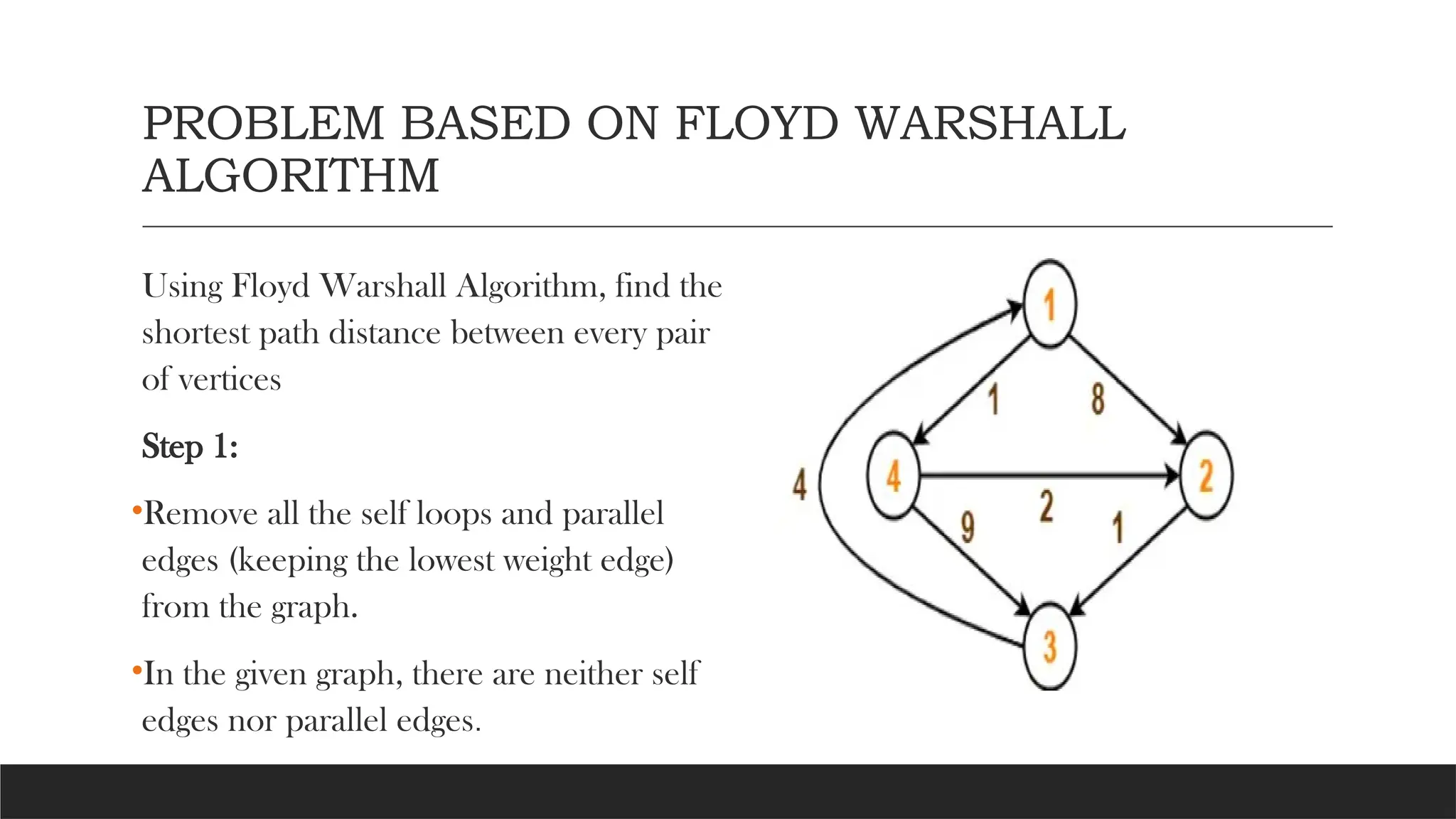
Floyd's algorithm is a dynamic programming-based method for finding the shortest paths between all pairs of vertices in a graph, with a time complexity of O(n^3). It is particularly useful for dense graphs and offers advantages like handling negative edge weights and providing transitive closures. The algorithm has applications in computer network routing, transportation logistics, and road network analysis.