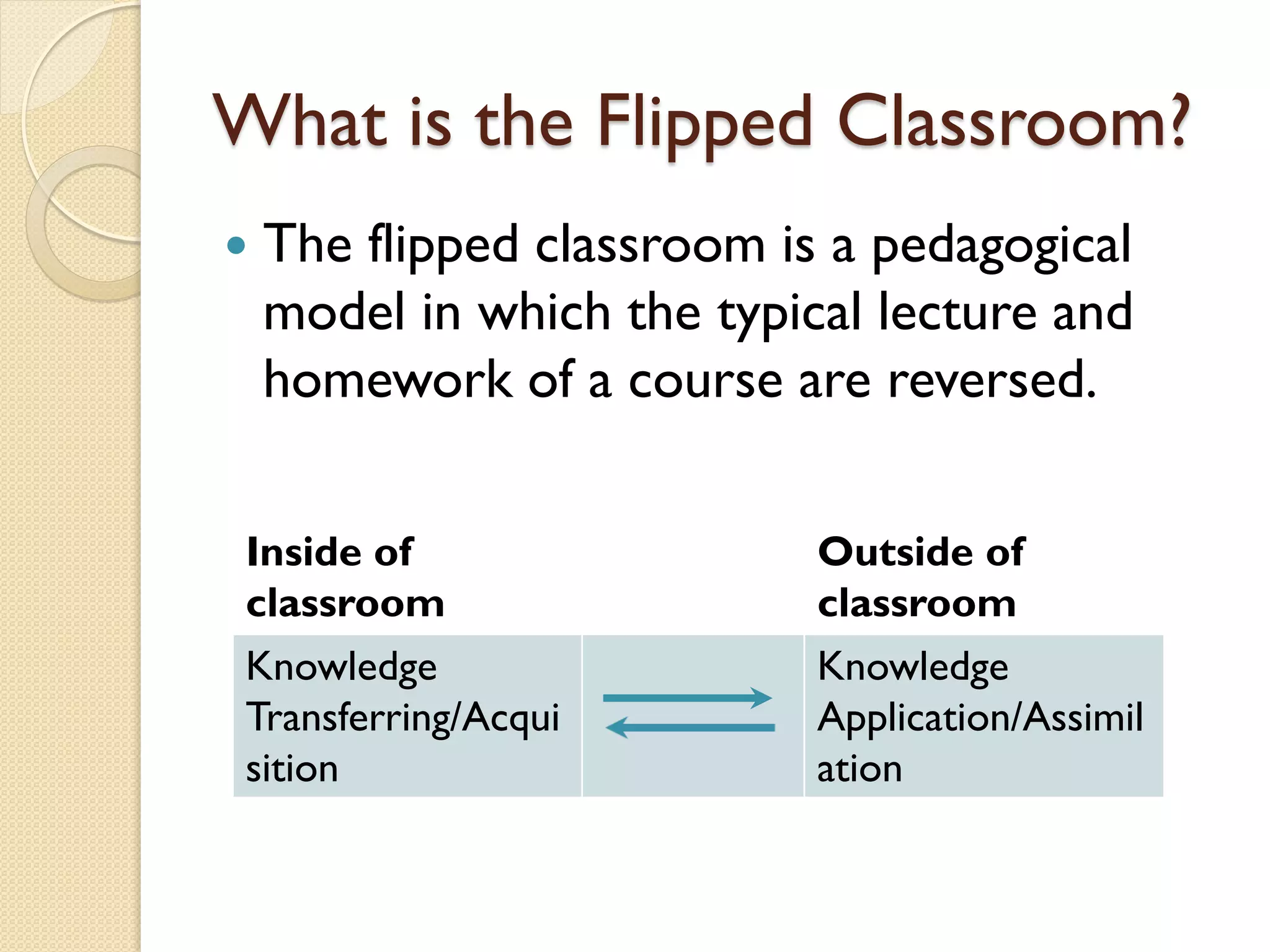
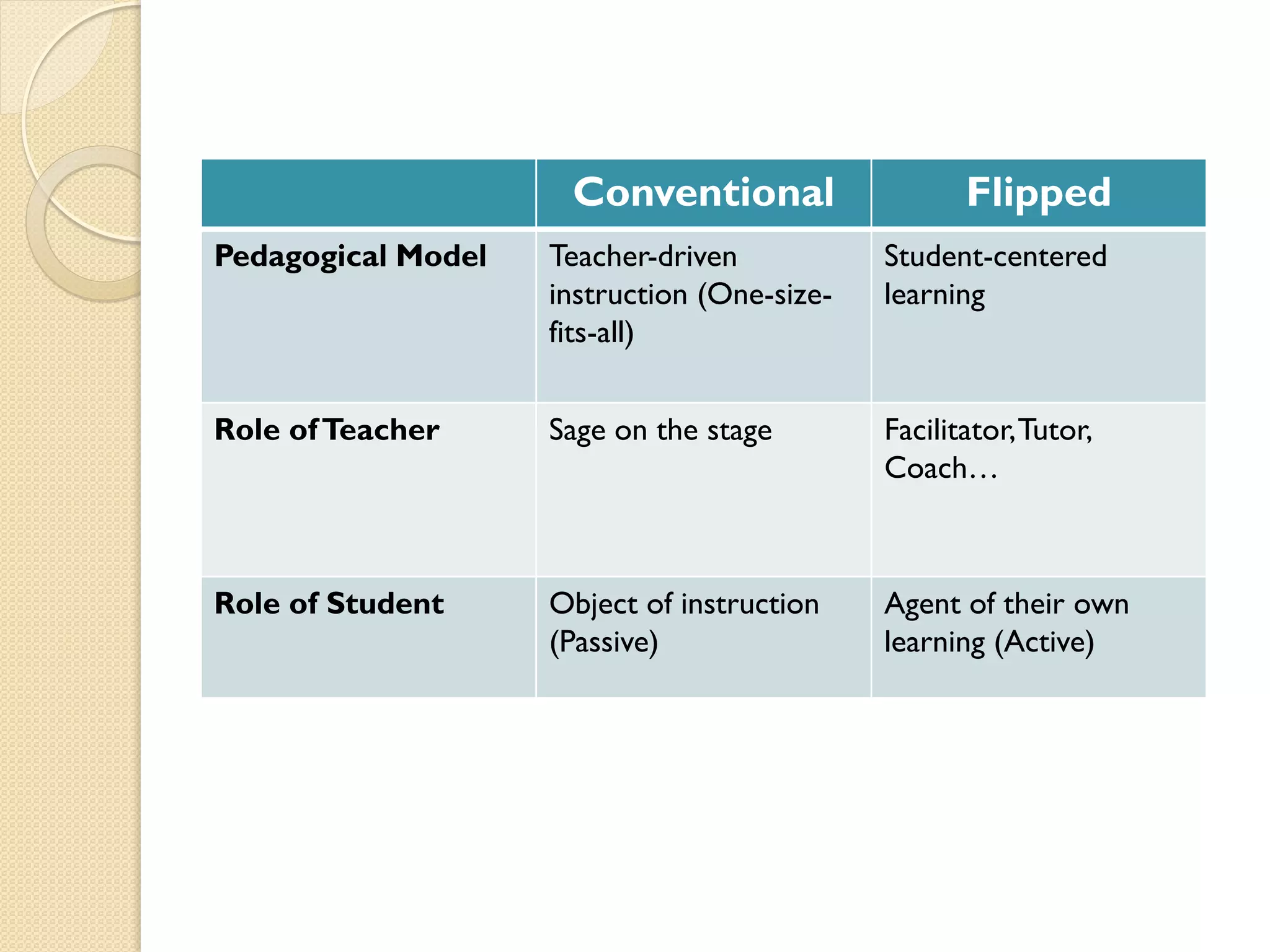
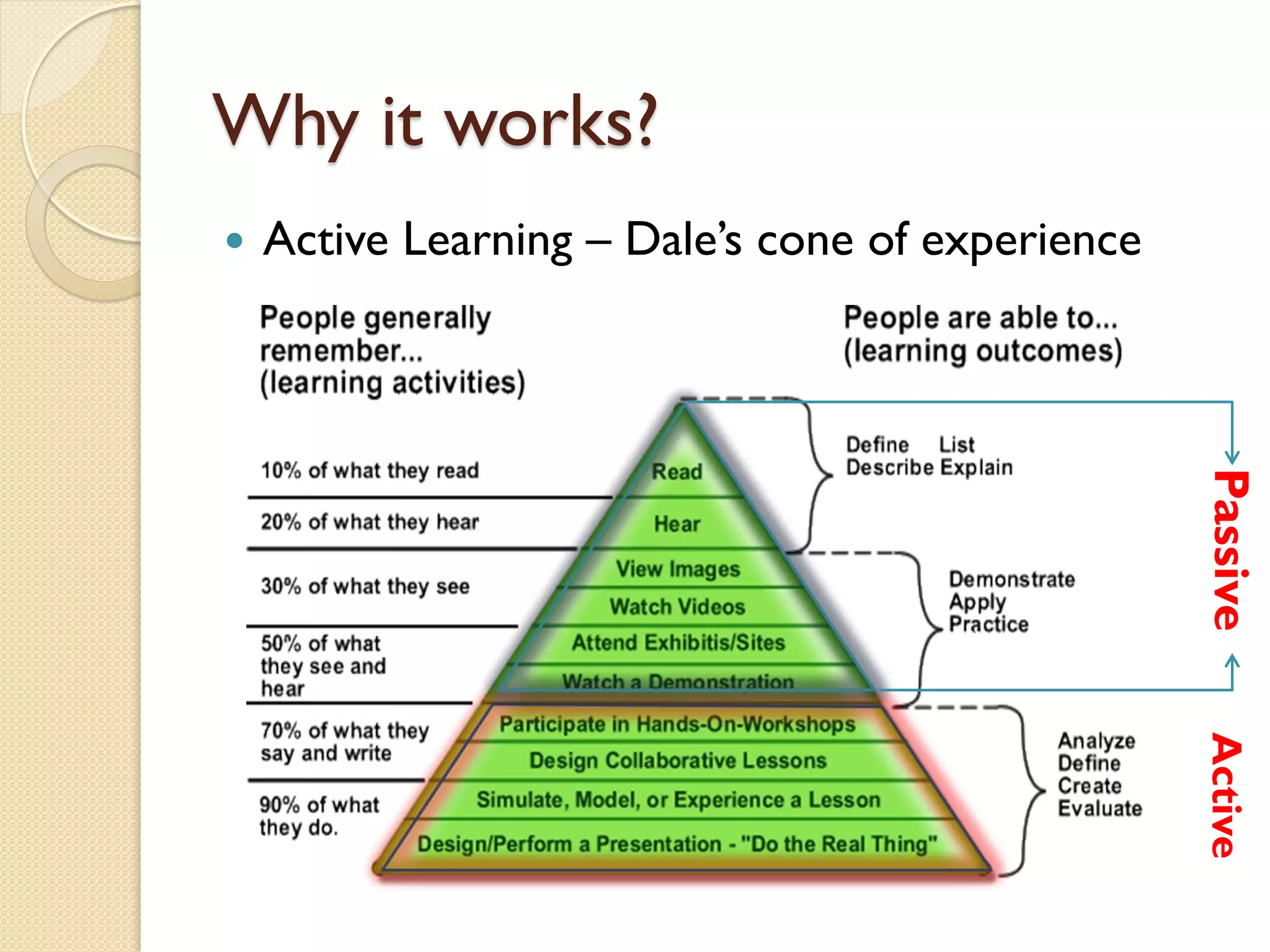
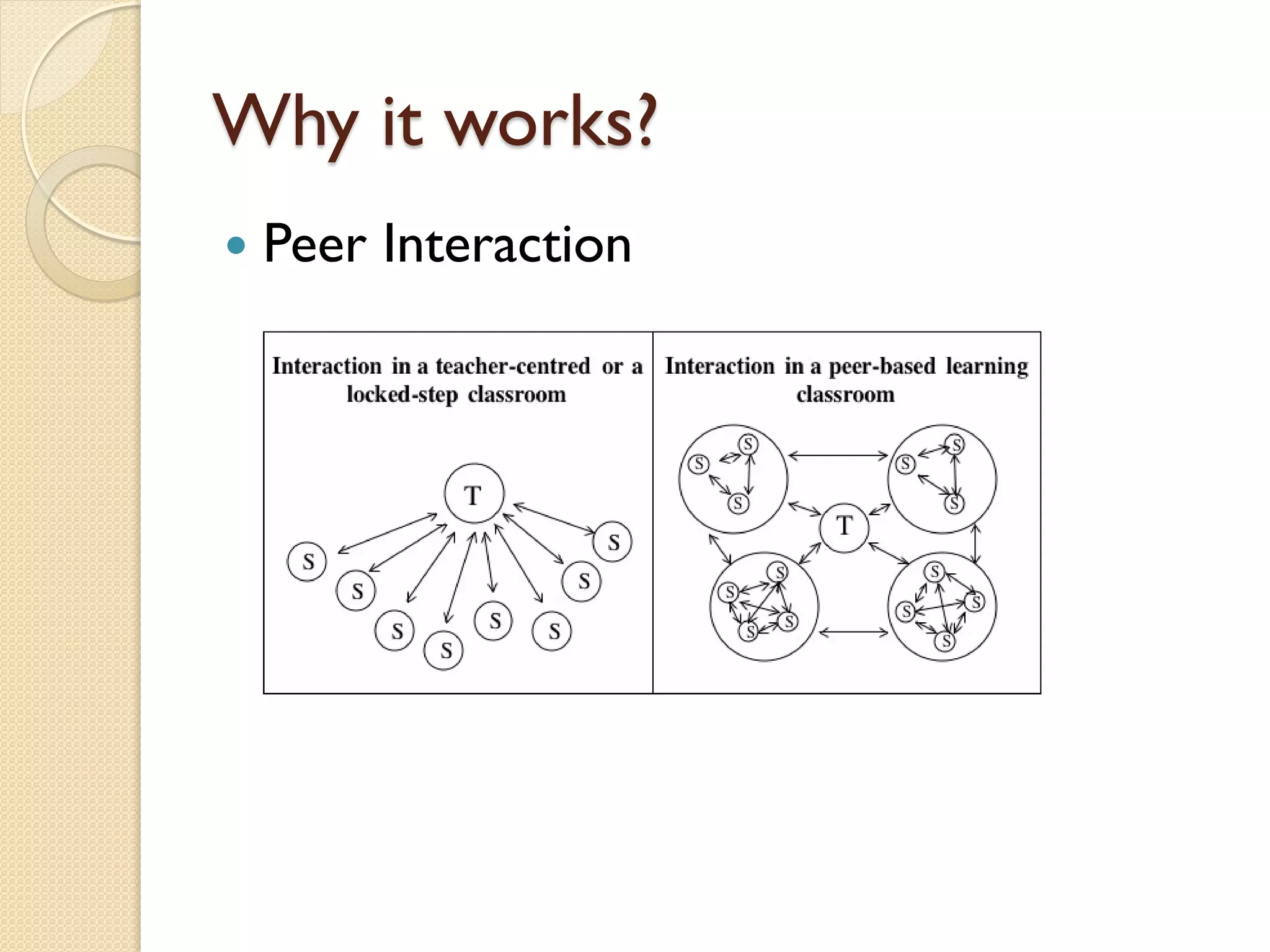
The flipped classroom model reverses traditional teaching methods by having students learn course content at home and apply it through interactive activities in class. Initiated in 2007 by educators Jonathan Bergmann and Aaron Sams, this approach fosters active learning, peer interaction, and allows for differentiated instruction. Feedback indicates that students appreciate increased opportunities for engagement and a more personalized learning experience.