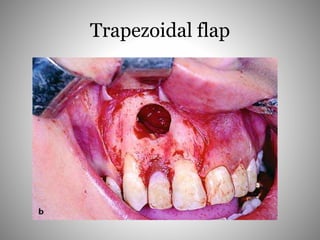
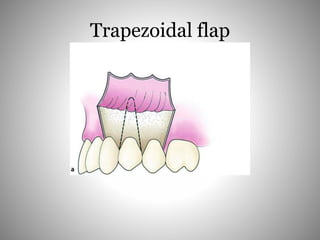
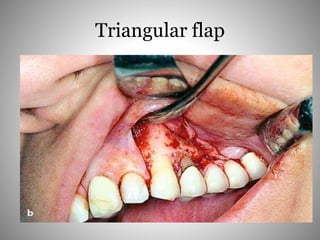
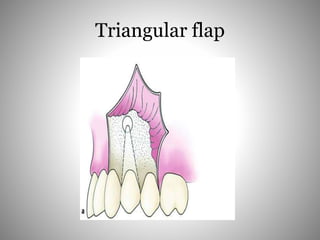
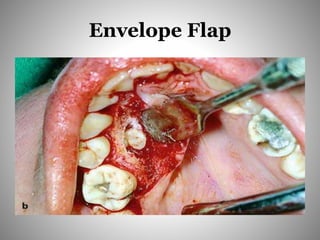
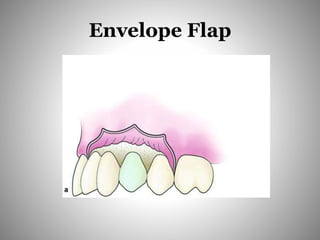
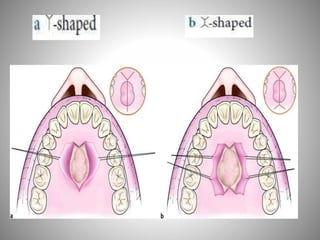
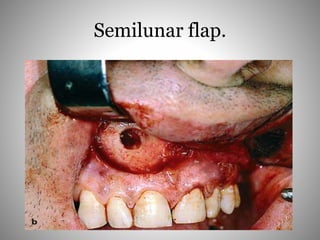
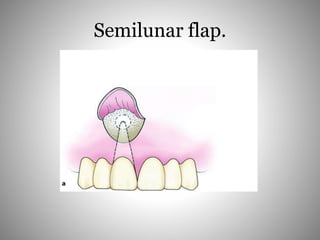
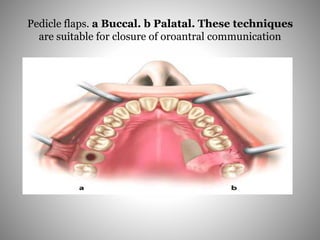
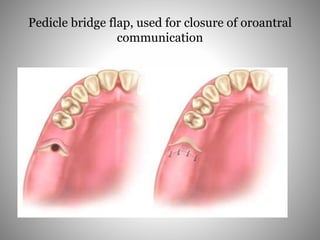
This document describes several types of flaps used in oral surgery, including trapezoidal, triangular, envelope, semilunar, and pedicle flaps. Trapezoidal flaps involve horizontal and oblique incisions to provide good access while minimizing tissue tension. Triangular flaps are formed with an L-shaped incision and ensure adequate blood supply. Envelope flaps extend along tooth cervical lines but can be difficult to reflect and cause tension. Semilunar flaps involve a curved incision and allow small procedures while avoiding gingival recession. Pedicle flaps like buccal, palatal, and bridge flaps are used to close oroantral communications.