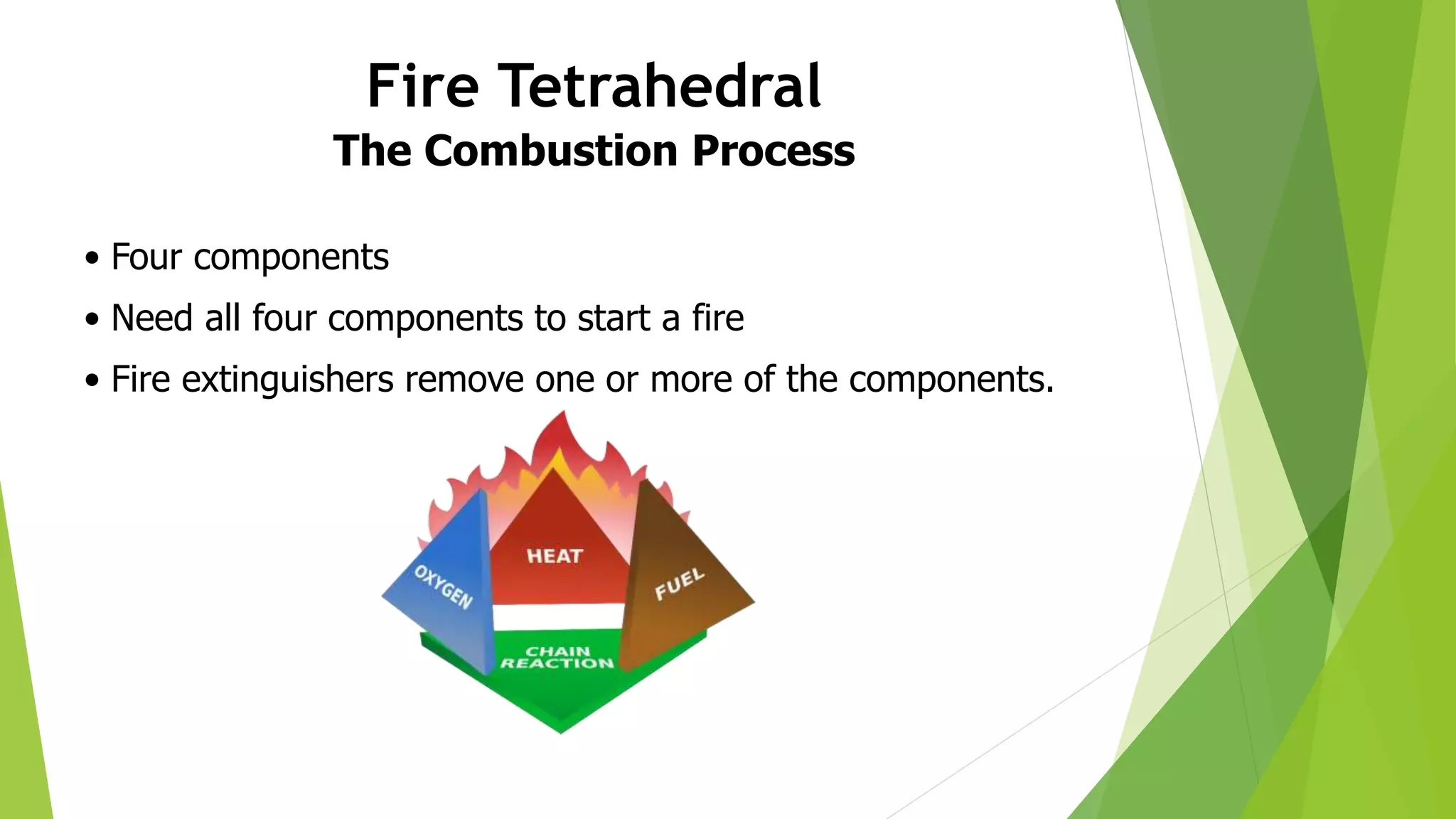
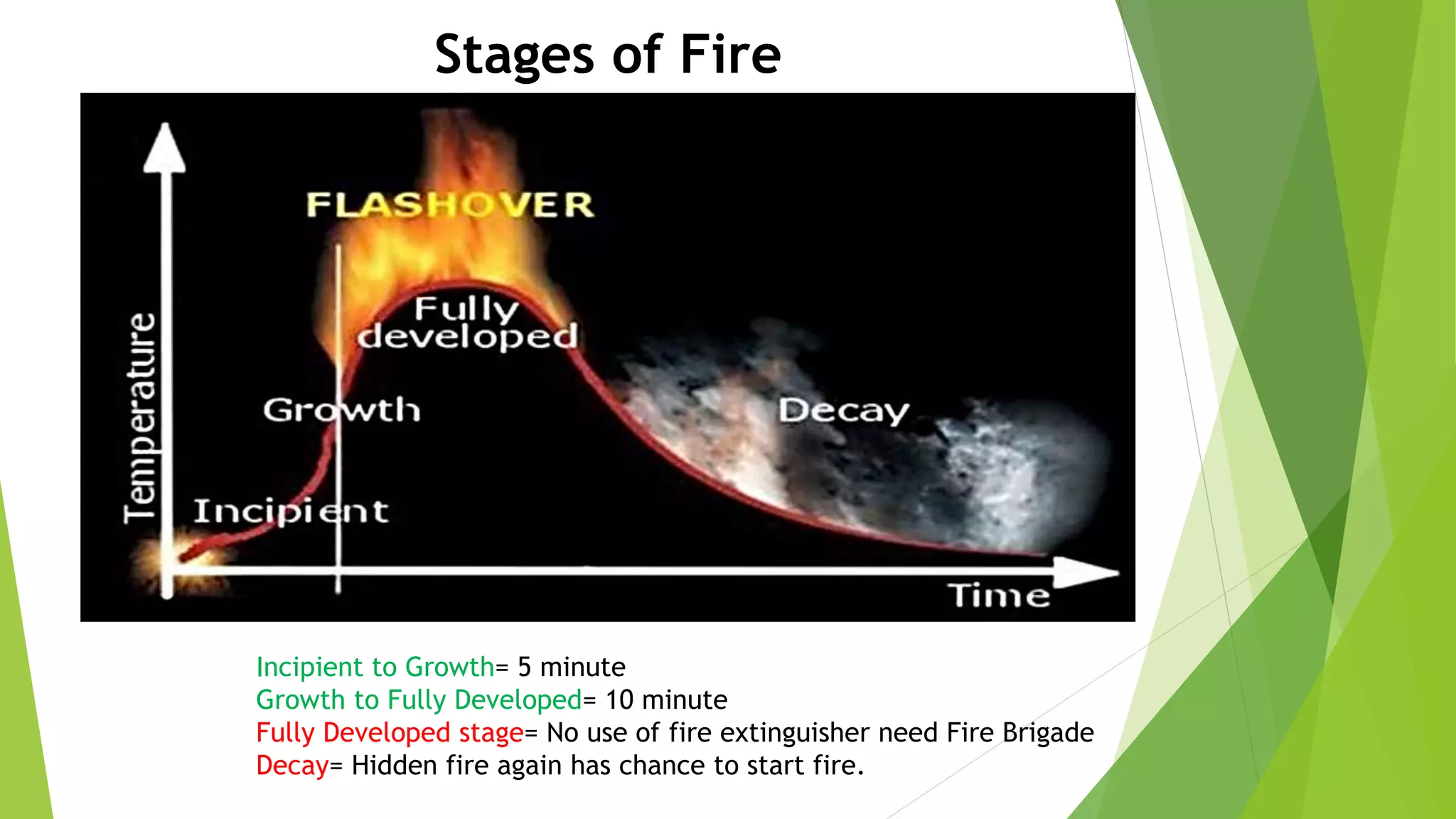
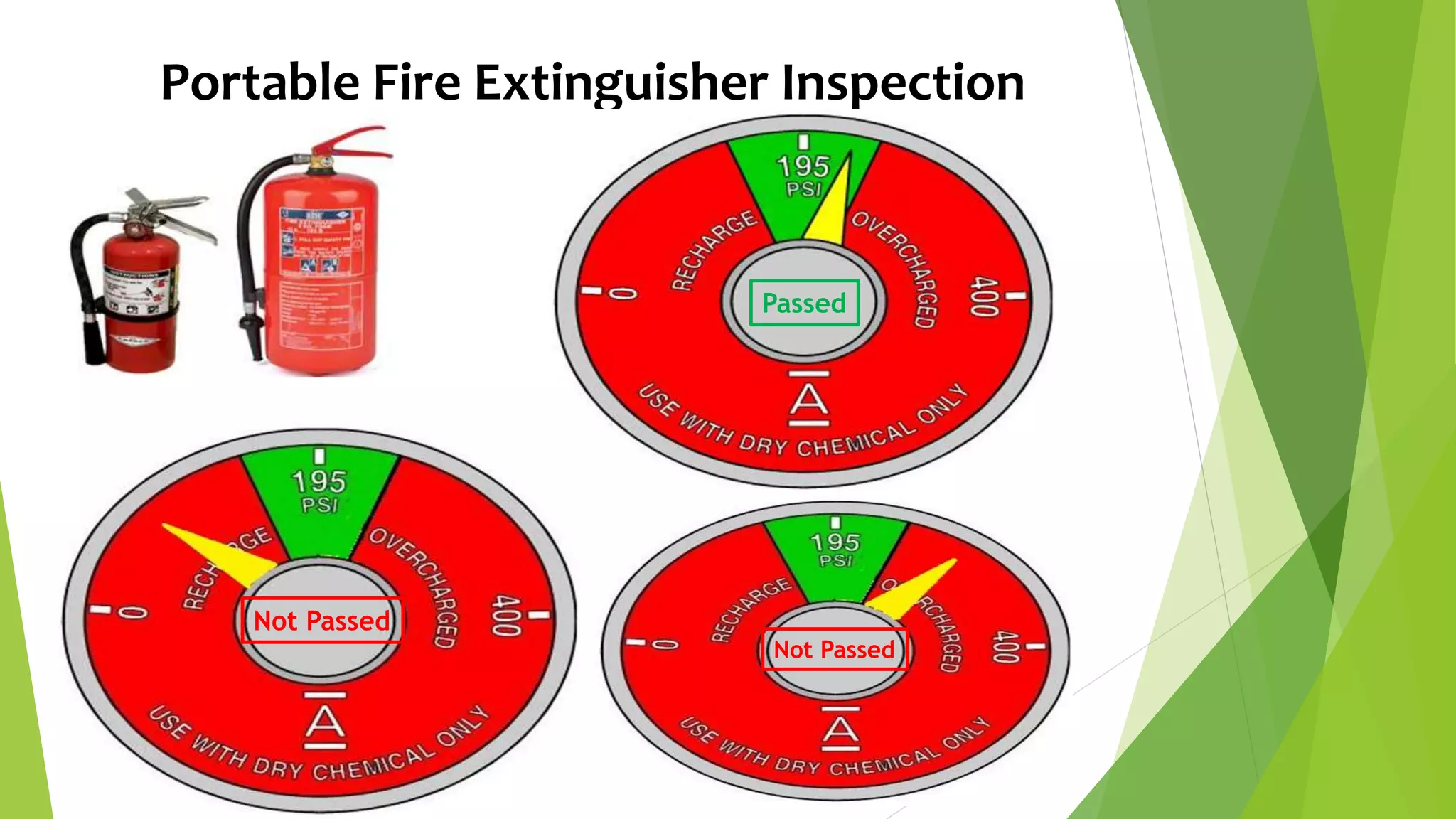
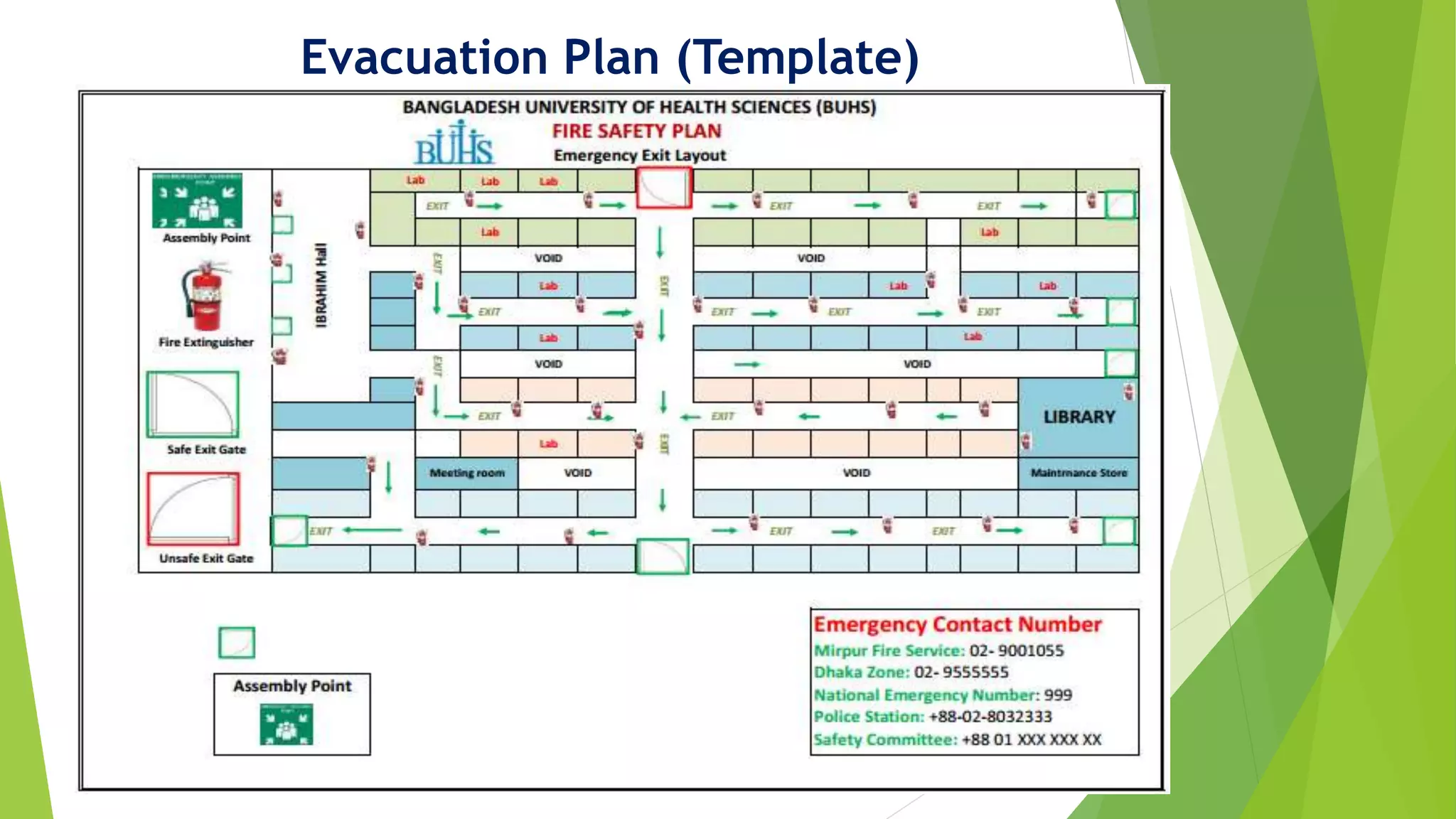
This document provides training on basic fire safety and fire extinguishing. It discusses the definition of fire, the fire tetrahedron, different classes of fire types, stages of fire, how to use a fire extinguisher, fire fighting systems, and forming a fire fighting team. The training covers identifying fires, appropriate extinguishing methods based on fire class, inspecting fire extinguishers, PASS techniques for operating an extinguisher, and establishing a fire prevention team with defined roles.