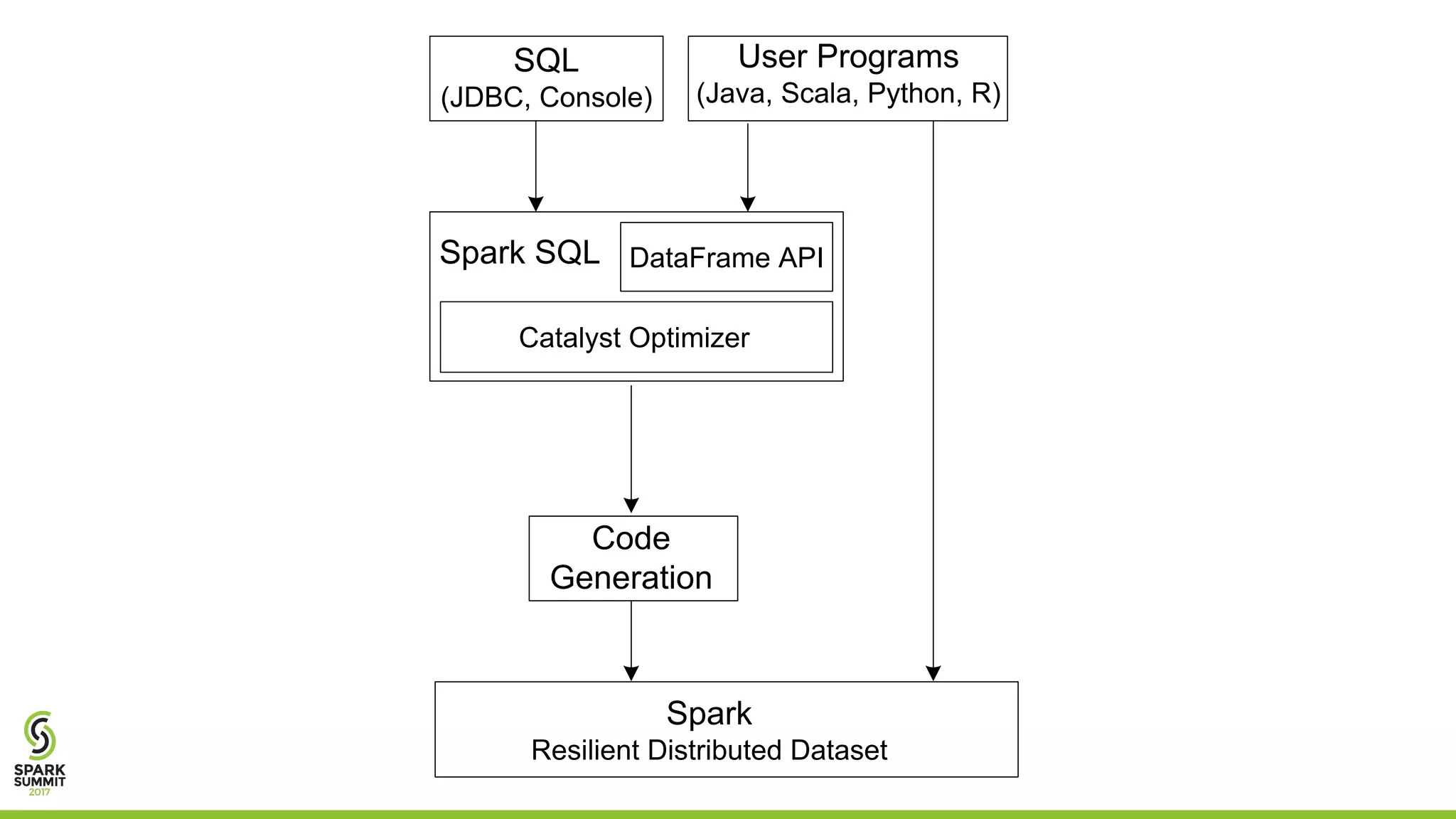
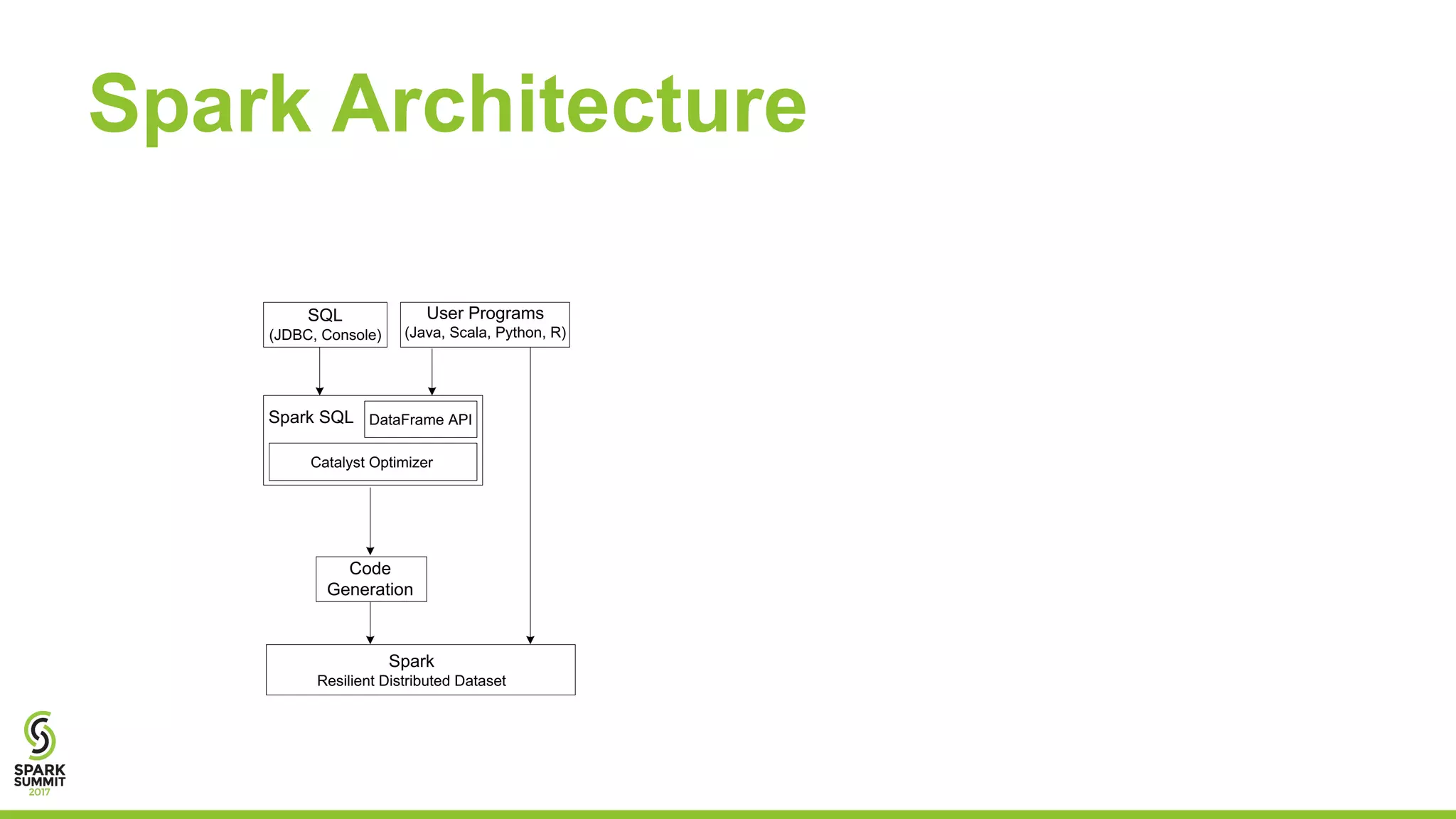
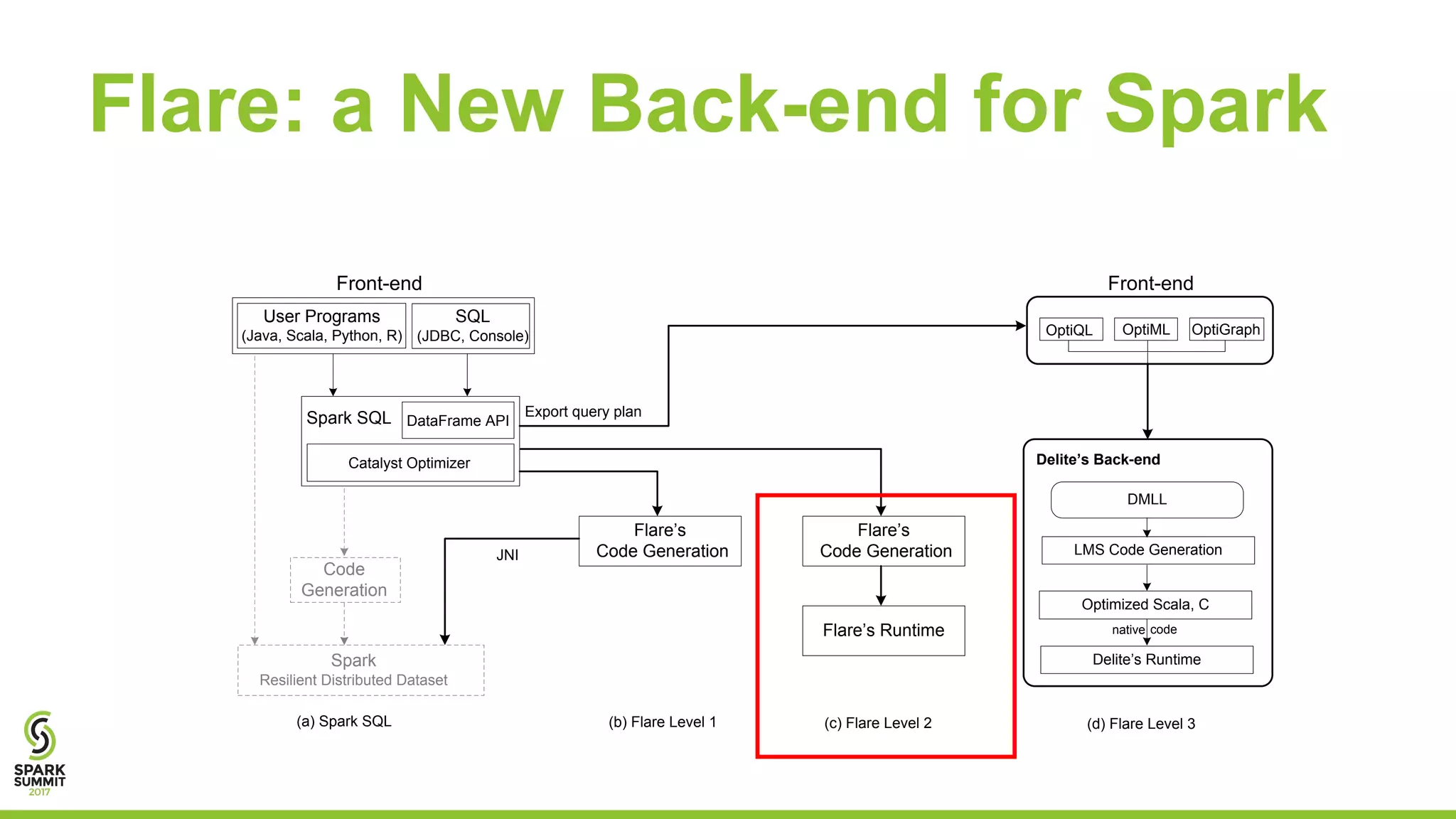
