Embed presentation
Download to read offline
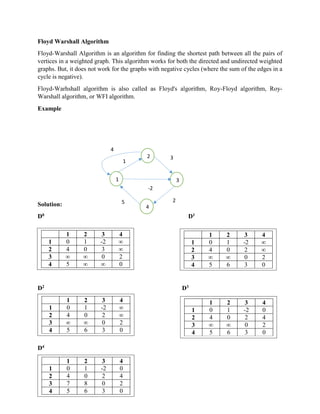
![Floyd Warshall Algorithm Pseudocode
n = no of vertices
D = matrix of dimension n*n
for k = 1 to n
for i = 1 to n
for j = 1 to n
Dk[i, j] = min (Dk-1[i, j], Dk-1[i, k] + Dk-1[k, j])
return D
Explanation
Dk[i, j] = min (Dk-1[i, j], Dk-1[i, k] + Dk-1[k, j])
D1[2, 3] = min (D1-1[2, 3], D1-1[2, 1] + D1-1[1, 3])
= min (D0[2, 3], D0[2, 1] + D0[1, 3])
= min (3, 4 + (-2)) = min (3, 2) = 2
D1[2, 4] = min (D1-1[2, 4], D1-1[2, 1] + D1-1[1, 4])
= min (D0[2, 4], D0[2, 1] + D0[1, 4])
= min (∞, 4+ ∞) = ∞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floydwarshallalgorithm-210706144334/85/Floyd-warshall-algorithm-2-320.jpg)

The Floyd-Warshall algorithm finds the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a weighted graph. It can handle both directed and undirected graphs, except those with negative cycles. The algorithm works by iteratively updating a distance matrix to track the shortest distances between all pairs as it considers paths that pass through intermediate vertices. It runs in O(n3) time, where n is the number of vertices.

![Floyd Warshall Algorithm Pseudocode
n = no of vertices
D = matrix of dimension n*n
for k = 1 to n
for i = 1 to n
for j = 1 to n
Dk[i, j] = min (Dk-1[i, j], Dk-1[i, k] + Dk-1[k, j])
return D
Explanation
Dk[i, j] = min (Dk-1[i, j], Dk-1[i, k] + Dk-1[k, j])
D1[2, 3] = min (D1-1[2, 3], D1-1[2, 1] + D1-1[1, 3])
= min (D0[2, 3], D0[2, 1] + D0[1, 3])
= min (3, 4 + (-2)) = min (3, 2) = 2
D1[2, 4] = min (D1-1[2, 4], D1-1[2, 1] + D1-1[1, 4])
= min (D0[2, 4], D0[2, 1] + D0[1, 4])
= min (∞, 4+ ∞) = ∞](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/floydwarshallalgorithm-210706144334/85/Floyd-warshall-algorithm-2-320.jpg)