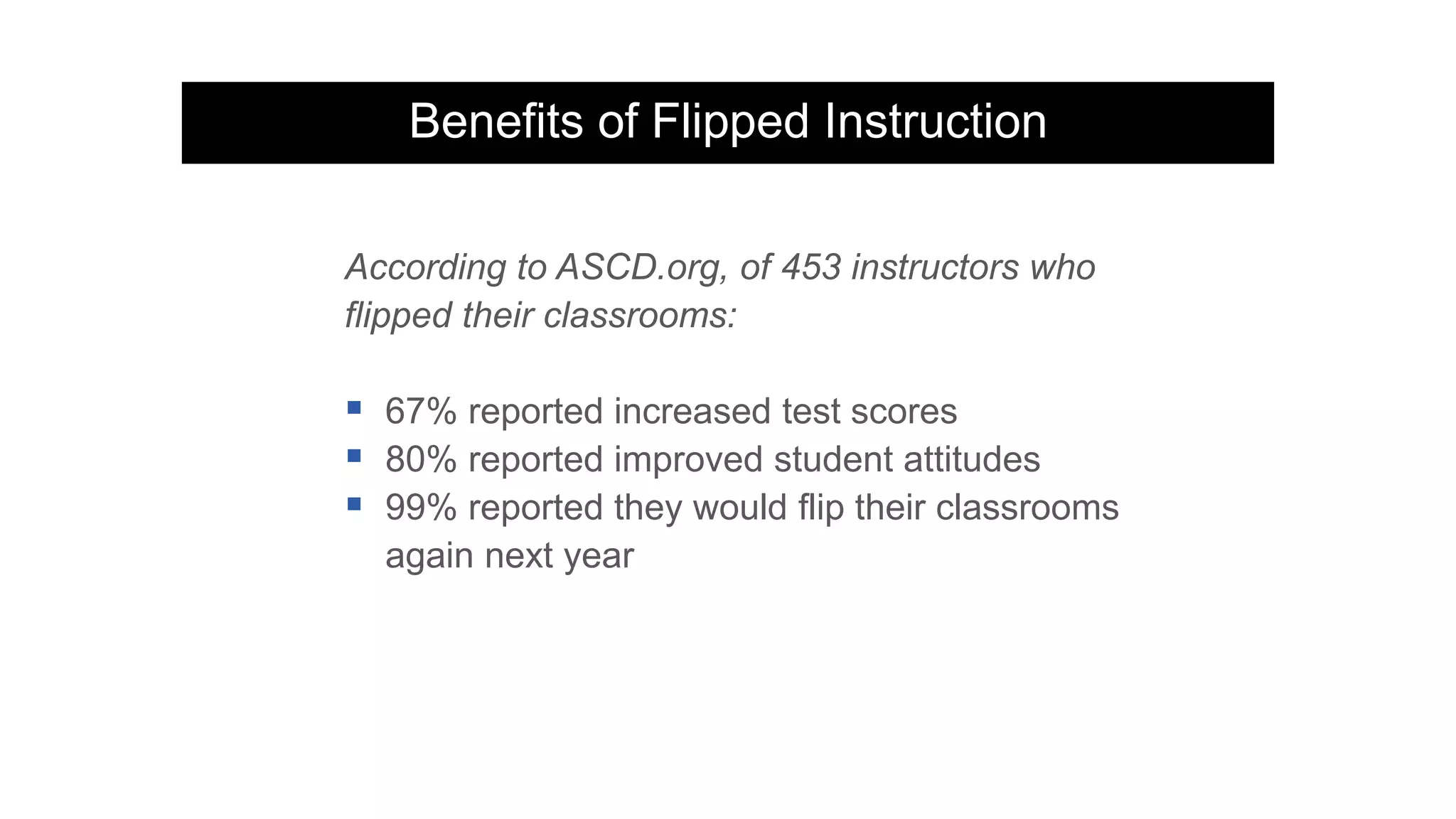
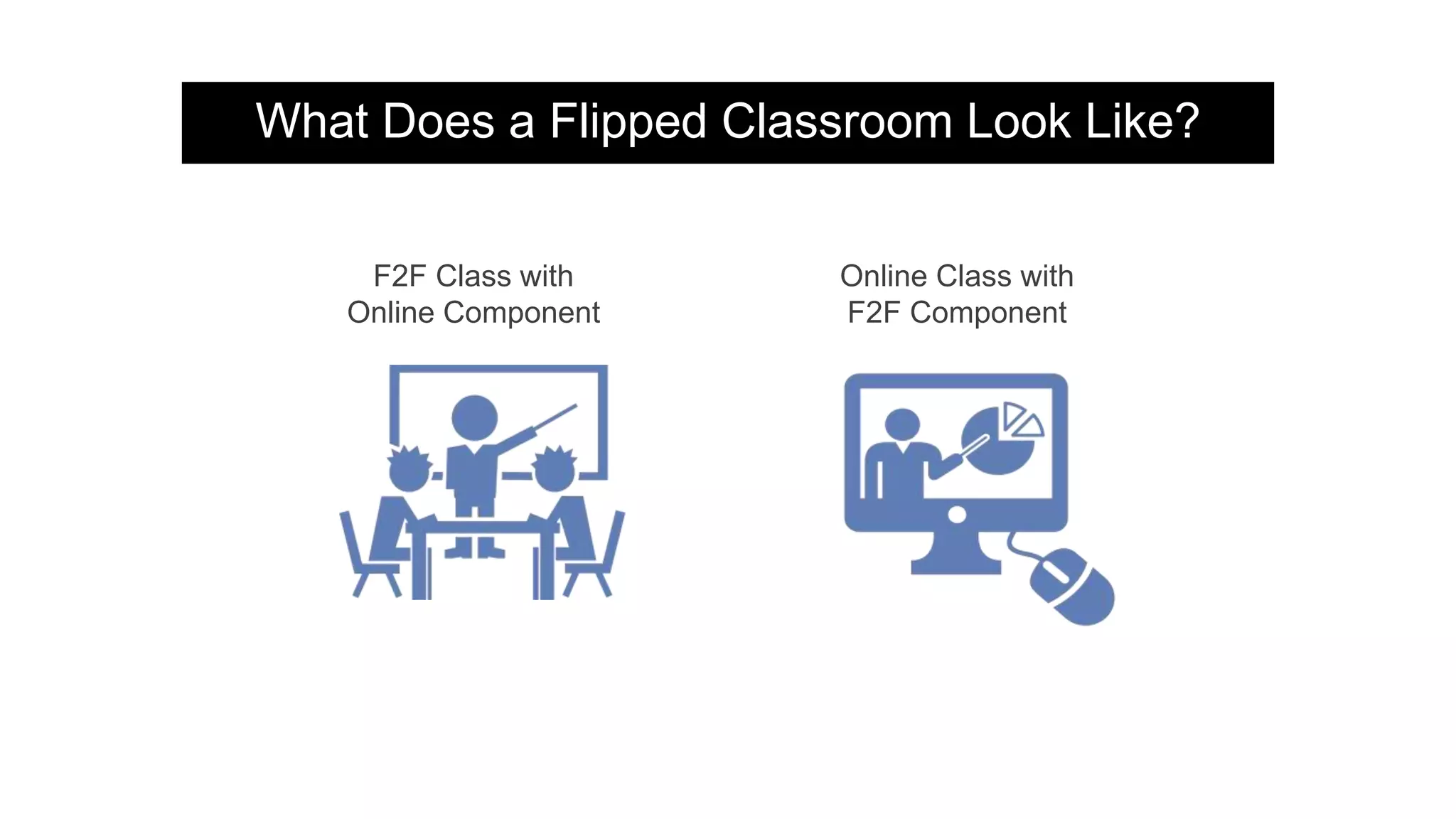
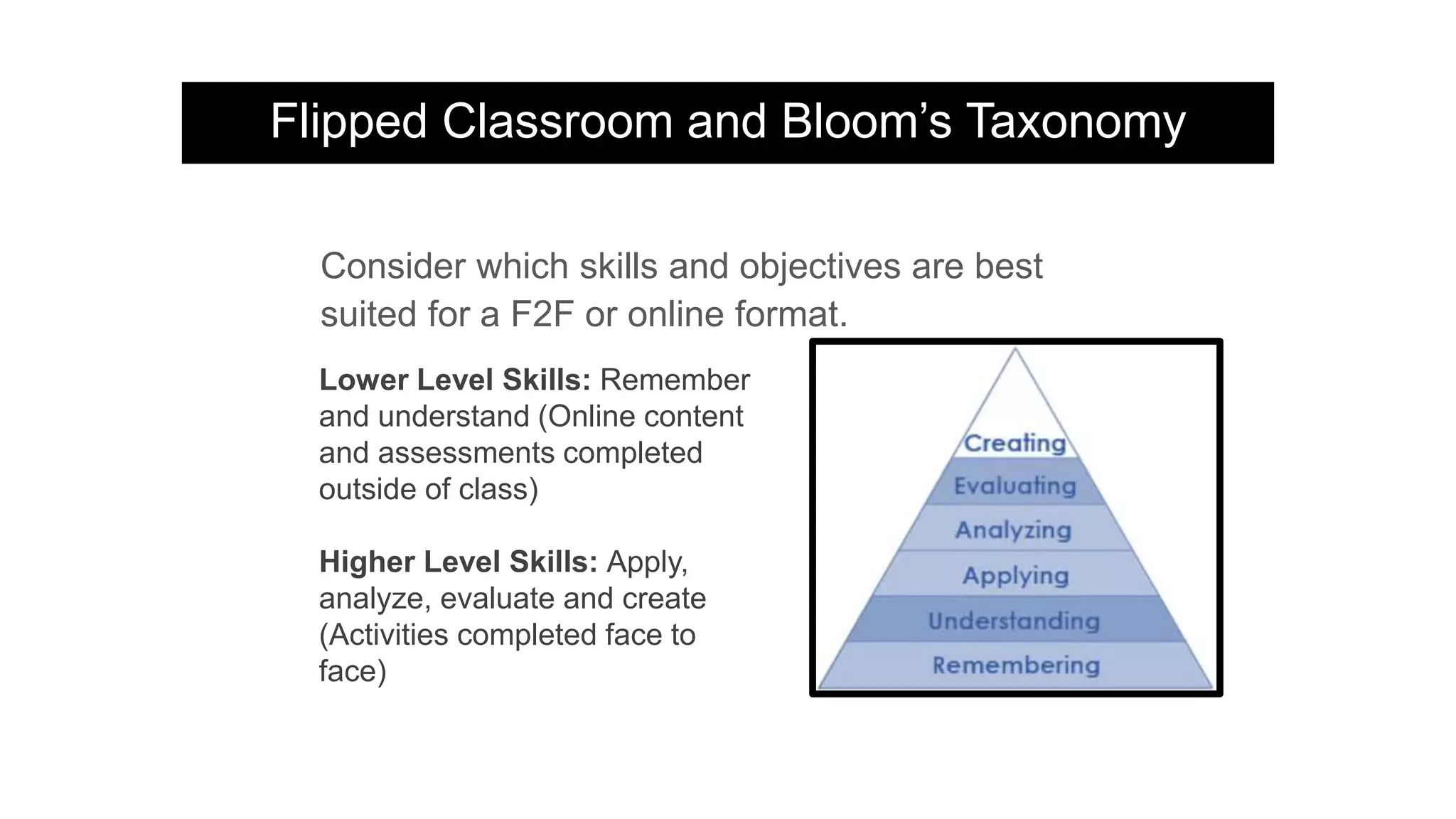
