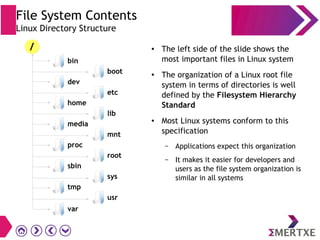
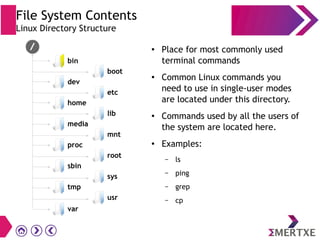
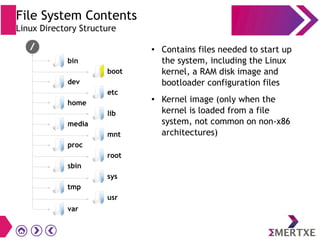
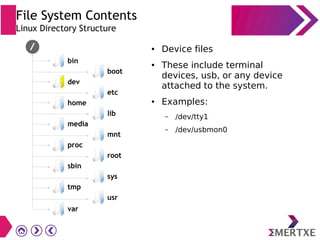
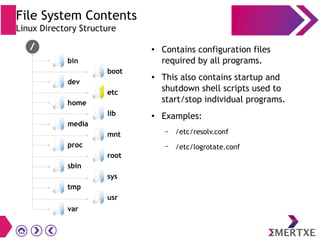
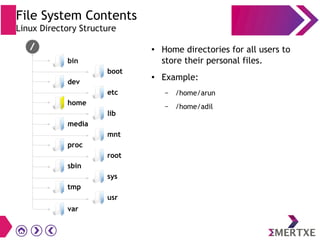
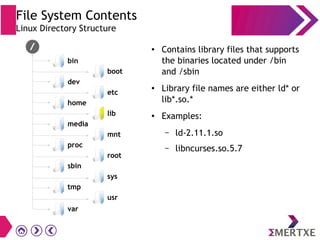
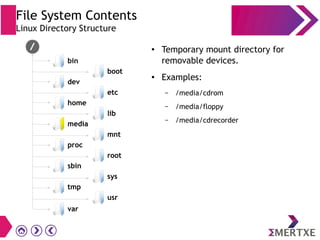
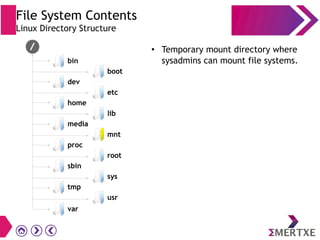
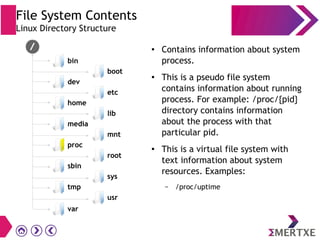
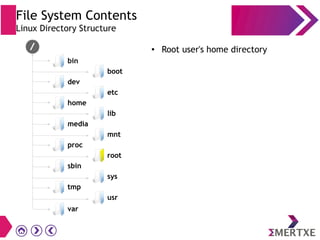
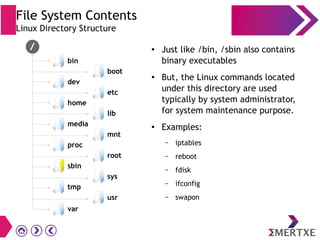
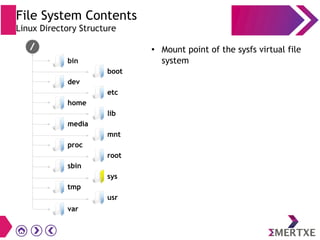
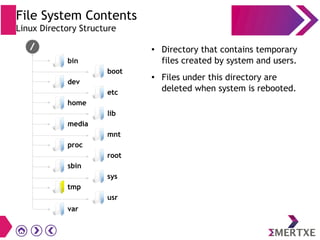
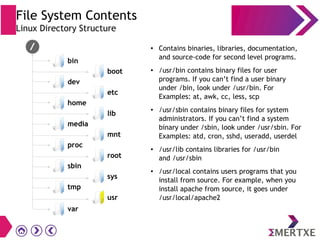
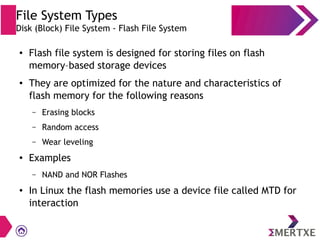
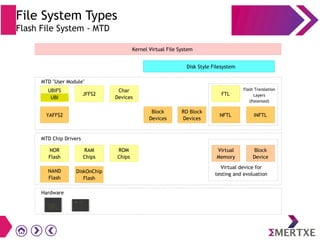
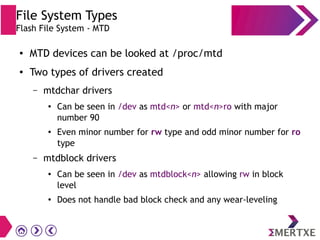
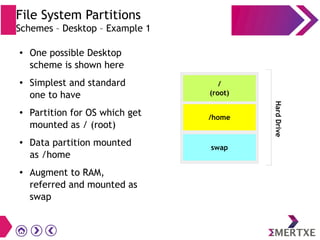
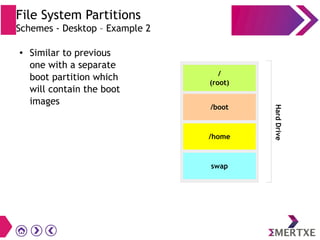
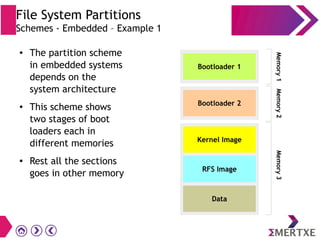
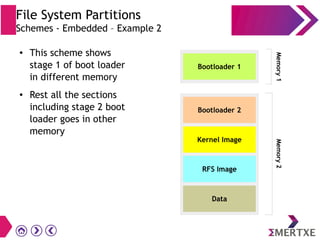
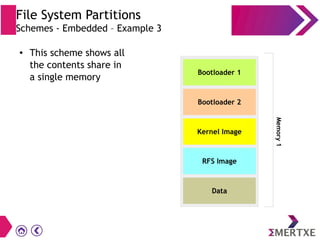
File systems provide an organized way to store and access data on storage devices like hard drives. The Linux file system hierarchy standard defines a common structure across Linux distributions with directories like /bin, /etc, /home, /usr, and /var. Common Linux file system types include ext2, ext3, ext4 for disks, initramfs for RAM, and JFFS2 for flash storage. File systems can also be distributed across a network using NFS or optimized for specific purposes like squashfs for read-only files. Partitions divide available storage space to better manage files, users, and data security.