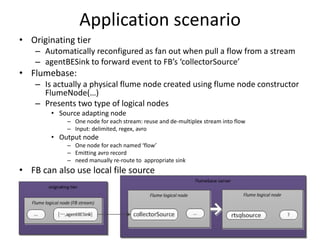
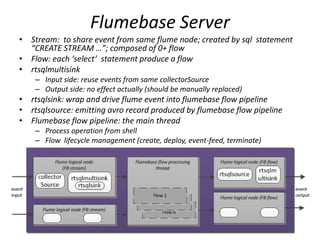
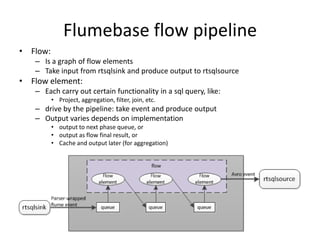
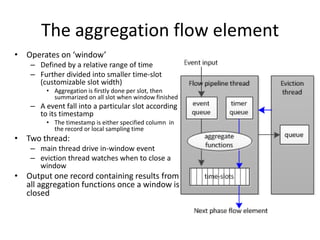
This document summarizes a study on FlumeBase, a system for processing streaming data using SQL queries. It describes FlumeBase's architecture, including how it integrates with Flume and uses SQL queries to define streams, flows, and flow elements for aggregating data. The document notes some potential issues with FlumeBase regarding window alignment, deployment integration with Flume, and code maturity.

![Features
• SQL
– CREATE STREAM stream_name (col_name data_type [, ...])
FROM [LOCAL] {FILE | NODE | SOURCE} input_spec
[EVENT FORMAT format_spec
[PROPERTIES (key = val, …)]]
– SELECT select_expr, select_expr ... FROM stream_reference
[ JOIN stream_reference ON join_expr OVER range_expr, JOIN ... ]
[ WHERE where_condition ]
[ GROUP BY column_list ] [ OVER range_expr ] [ HAVING
having_condition ]
[ WINDOW window_name AS ( range_expr ), WINDOW ... ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flumebase-study-willis-130319035743-phpapp01/85/FlumeBase-Study-7-320.jpg)