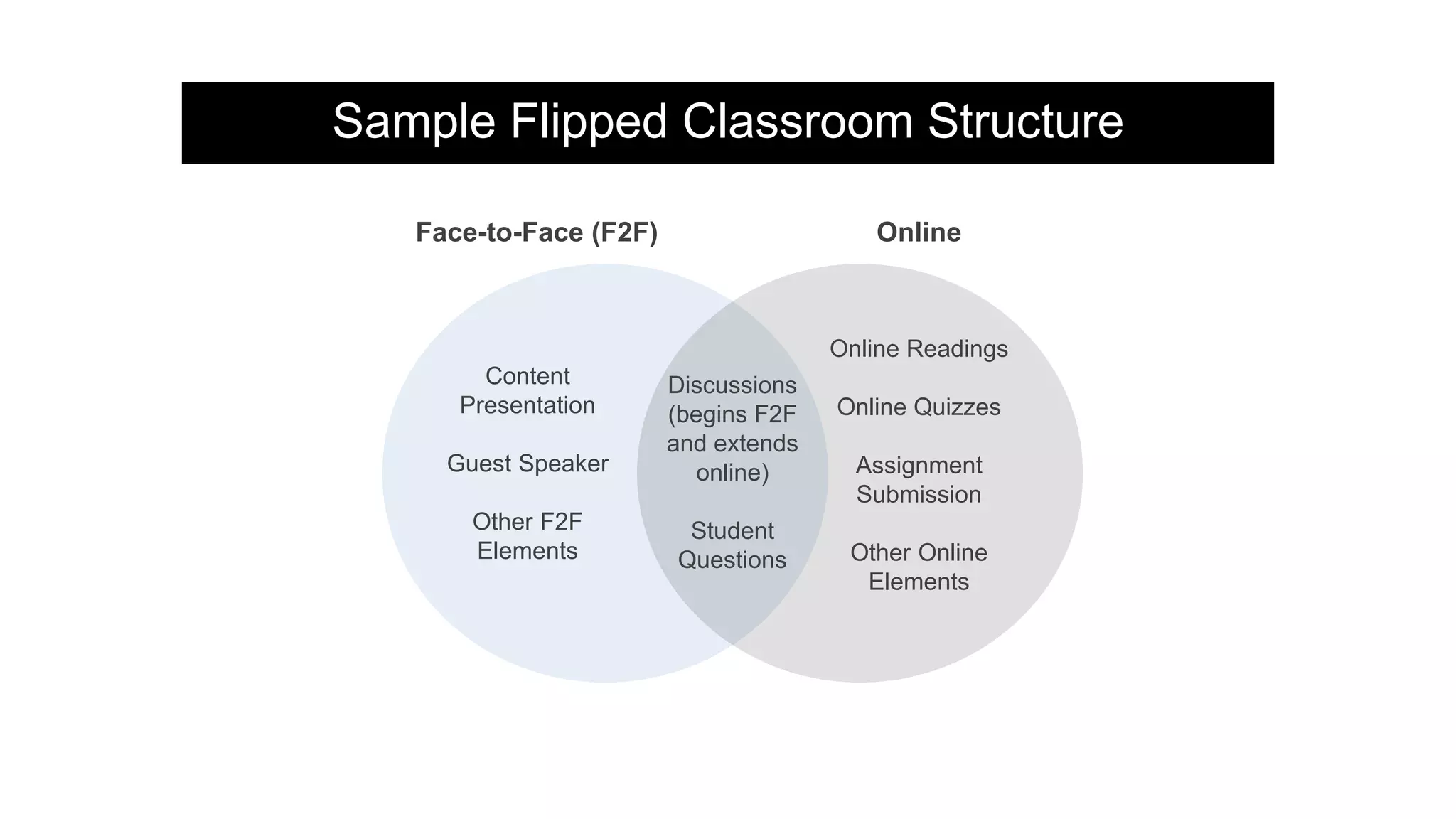
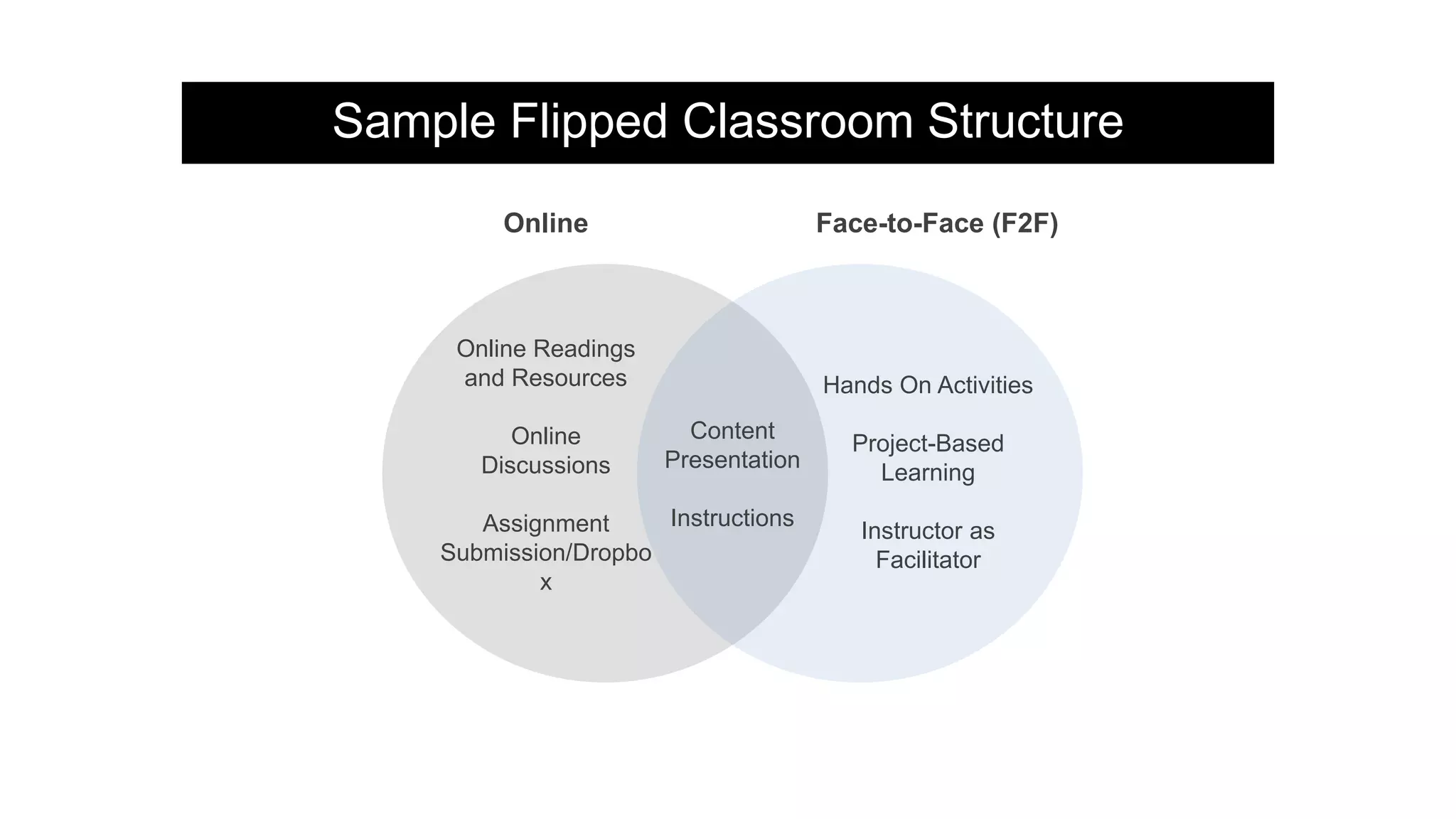
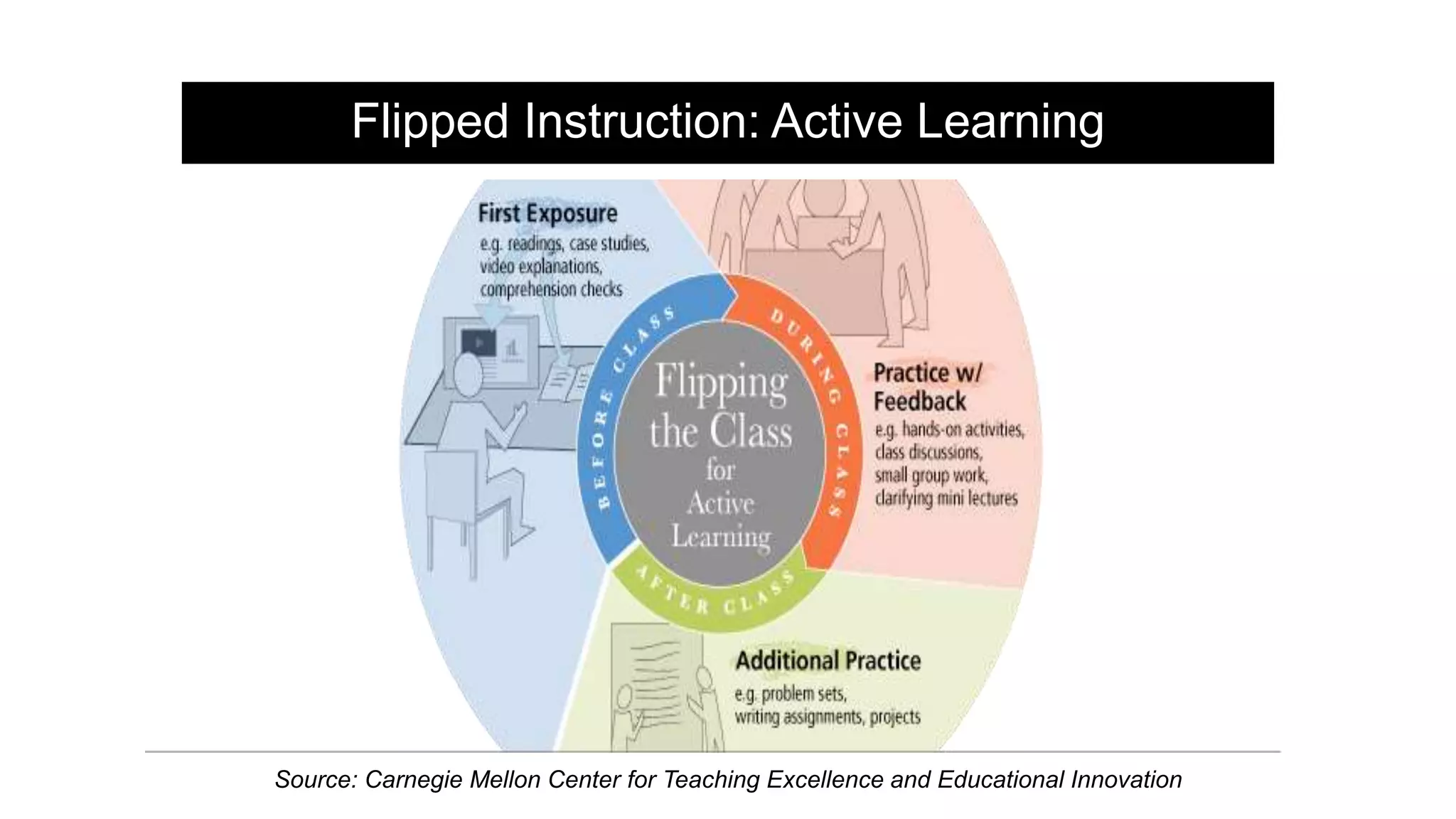
