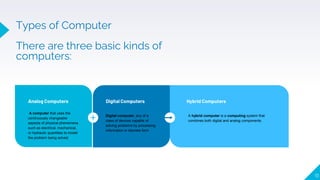
The document provides an introduction to computers, explaining their definition, characteristics, and functionalities, such as input, processing, output, and storage. It categorizes computers into digital, analog, and hybrid types, along with classifications like microcomputers, mini computers, mainframe computers, and supercomputers. Additionally, it discusses networks, the internet, intranets, applications, and software, highlighting both the advantages and disadvantages of computer use.