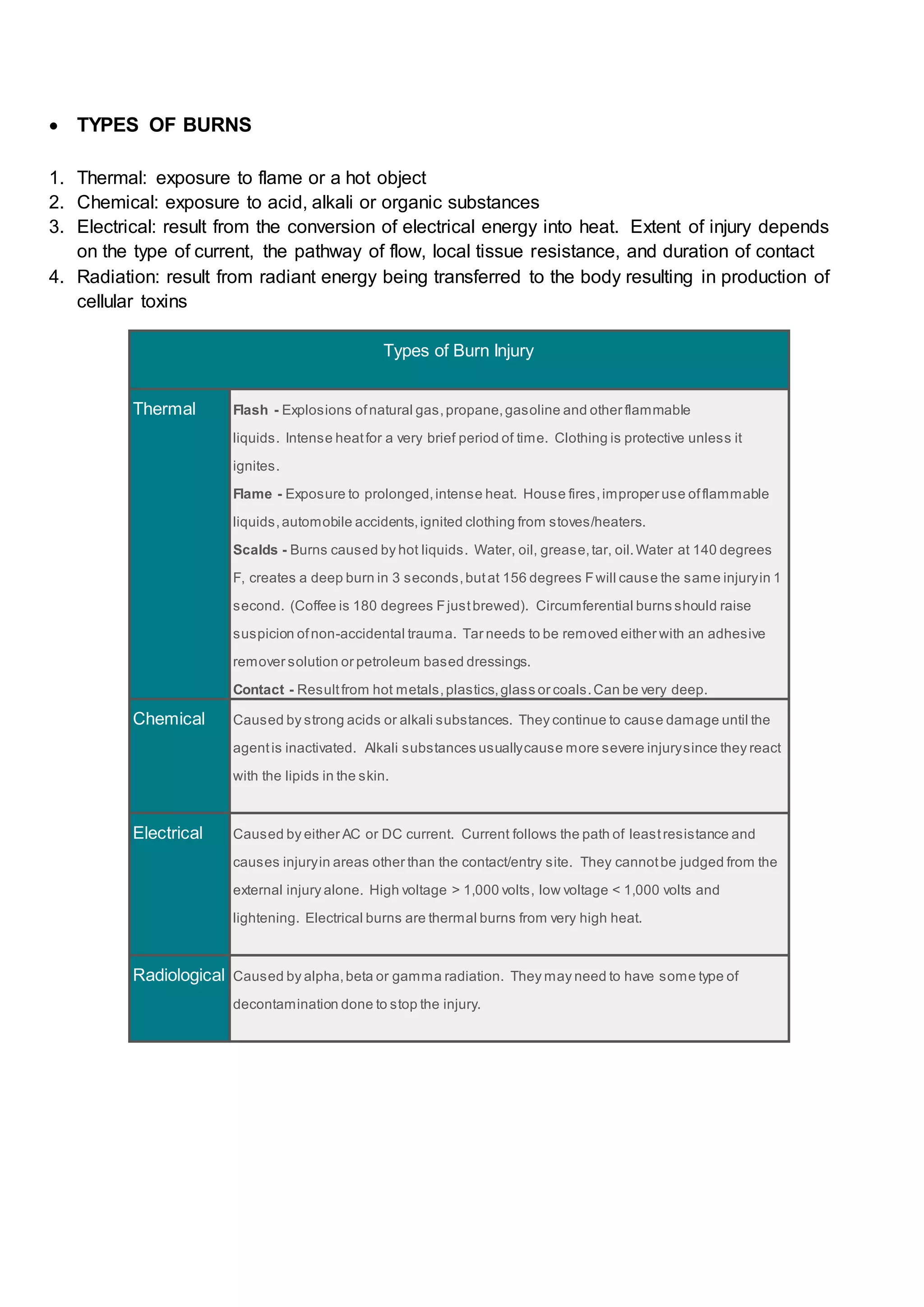
This document provides information on burns, including causes, assessment, treatment and prevention. Burns are injuries caused by heat, chemicals, electricity or radiation. Assessment involves checking the airway, breathing, circulation, disability and exposure. Treatment depends on the severity and depth of the burn, and may include cleaning, dressing and fluid replacement. Deeper burns require specialist care. Prevention strategies include smoke alarms, fire safety education, and safe cooking and electrical practices.