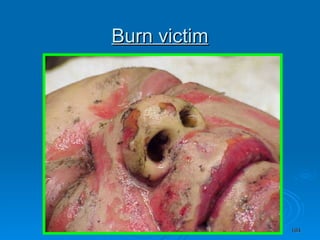
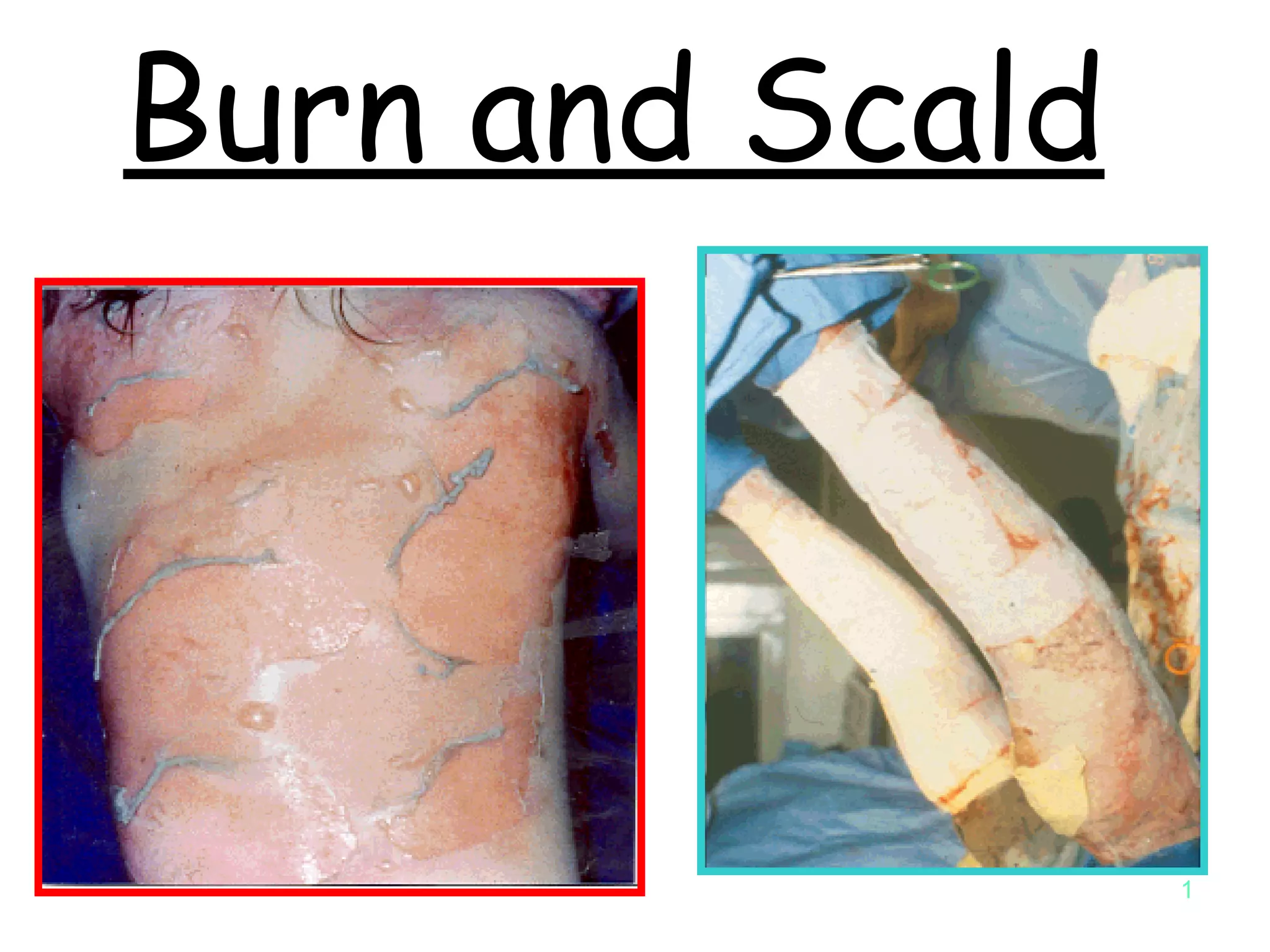
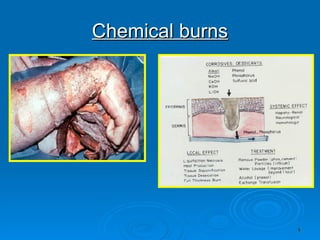
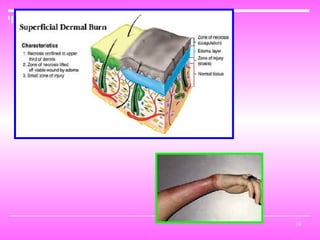
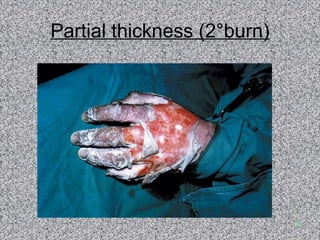
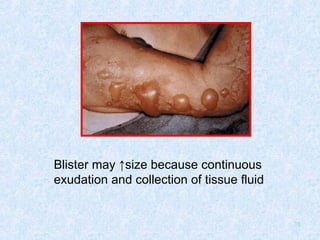
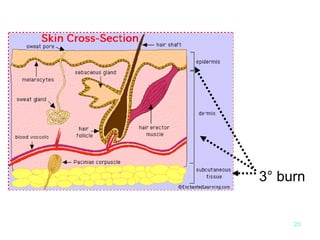
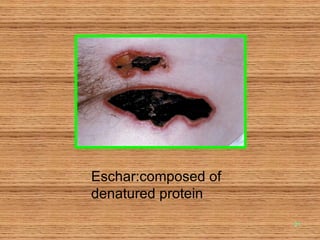
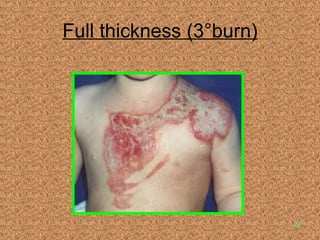
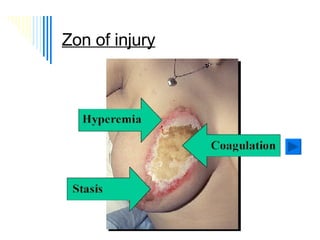
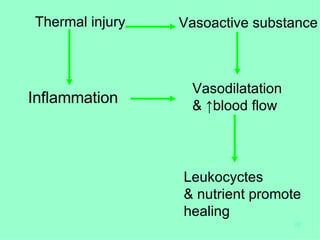
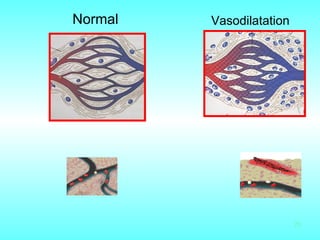
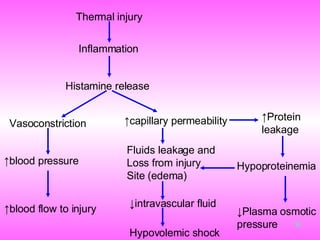
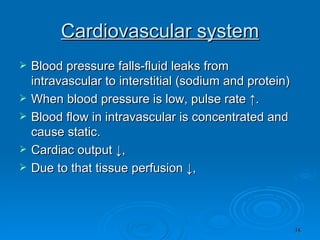
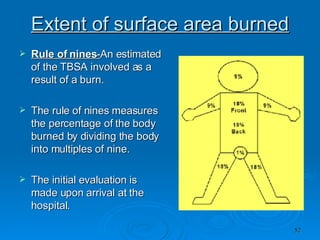
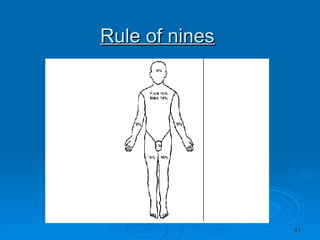
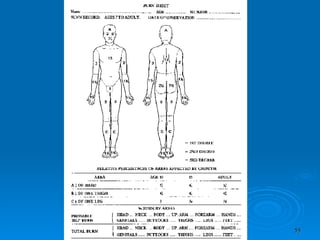
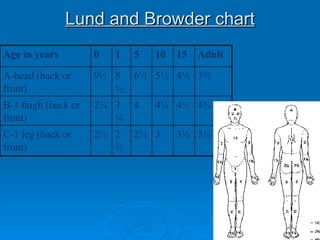
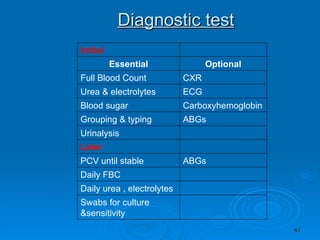
Burn and scald injuries can be caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, or radiation. Thermal burns are the most common and are classified as superficial, partial thickness, or full thickness depending on the depth of tissue damage. A severe burn over 25% of the total body surface area can cause systemic effects like shock due to fluid loss, decreased blood pressure, and increased heart rate. Complications include infection, respiratory failure, renal failure, and contractures. The severity of the burn is estimated using methods like the Rule of Nines or Lund and Browder chart which divide the body into sections and assign a percentage of total body surface area to each.






















