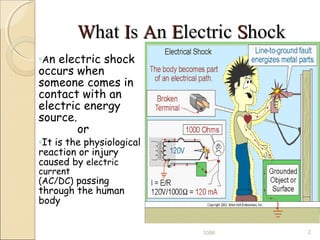
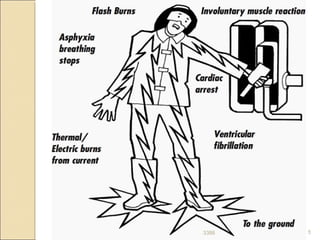
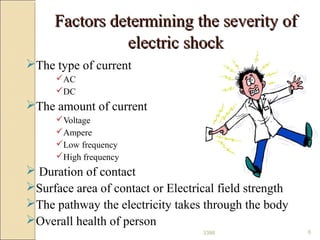
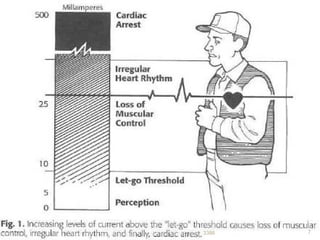
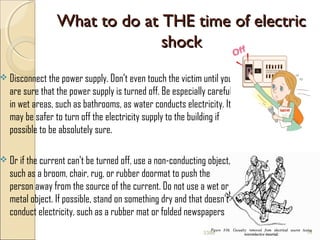
An electric shock occurs when someone comes into contact with an electric current from sources like poorly insulated wires, electrical equipment in contact with water, or lightning. Effects can range from no injury to death, depending on factors like current type, voltage, duration of contact, and individual health. Immediate first aid involves disconnecting the power source without direct contact, attending to injuries like burns, and seeking emergency help. Ongoing treatment may include examination, resuscitation, wound care and cardiac monitoring.