Embed presentation
Downloaded 173 times

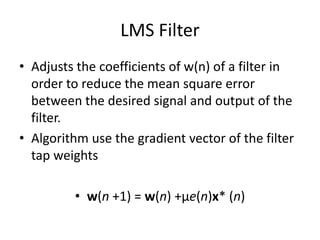




The document discusses the NLMS adaptive filter algorithm. The LMS algorithm adjusts the coefficients of a filter to minimize the mean square error between the desired and actual output signals. The NLMS algorithm normalizes the step-size parameter based on the input signal power to overcome issues from changing input power levels. A result is shown comparing actual and estimated filter weights using the NLMS algorithm.