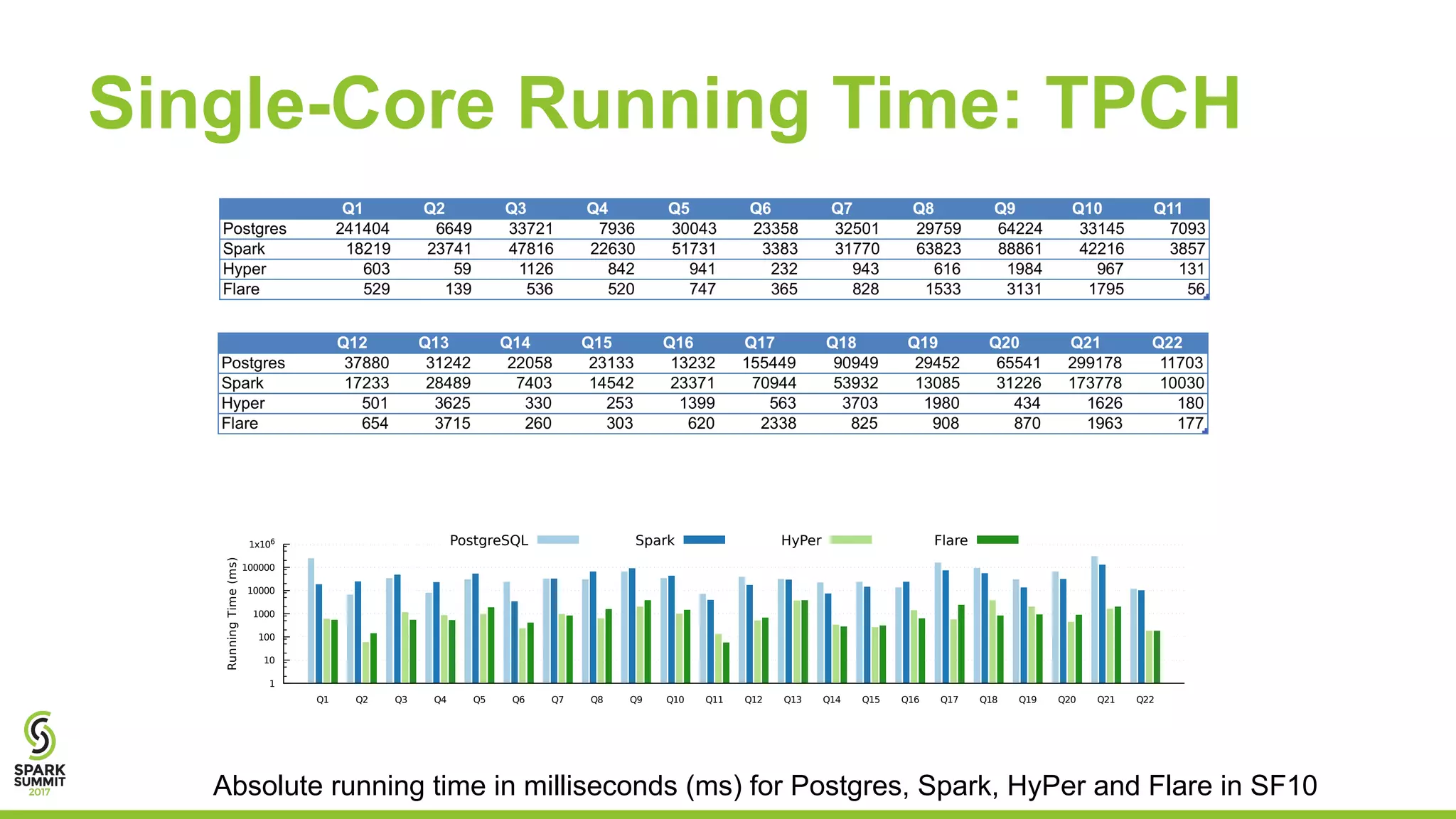
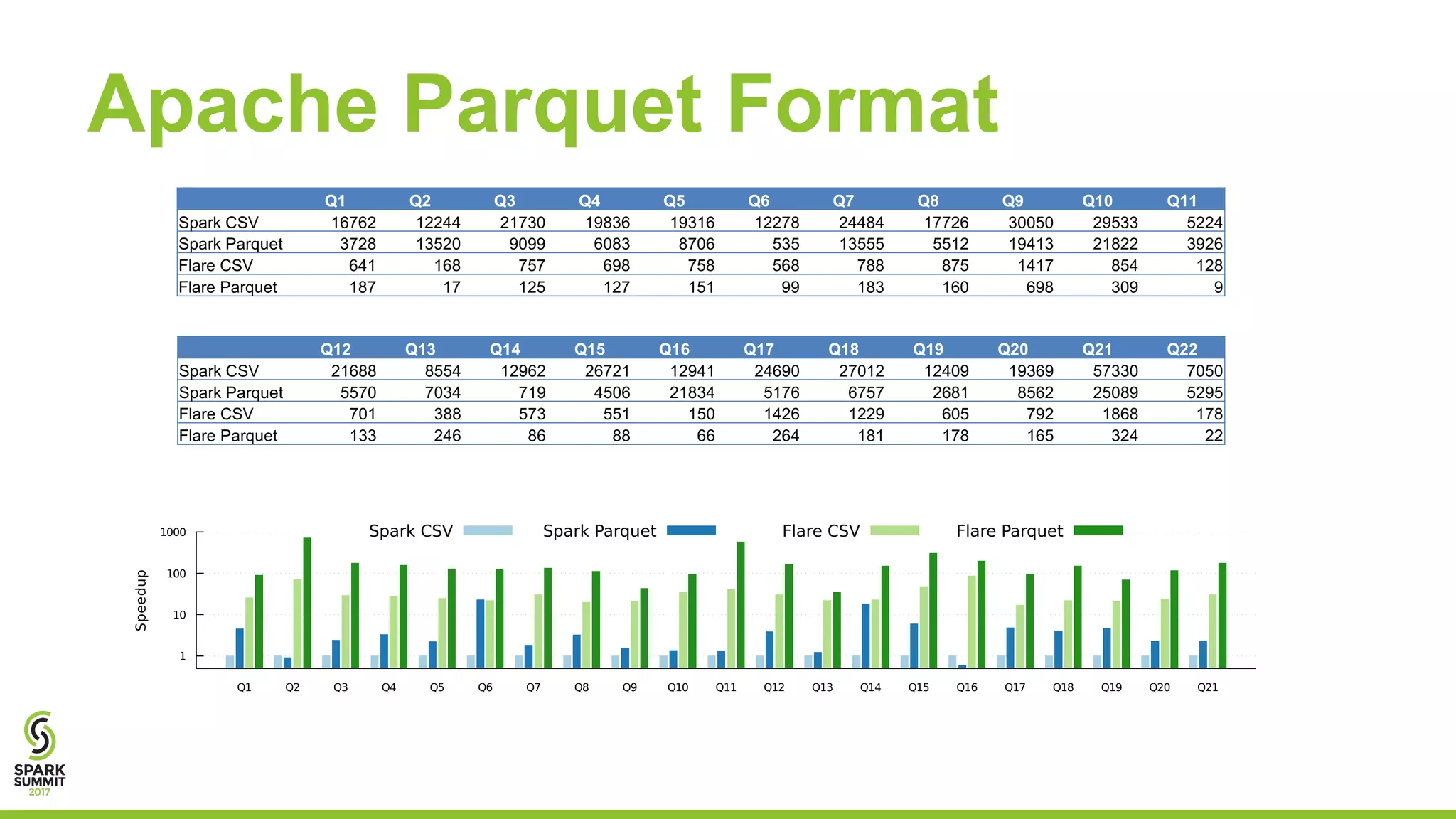
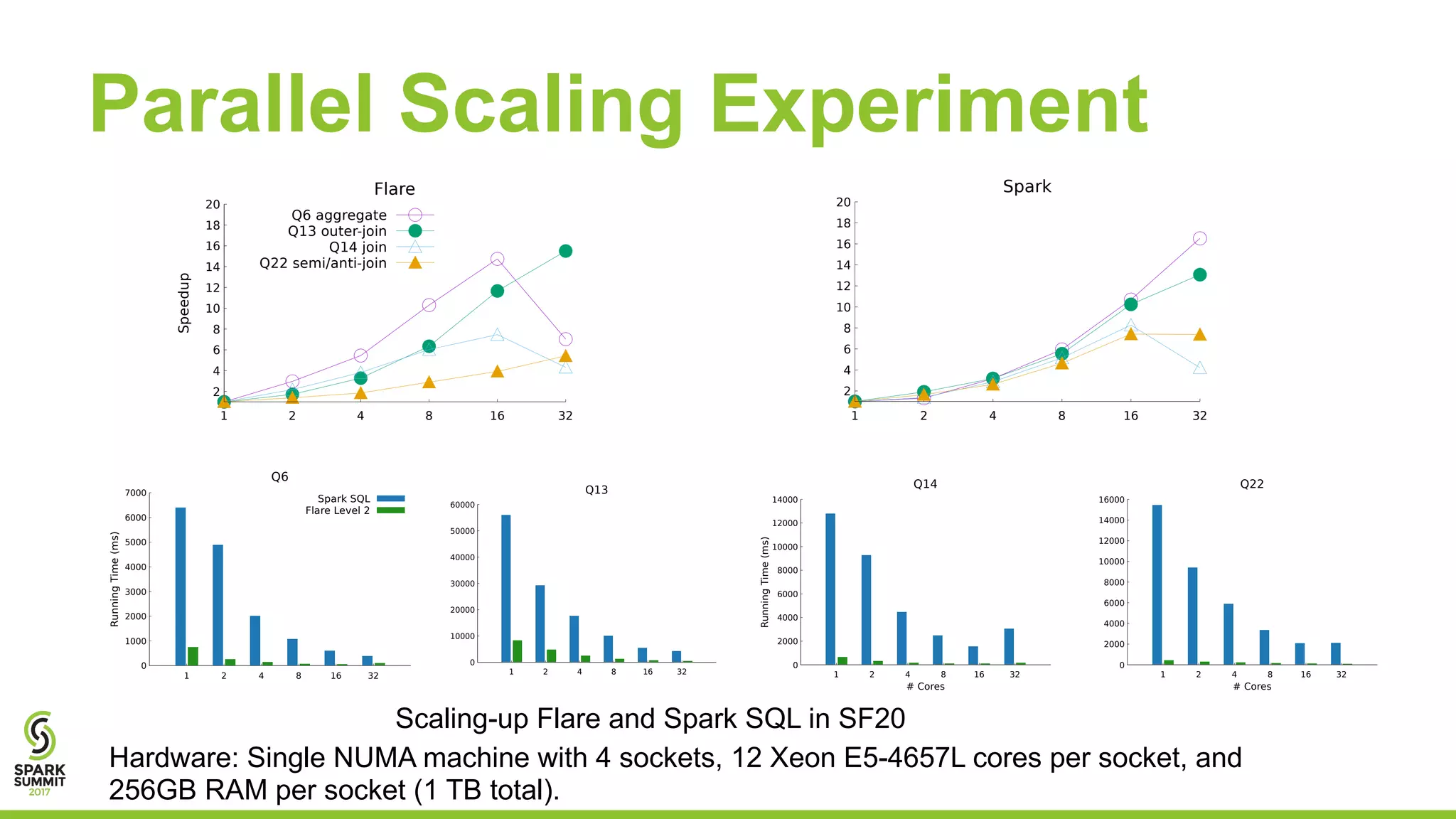