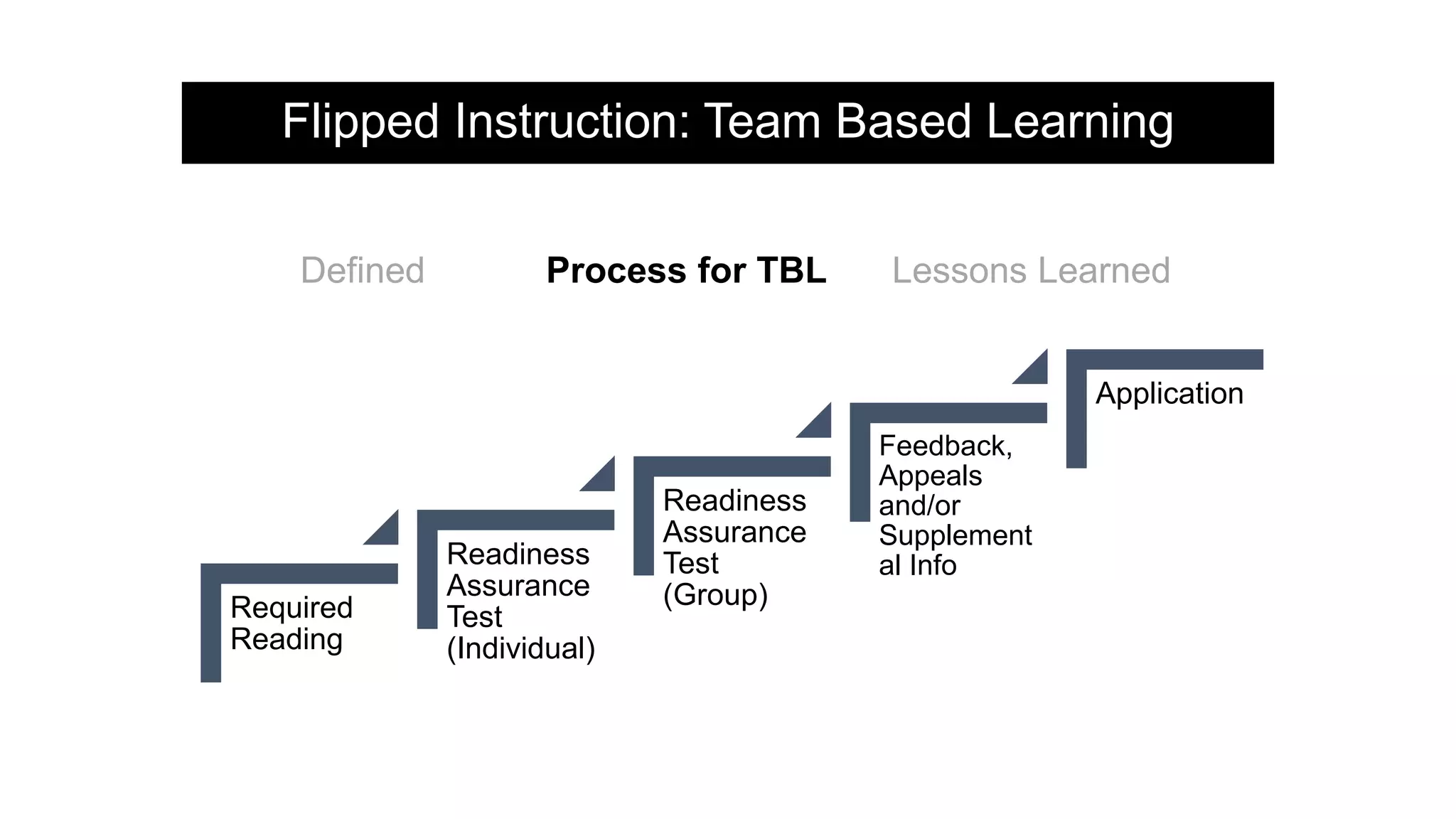
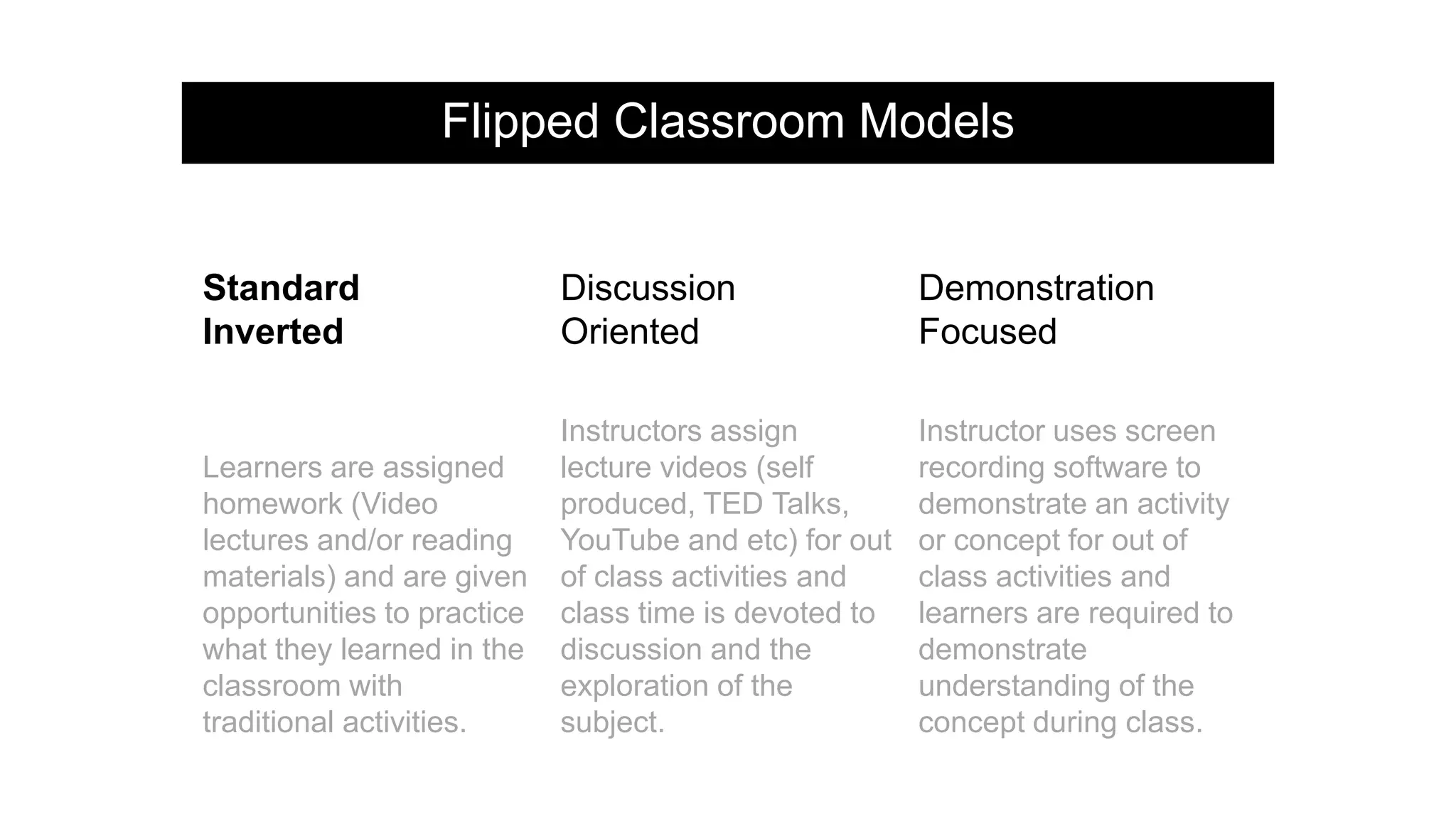
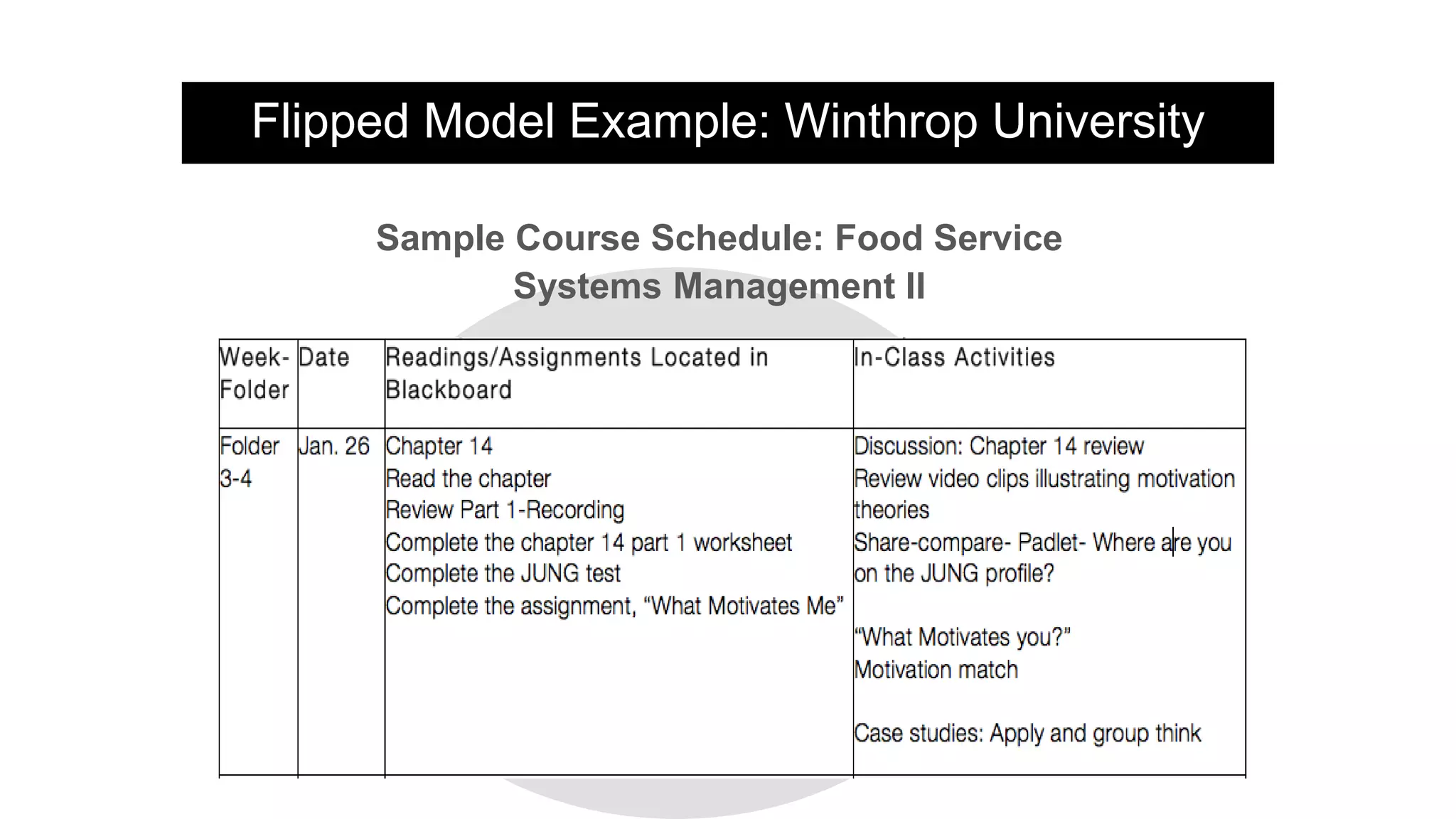
