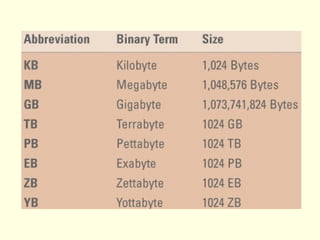
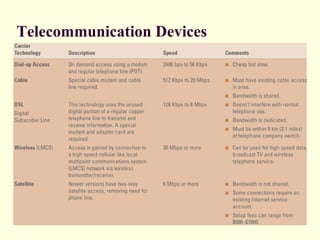
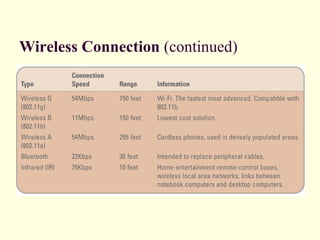
This document defines hardware and software, describes common hardware and software categories, and provides examples. It discusses input, output, storage, and telecommunication devices. The key points are: Hardware are physical computer components while software are programs. There are six hardware categories including input/output devices, storage, and CPUs. There are two main types of software: application software for specific tasks and system software to manage hardware and applications. Common devices include keyboards, monitors, printers, and network cards.