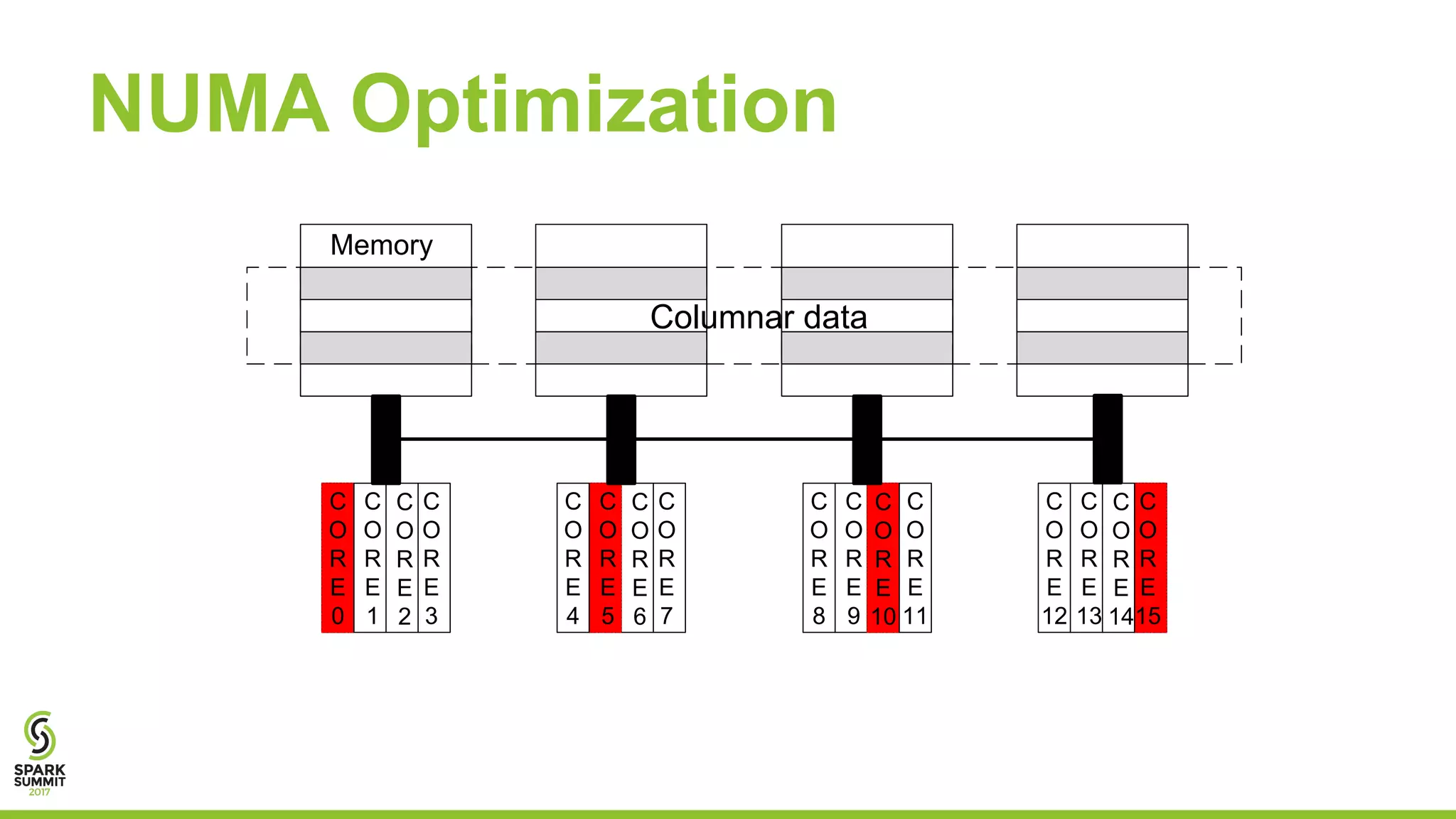
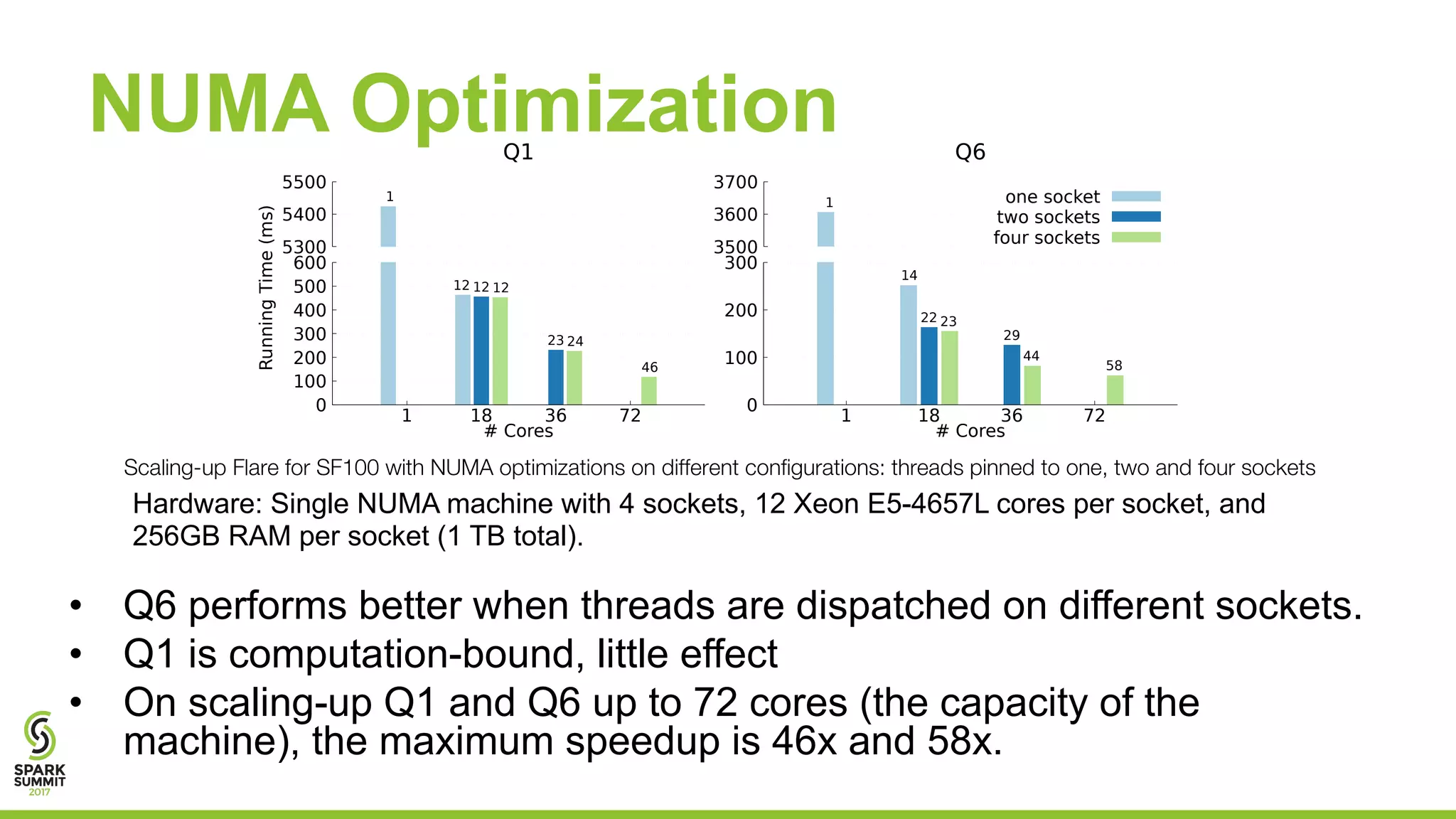
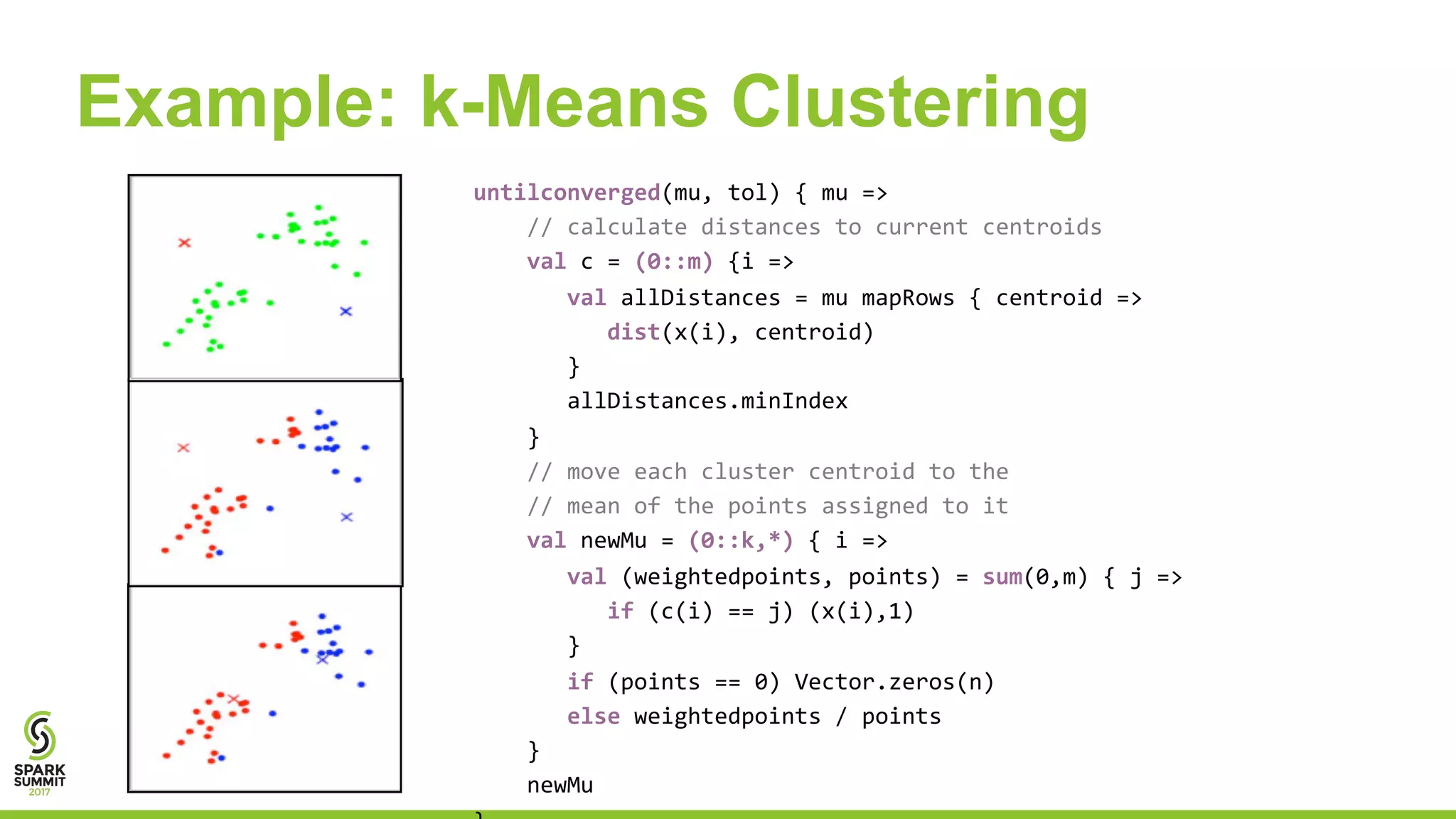
