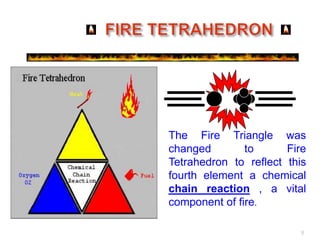
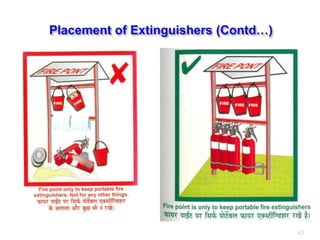
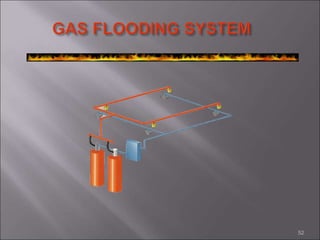
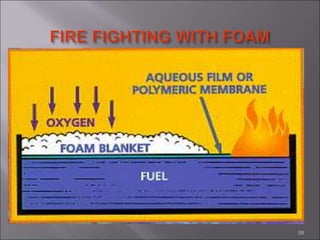
This document provides information on fire causes, fire triangle/tetrahedron, fire classification, portable fire extinguishers, firefighting rules, and other fire protection systems. The main causes of fire are identified as electrical short circuits, smoking, hot works, and static electricity. It discusses the three elements (oxygen, heat, fuel) needed for combustion. Portable extinguishers are classified by the type of fire they can extinguish such as water, foam, dry chemical powder, CO2. Proper use and maintenance of extinguishers is also covered. Other fire protection methods include detectors, sprinklers, fire hydrants, tenders, and passive protections like compartments.