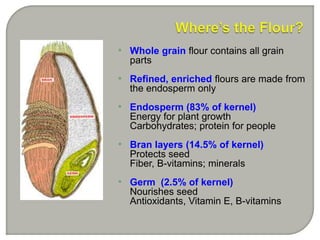
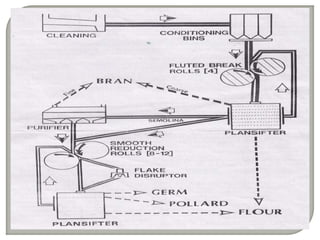
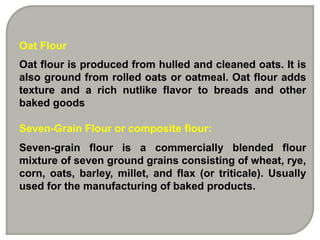
Wheat flour is produced through a milling process that breaks and grinds wheat kernels to extract the endosperm for flour while removing the bran and germ. The milling process produces different types of flour based on gluten content and particle size. Flour can be made from other grains like corn, rice, rye and produces different flour types based on degree of milling and grain used.