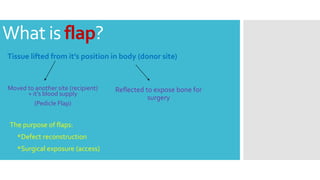
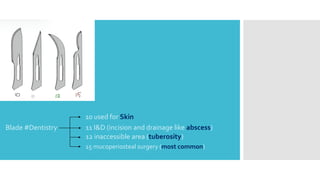
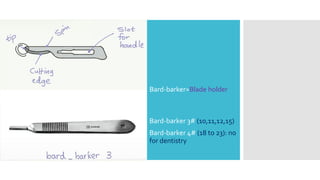
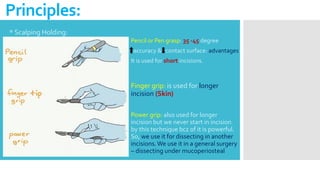
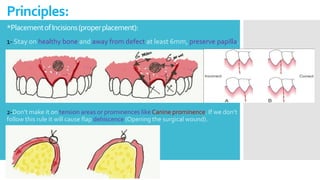
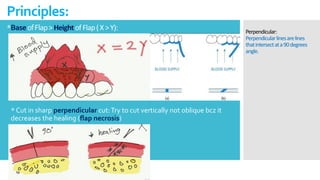
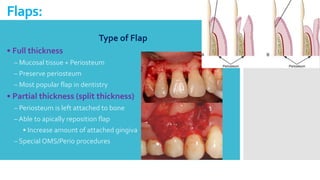
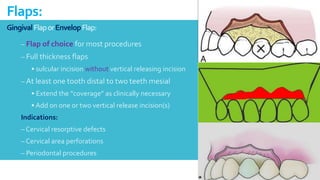
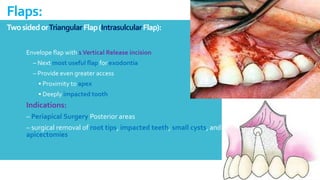
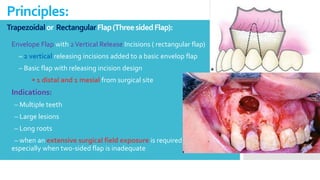
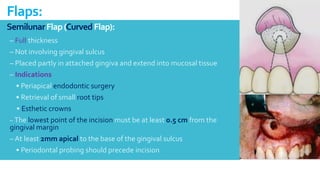
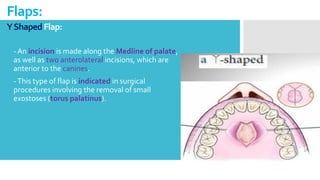
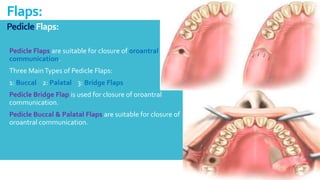
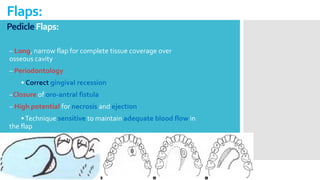
This document discusses different types of flaps used in oral and dental surgery. It defines a flap as tissue lifted from its original position and moved to another site along with its blood supply. The main purposes of flaps are defect reconstruction and providing surgical access. It describes several types of flaps including gingival/envelope flaps, two-sided/triangular flaps, three-sided/trapezoidal flaps, semilunar flaps, submarginal flaps, and pedicle flaps. It also discusses principles of flap design such as placement of incisions, base width relative to height, and techniques for reducing complications.