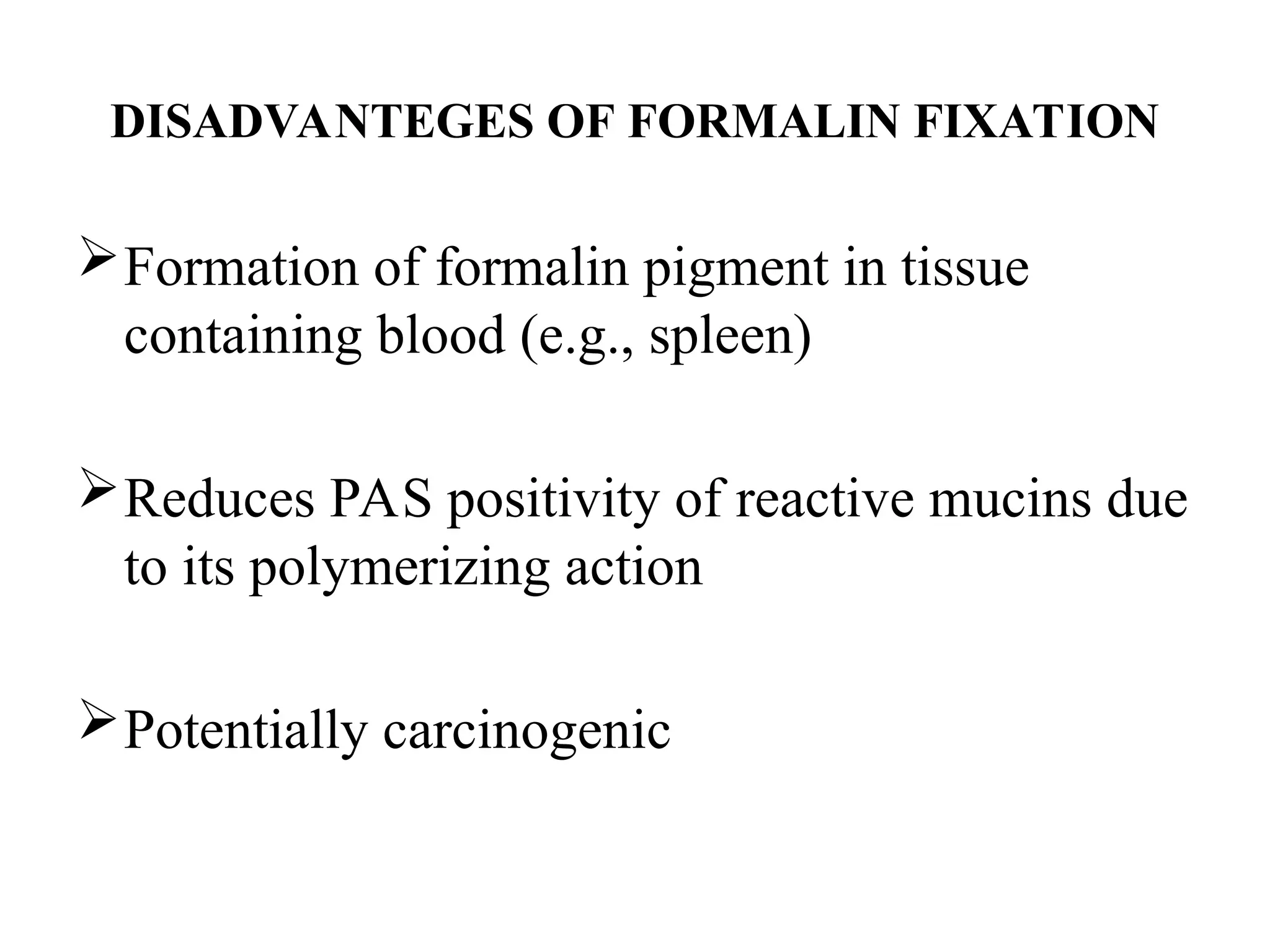
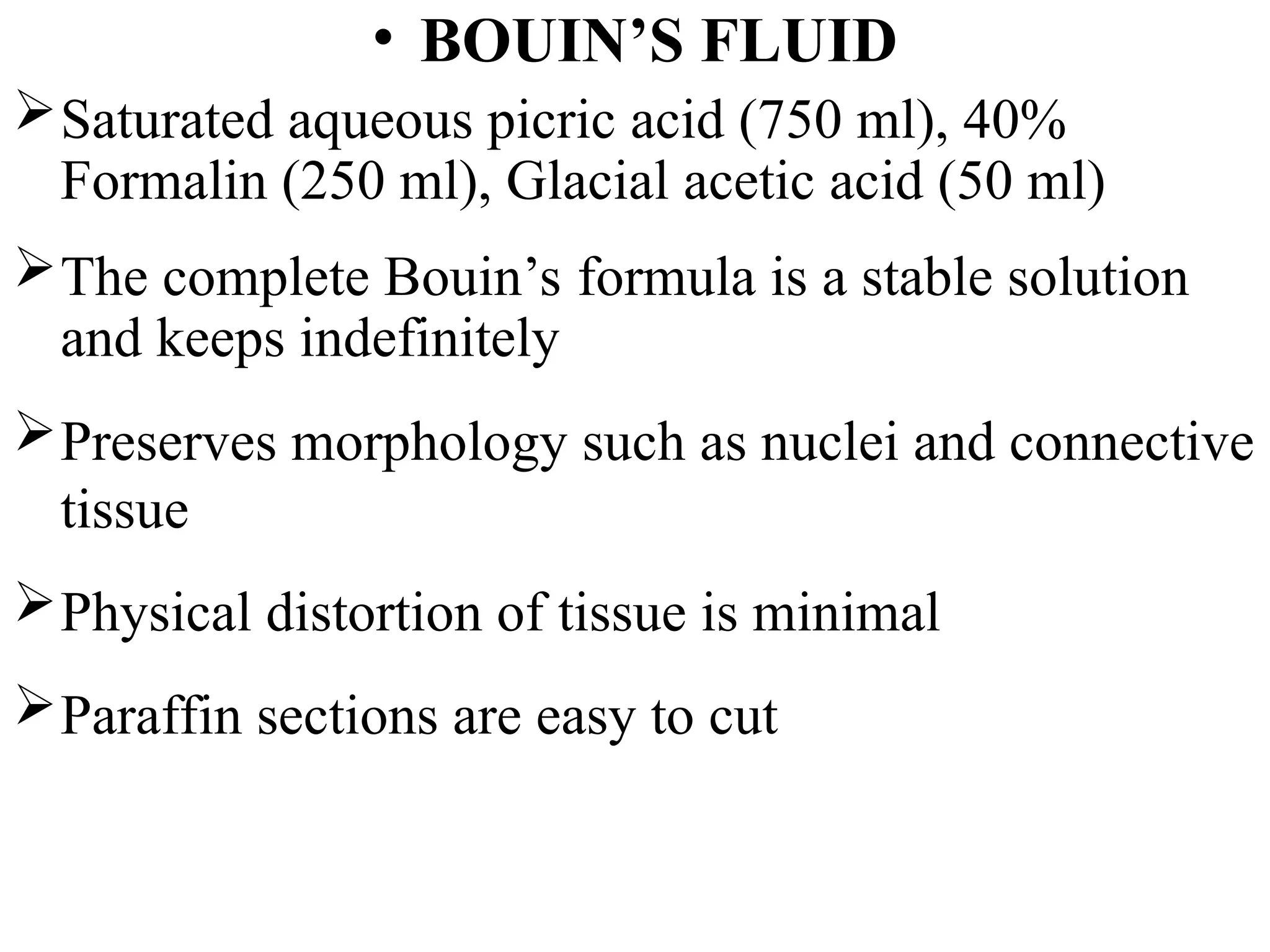
The document discusses the processes of fixation in histopathology, emphasizing the preservation of tissues to prevent autolysis and putrefaction for accurate microscopic examination. It details the various types of fixatives, their mechanisms of action on different tissue components like proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates, and the advantages and disadvantages of common fixatives such as formaldehyde, alcohols, and picric acid. The ideal fixative properties are outlined, alongside the challenges faced in achieving optimal preservation during tissue preparation.