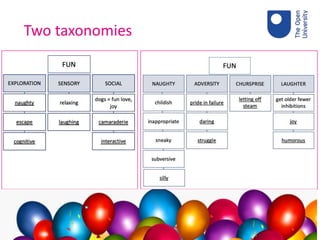
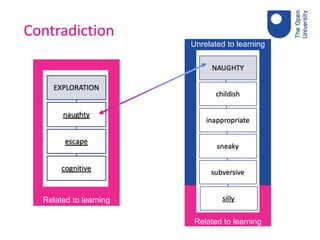
The document discusses the role of fun in learning, highlighting that while fun can enhance engagement and promote a positive learning environment, it can also distract and detract from educational goals. A consensus workshop was conducted with educators to identify and categorize elements of fun, resulting in two taxonomies that differentiate between fun associated with learning and that which is not. Key takeaways include the contextual nature of fun, its multi-layered aspects, and the necessity for educators to create a safe environment for engaging learning experiences.