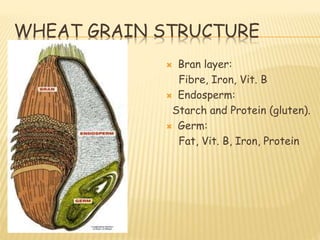
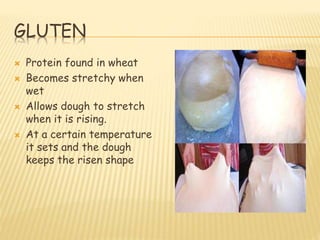
This document provides information about various cereal grains and seeds that are cultivated for food. It discusses the main cereals - wheat, oats, rice, maize, rye and barley. For each cereal, it outlines their nutritional composition and common uses. The document also covers the structure of wheat grains, the role of gluten in breadmaking, different types of flour, and other wheat and rice products. It concludes with a brief overview of other seeds that are rich in nutrients.