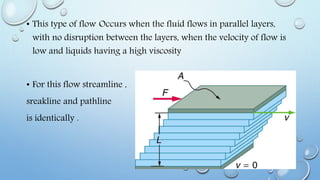
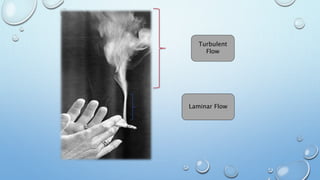
1) The document discusses laminar and turbulent fluid flow. Laminar flow involves fluid particles moving in parallel layers with no disruption between layers, while turbulent flow involves fluid particles moving in a zig-zag pattern and mixing with each other.
2) Key properties of laminar flow include a Reynolds number less than 2000, low velocity, dye not mixing with water, and simple mathematical analysis. Turbulent flow has a Reynolds number greater than 4000, high velocity, rapid dye mixing, and irregular particle paths.
3) Examples given of laminar flow include blood flow through capillaries and fountains like in Burj Al Arab in Dubai. Turbulent flow is much more common.