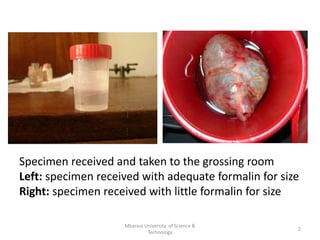
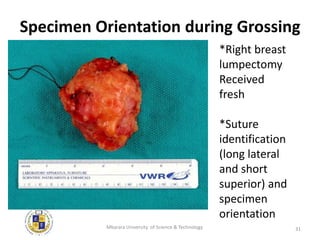
This document provides information and guidelines for grossing tissue specimens in the laboratory. It discusses:
- The key requirements for a grossing room, including equipment, supplies, and personal protective equipment.
- General principles and rules for grossing, such as maintaining specimen orientation, labeling, and documenting findings.
- The general procedure for grossing a specimen, which involves examining, describing, sampling, and preparing the tissue for further processing.
- Safety considerations like using protective equipment and working under a fume hood to minimize exposure to formalin fumes.