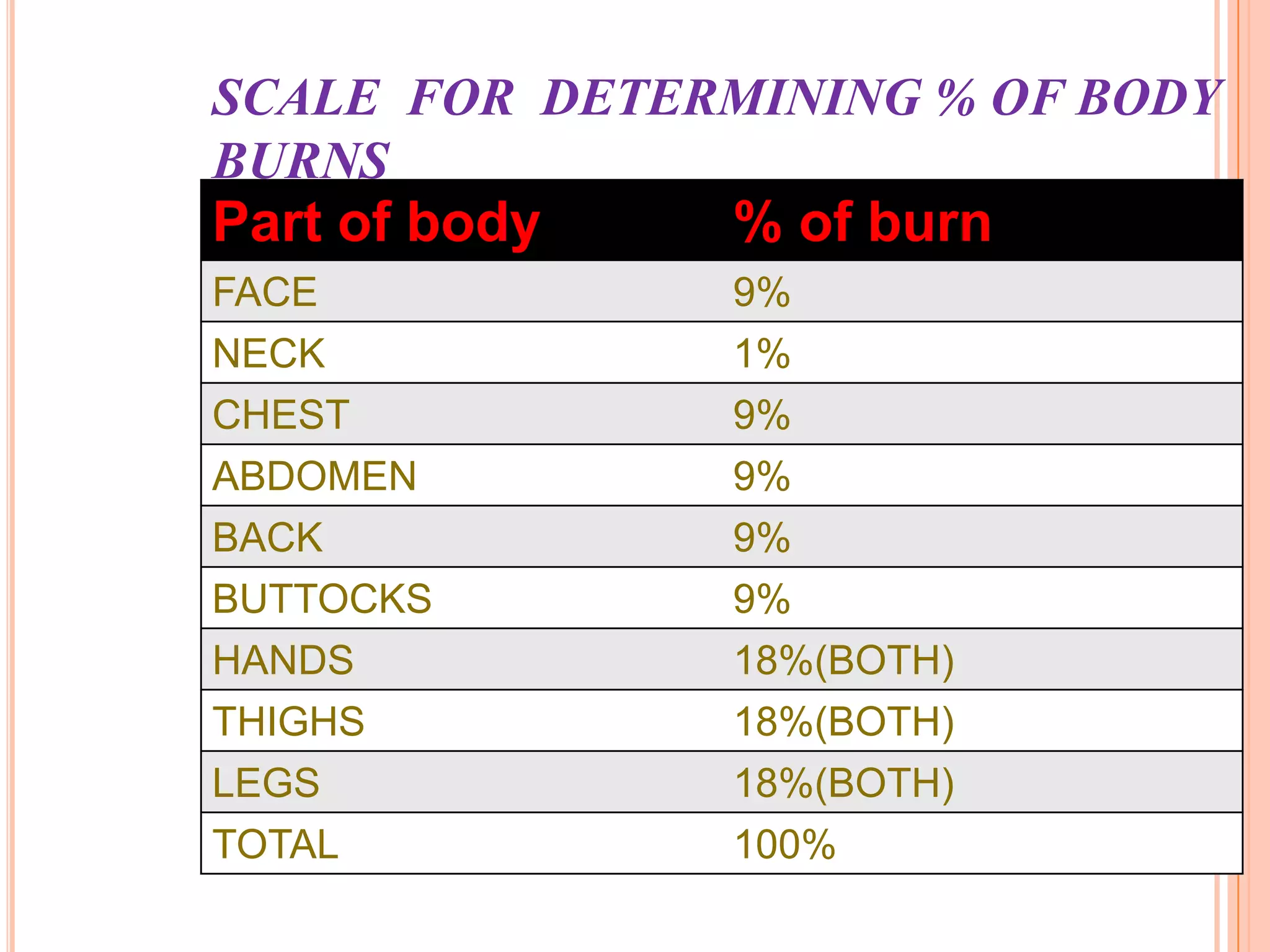
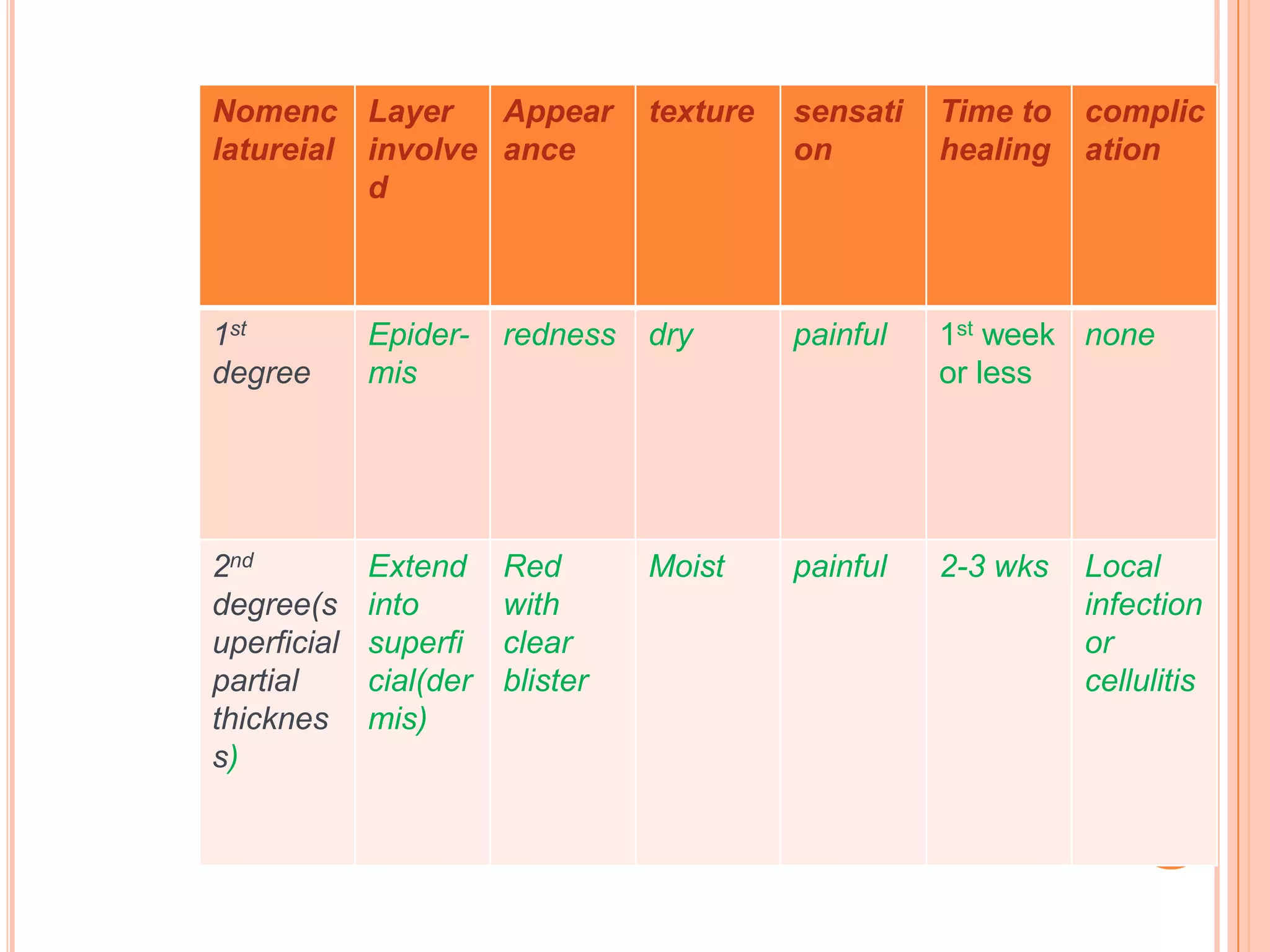
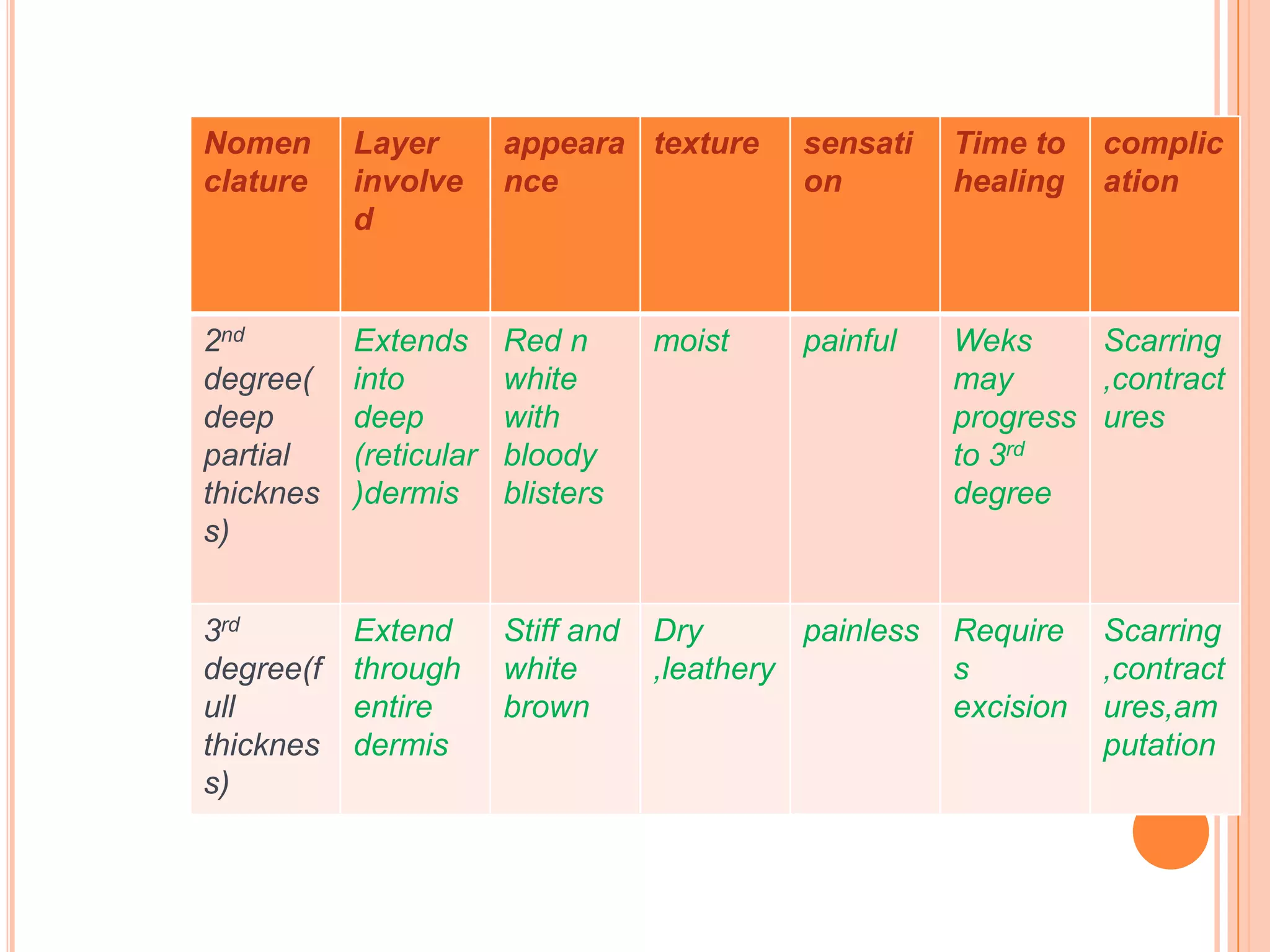
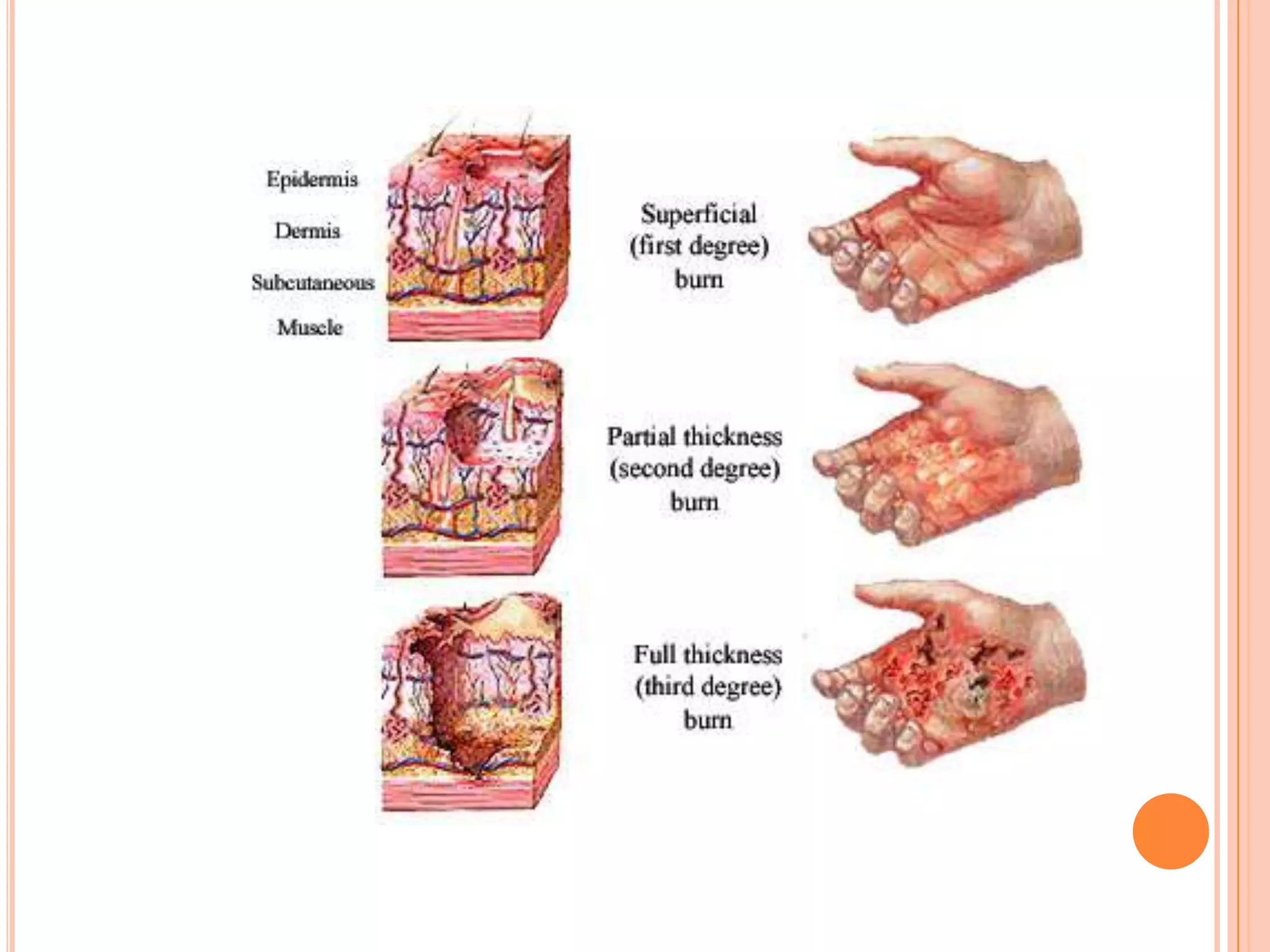