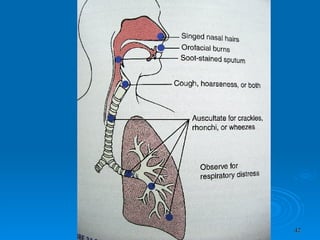
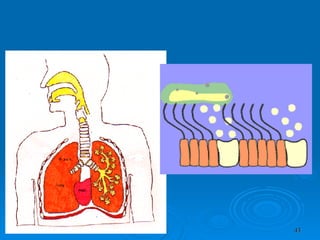
![Features of respiratory failure Inability to speak due to dyspnea Sweating Apparent exhaustion/tired Tachycardia Tachypnea [R. Rate > 40 /min in adults ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burn-and-scald1414/85/Burn-And-Scald-44-320.jpg)
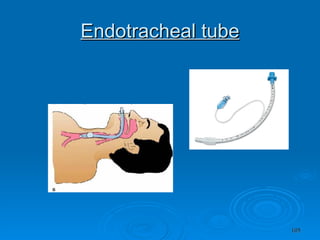
![Management Anaesthetic consultation High flow oxygen Tracheobronchial [ bronchoscopy] Physiotherapy Close monitoring [preferably ICU ] Ventilatory support Hemodynamic support, when required](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burn-and-scald1414/85/Burn-And-Scald-45-320.jpg)




























![Emergency Management Hospital Priorities -Airway -IV access – large bore peripheral line -Analgesia – diluted opioids, - intravenously, large bore. Catheterise bladder Investigations [ see box below]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burn-and-scald1414/85/Burn-And-Scald-80-320.jpg)

![Estimation of Total Body Surface Area Burned [ TBSA] Major Burns : >10 % BSA deep burn in a child >25% BSA deep burn in an adult All major burns WILL need parenteral fluid resuscitation , since the main cause of early mortality is Burns Shock.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burn-and-scald1414/85/Burn-And-Scald-83-320.jpg)








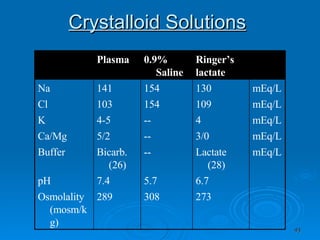
![Fluids resuscitation Calculate fluid deficit and decide fluid requirement 2 types of fluids – Crystalloids and Colloids Crystalloids [e.g. –Ringer’s Lactate] -Several formulas: Evans, Brookland etc. 3 – 4 ml / Kg. bodyweight / % Burn during the first 24 hours, -half of which is to be given in the first 8 hrs [ from the time of injury ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burn-and-scald1414/85/Burn-And-Scald-92-320.jpg)
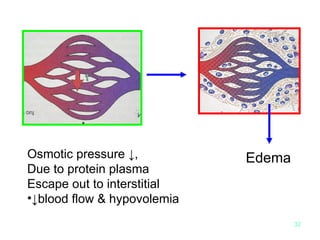
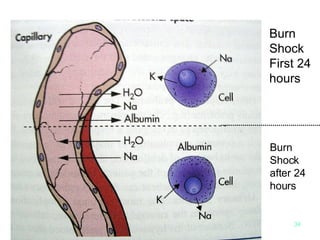
![Colloids [e.g. Human Albumin Solution ] 1.Proteins in plasma generate osmotic pressure and serve to maintain the intravascular volume. -The administration of colloid compensates for this protein lost. 2 . Much debate exists as to when capillary integrity is established and when or if colloid should be given 3. Early infusion of colloid solutions may decrease overall fluid requirements and reduce edema. However, excessive use of colloid risks iatrogenic pulmonary complications.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/burn-and-scald1414/85/Burn-And-Scald-94-320.jpg)