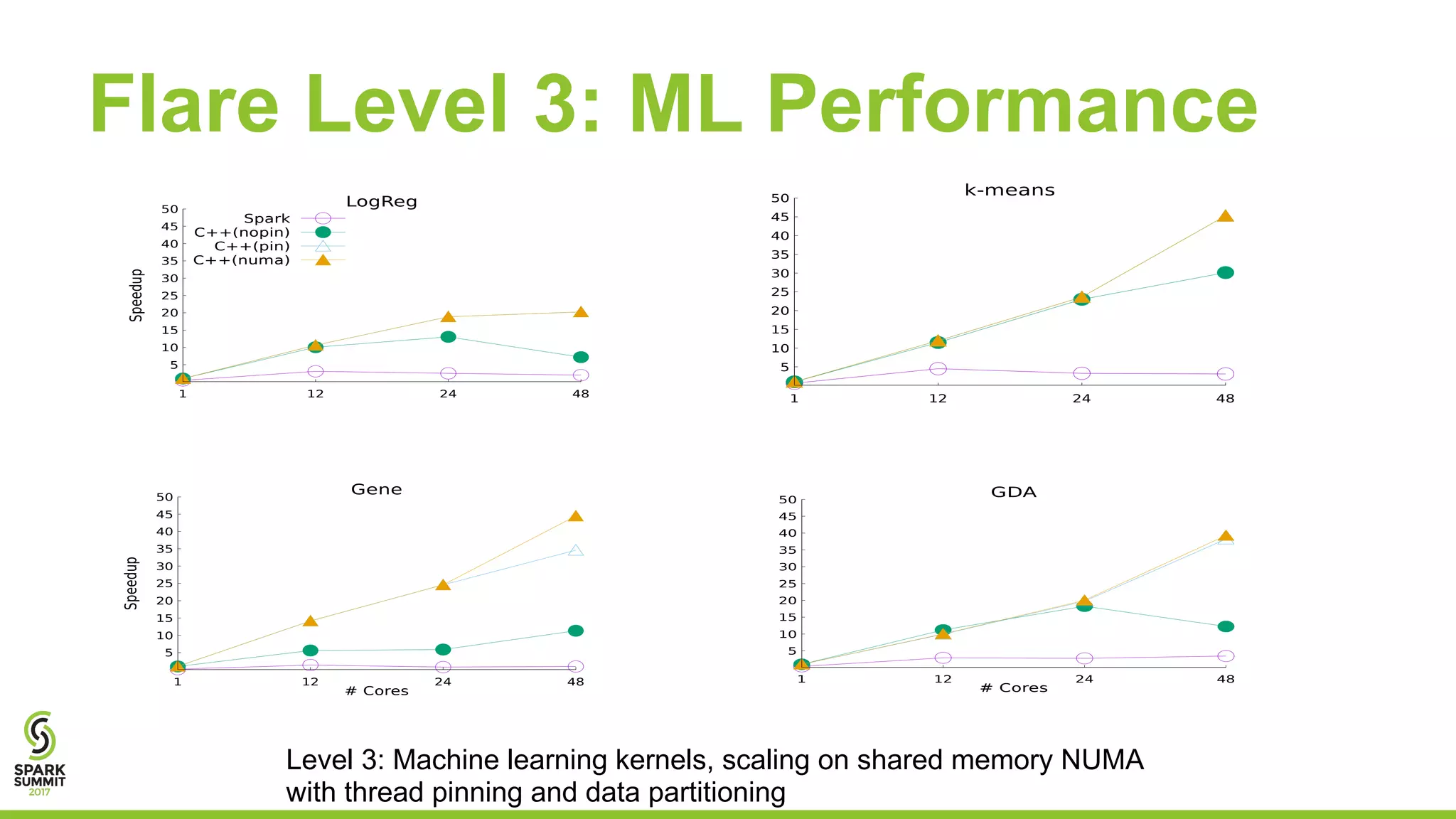
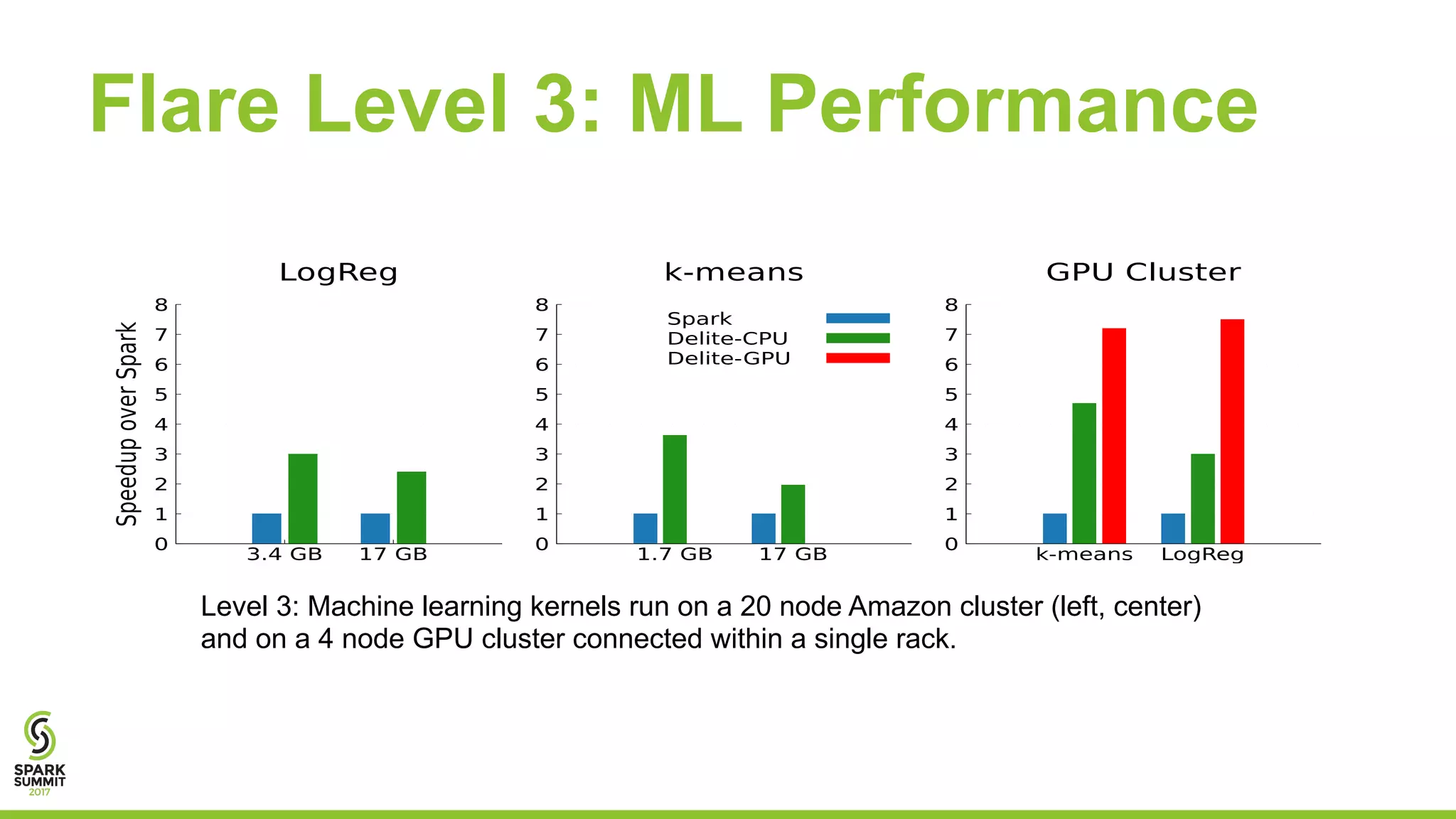
The document discusses the performance and architecture of Flare, a back-end for Spark SQL, which includes features like native code compilation and optimized execution for various user programs (Java, Scala, Python, R). It highlights the efficiency gains of Flare over traditional systems such as PostgreSQL and Spark, particularly in terms of running time and speedup metrics across various queries. It also covers Flare's code generation capabilities, parallel scaling experiments, and performance improvements for machine learning workloads.