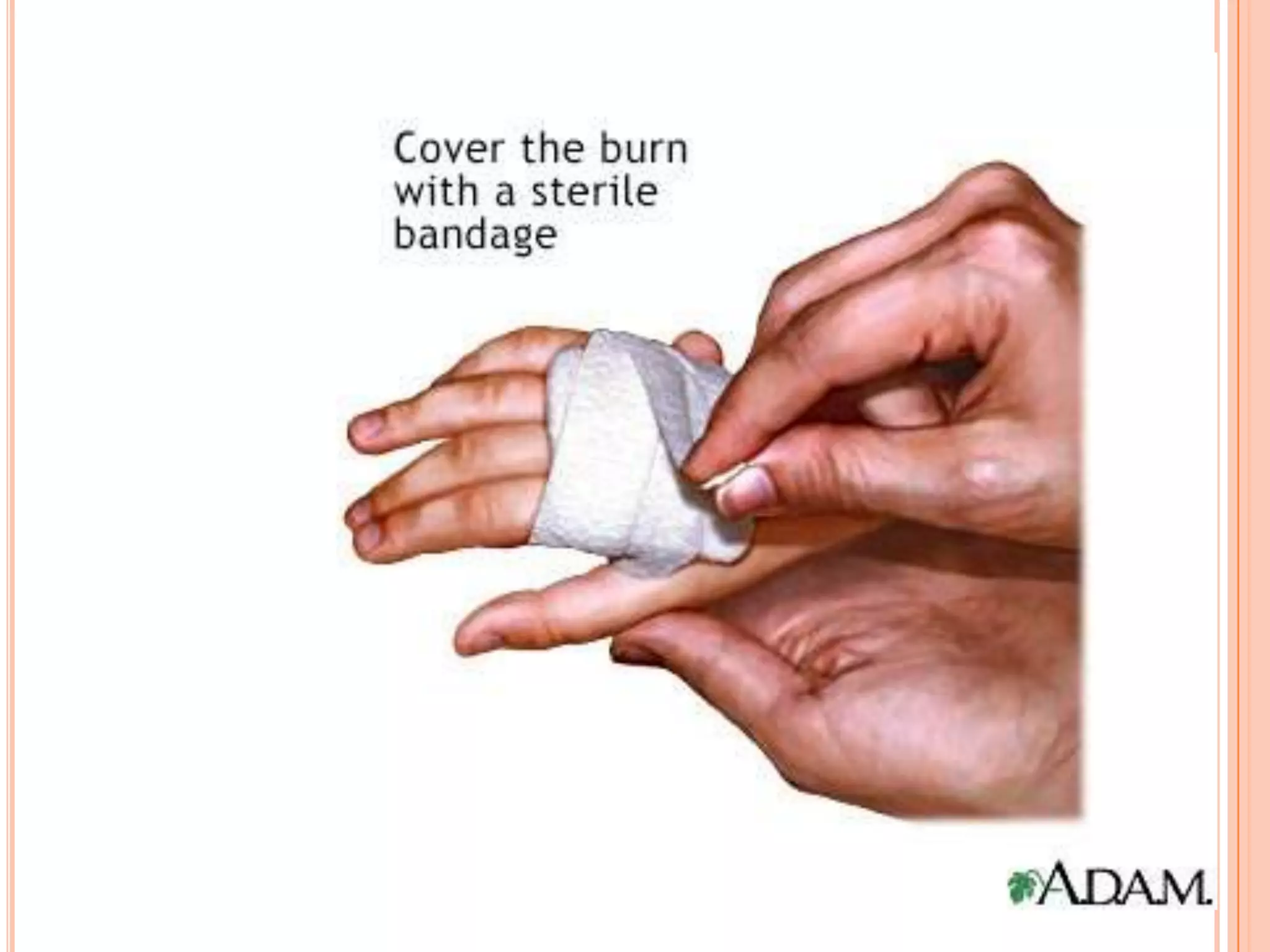
This document provides information on first aid for burn injuries. It describes the causes and degrees of burns, as well as how to assess the severity. For minor burns, it recommends cooling the affected area with water or other cold liquids for 10 minutes. For more severe burns, it says to protect the burned area and seek immediate medical help. First aid involves removing constricting clothing and jewelry near the burn, cleaning and dressing the wound but not applying any creams or ointments. Special precautions are outlined for burns in the mouth, eyes, and those caused by electricity.