This document provides information on wound types, bleeding control techniques, and guidelines for treating different types of wounds. It discusses:
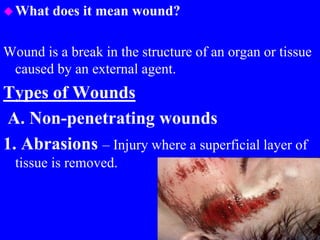
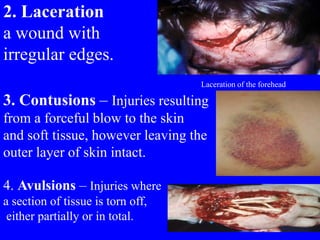
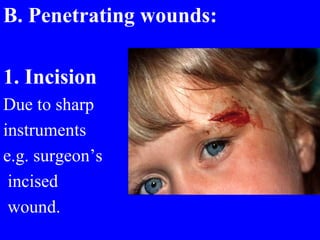
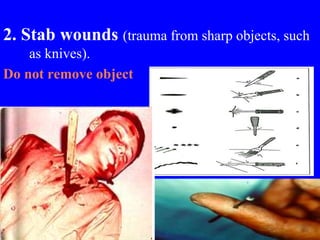
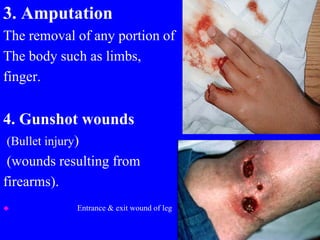
1) The types of wounds including abrasions, lacerations, contusions, avulsions, incisions, stab wounds, amputations, and gunshot wounds.
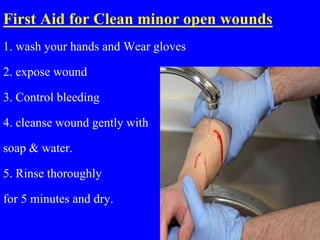
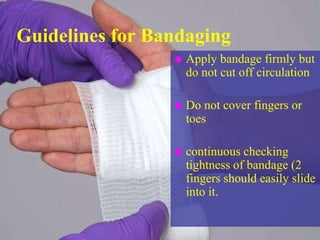
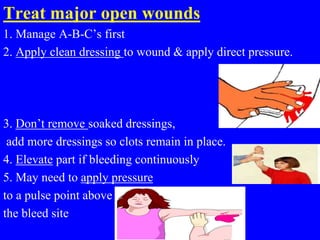
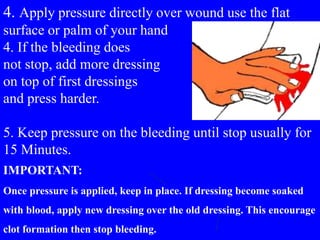
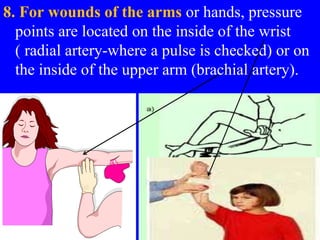
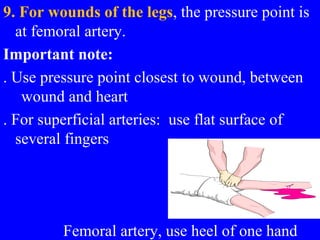
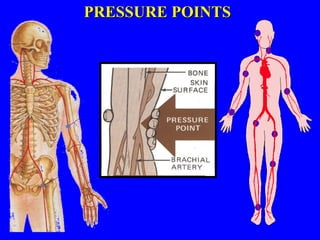
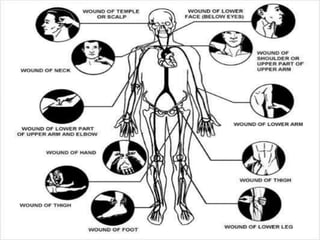
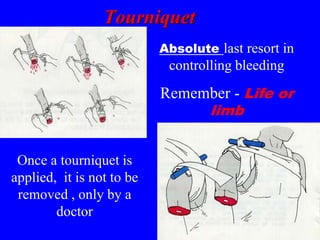
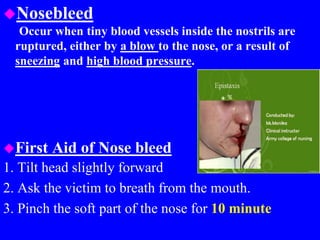
2) First aid procedures for controlling bleeding including applying direct pressure, adding additional dressings, elevating the wound, and applying pressure to pressure points if needed.
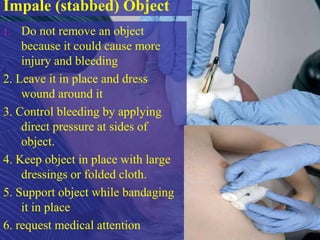
3) When medical attention is required such as for wounds that won't stop bleeding, deep or large wounds, infected wounds, bites, impaled objects, and wounds requiring stitches.
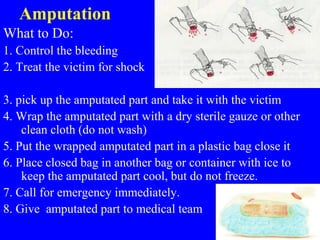
4) Specific treatments for injuries like amputations where the