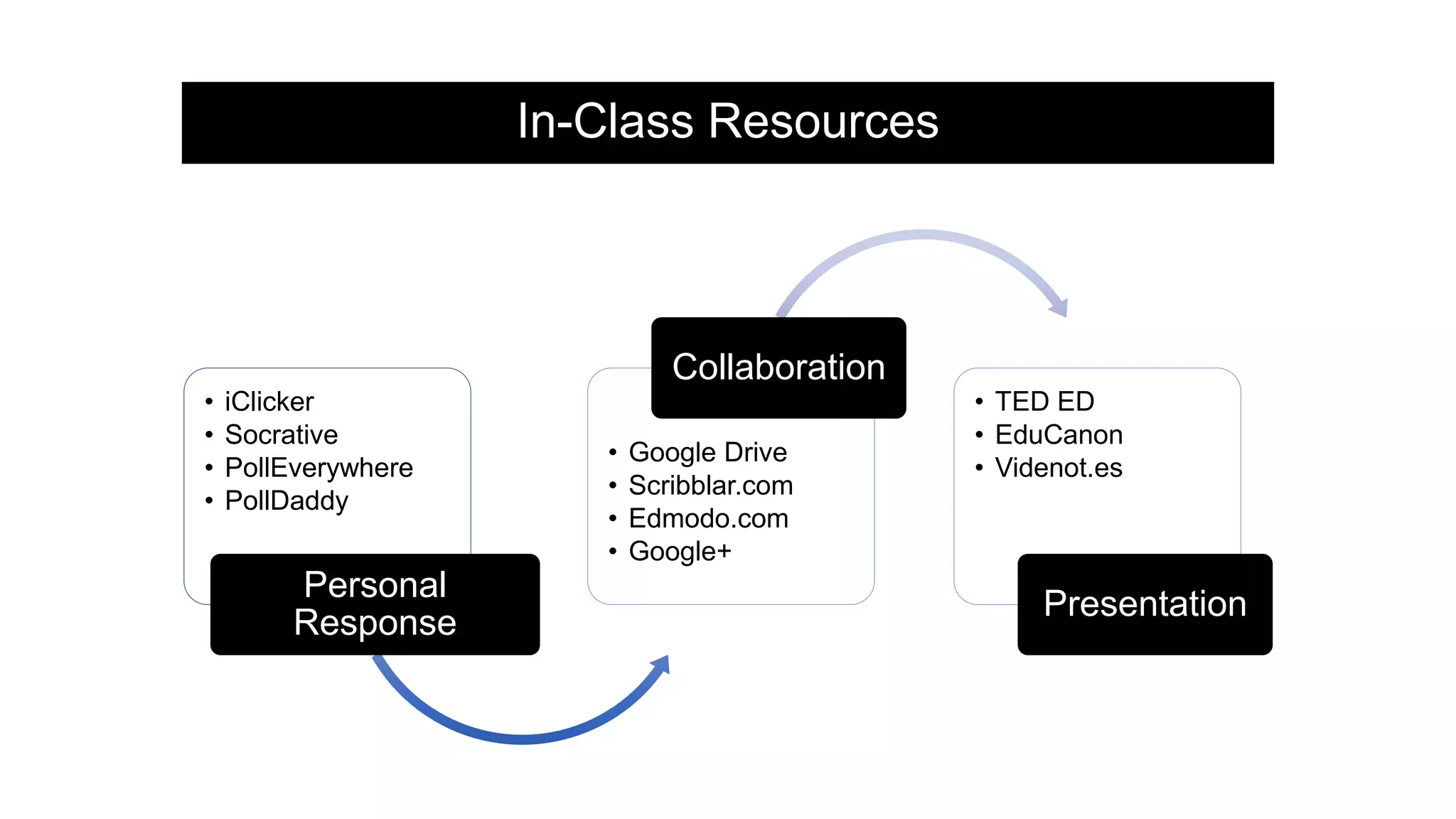
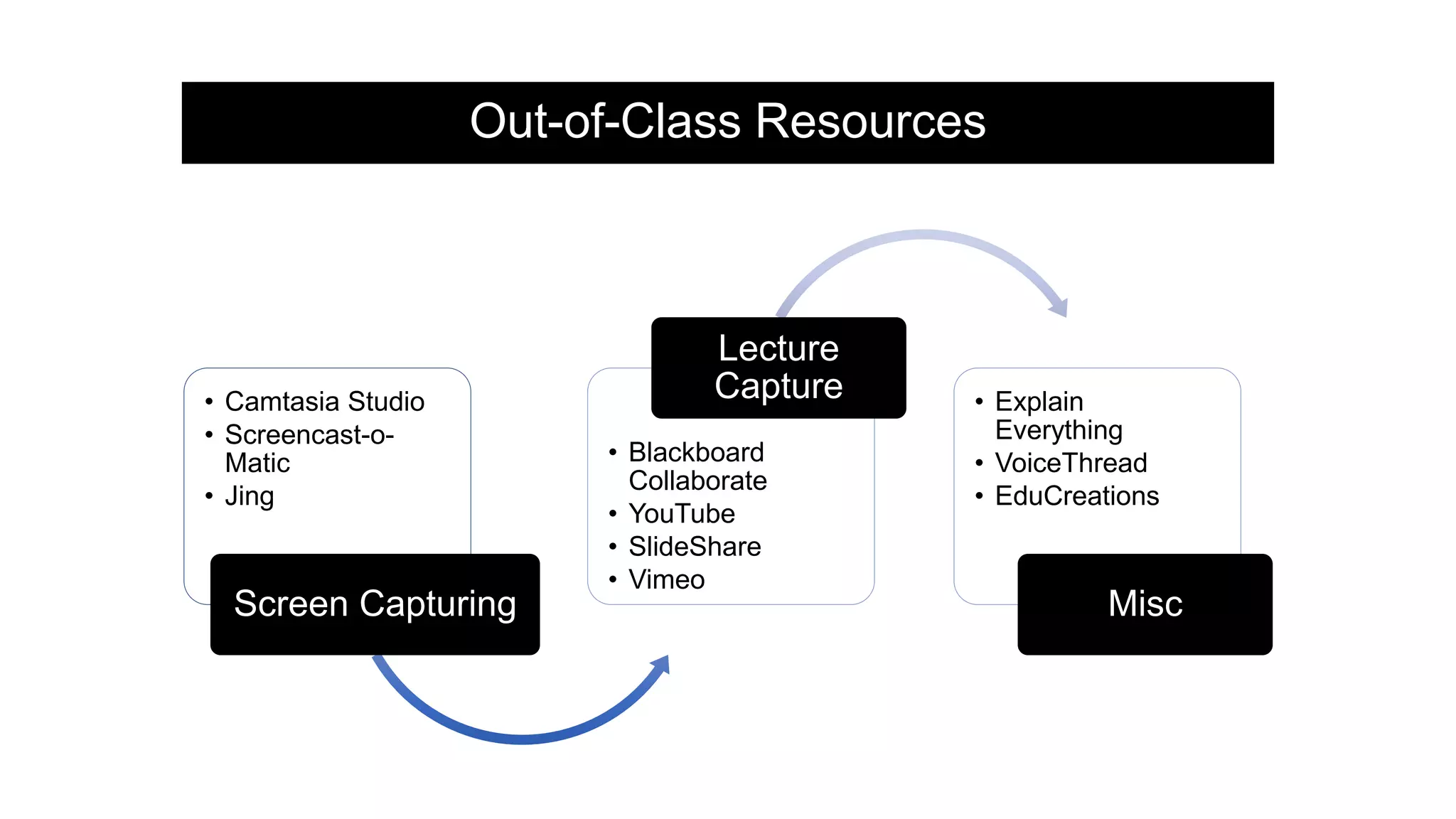
The document provides an overview of flipped instruction, a pedagogical model that reverses the traditional lecture-homework structure to enhance learning outcomes. It outlines the benefits, including increased flexibility, student engagement, and improved test scores, and discusses various models and strategies for implementing a flipped classroom. Furthermore, it highlights practical steps and resources for instructors to design and structure their flipped courses effectively.