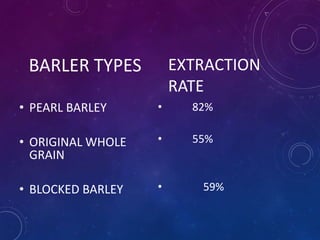
This document discusses the milling process for barley. It begins with an introduction to barley, including that it is the fourth most important cereal. The objectives of milling barley are then outlined. The milling process involves several steps: preliminary cleaning, conditioning, blocking/pearling, aspiration, and bleaching. Blocking removes the husk while pearling removes more layers. Bleaching removes the aleurone layer and gives the barley a white color. The output of the milling process can be pearl barley, blocked barley, or barley grits.