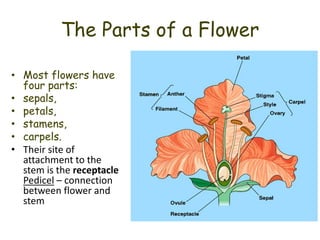
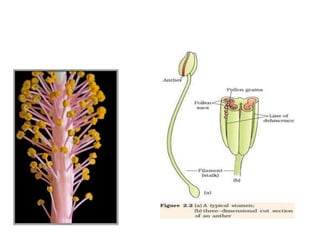
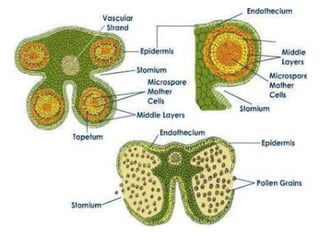
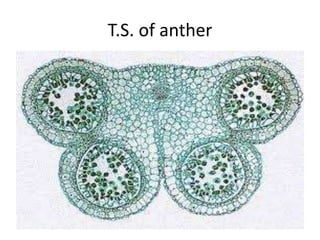
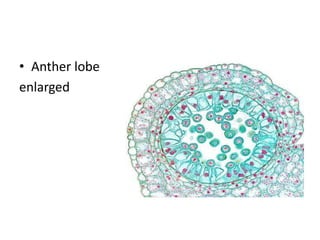
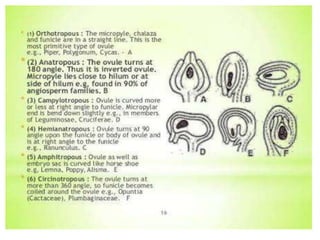
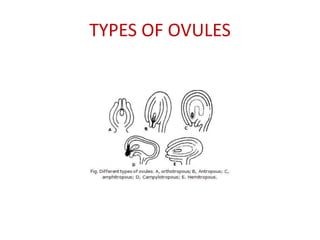
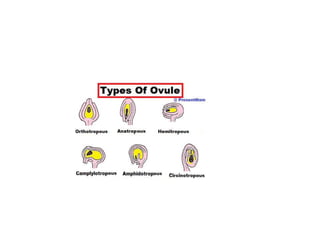
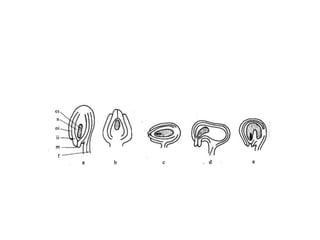
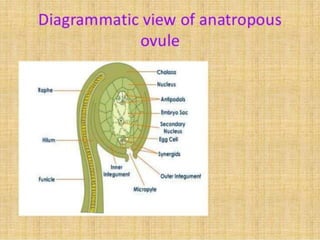
The document summarizes the structure and development of flowers and their reproductive organs. It describes that a flower contains four main parts - sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. Sepals and petals are non-reproductive, while stamens are the male organs that produce pollen and carpels are the female organs containing ovules. It then explains the structure of these reproductive organs in detail and the development of pollen grains into male gametophytes and fertilization of ovules to form seeds.