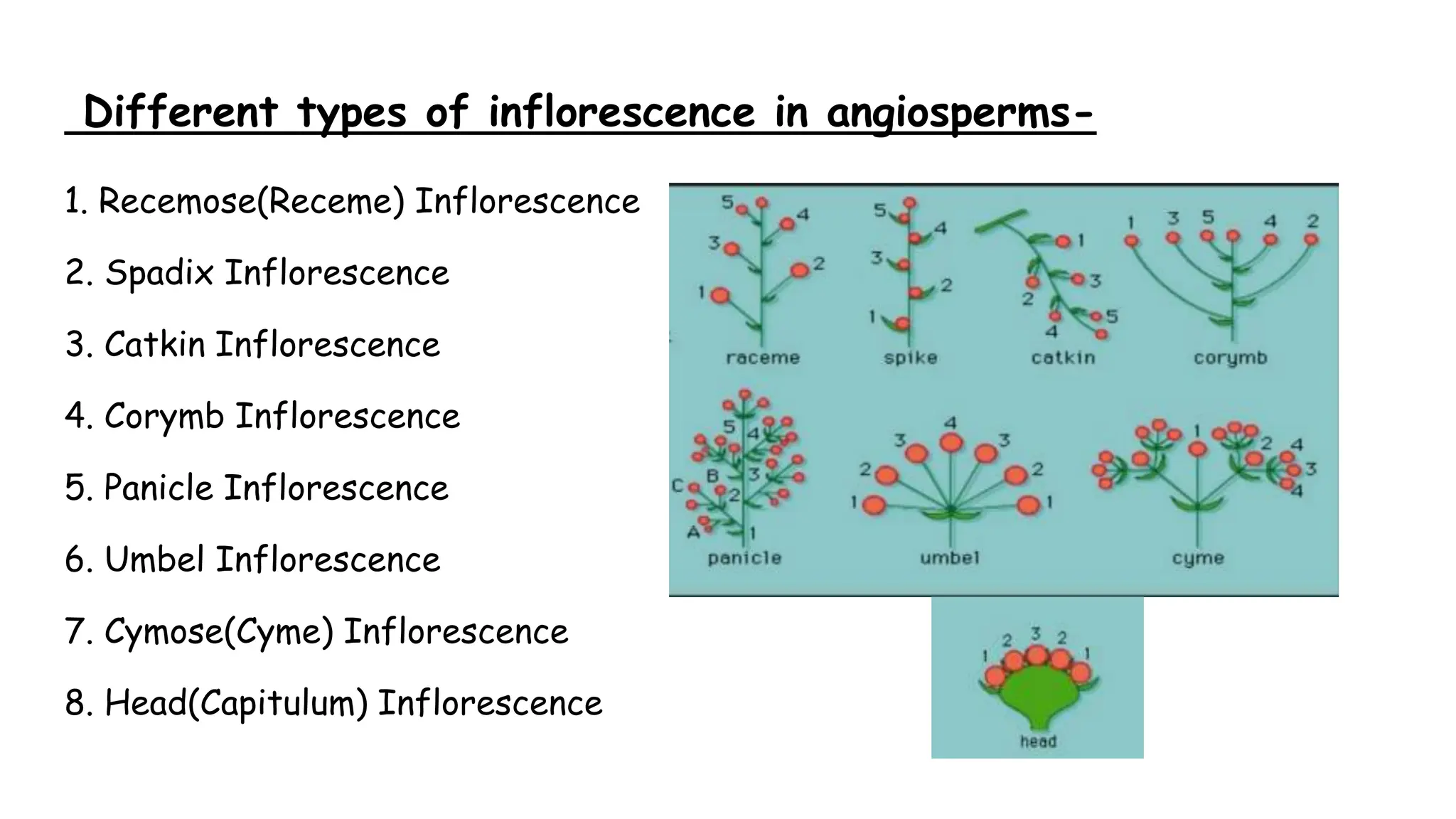
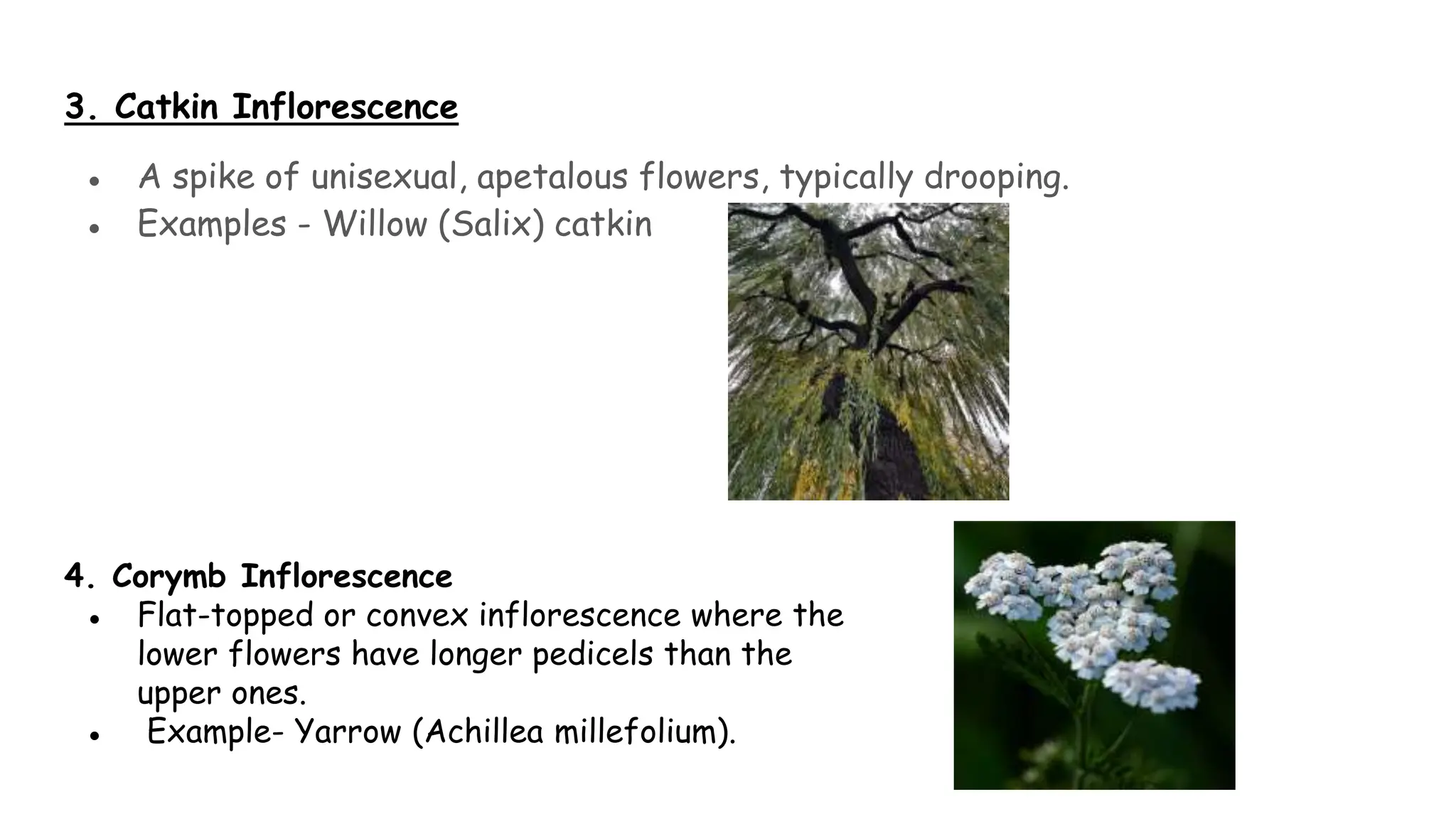
The document discusses the different types of inflorescences found in angiosperms. It identifies 8 main types: recemose, spadix, catkin, corymb, panicle, umbel, cymose, and head inflorescences. Each has distinct characteristics, such as spadix having small, densely packed flowers surrounded by a spathe, while panicles are branched racemes. The inflorescence structures play an important role in the reproduction of flowering plants.