Embed presentation
Downloaded 17 times

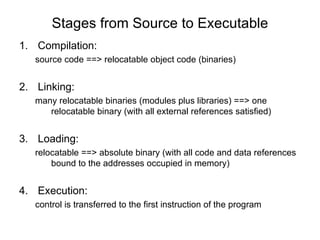
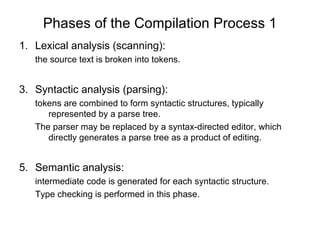
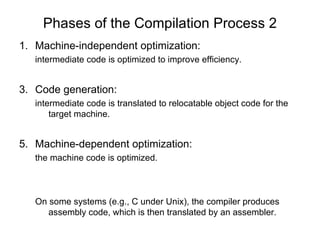

The document outlines the stages of compilation from source code to executable files, including key processes like lexical analysis, syntactic analysis, and semantic analysis. It describes the conversion of code into relocatable object code, the linking of multiple binaries, and the final loading into memory for execution. The document also touches on optimization stages that enhance code efficiency and address machine-specific requirements.



