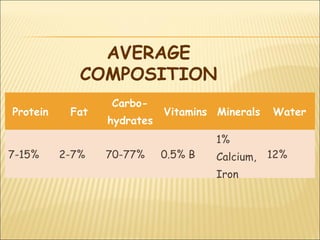
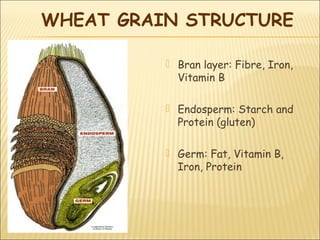
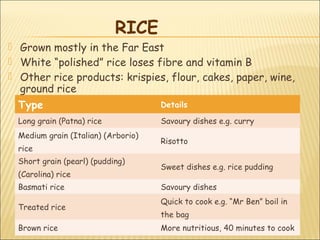
This document summarizes information about cereals including the main types of cereals like wheat, oats, rice, maize, rye and barley. It provides details on the average nutritional composition of cereals, their nutritive value, effects of cooking on cereals, wheat grain structure and gluten, different types of flour, pasta, rice and other seeds.