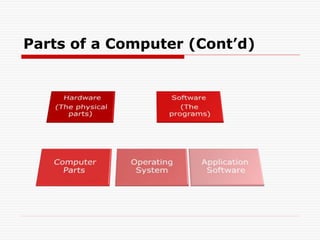
The document outlines fundamental concepts and skills related to computers, devices, file management, networks, and data security, aiming to equip candidates with basic ICT proficiency. It covers types of computers and devices, their components, as well as software types and licensing agreements. The goal is to enable users to effectively manage files, understand data protection, and utilize various communication technologies.