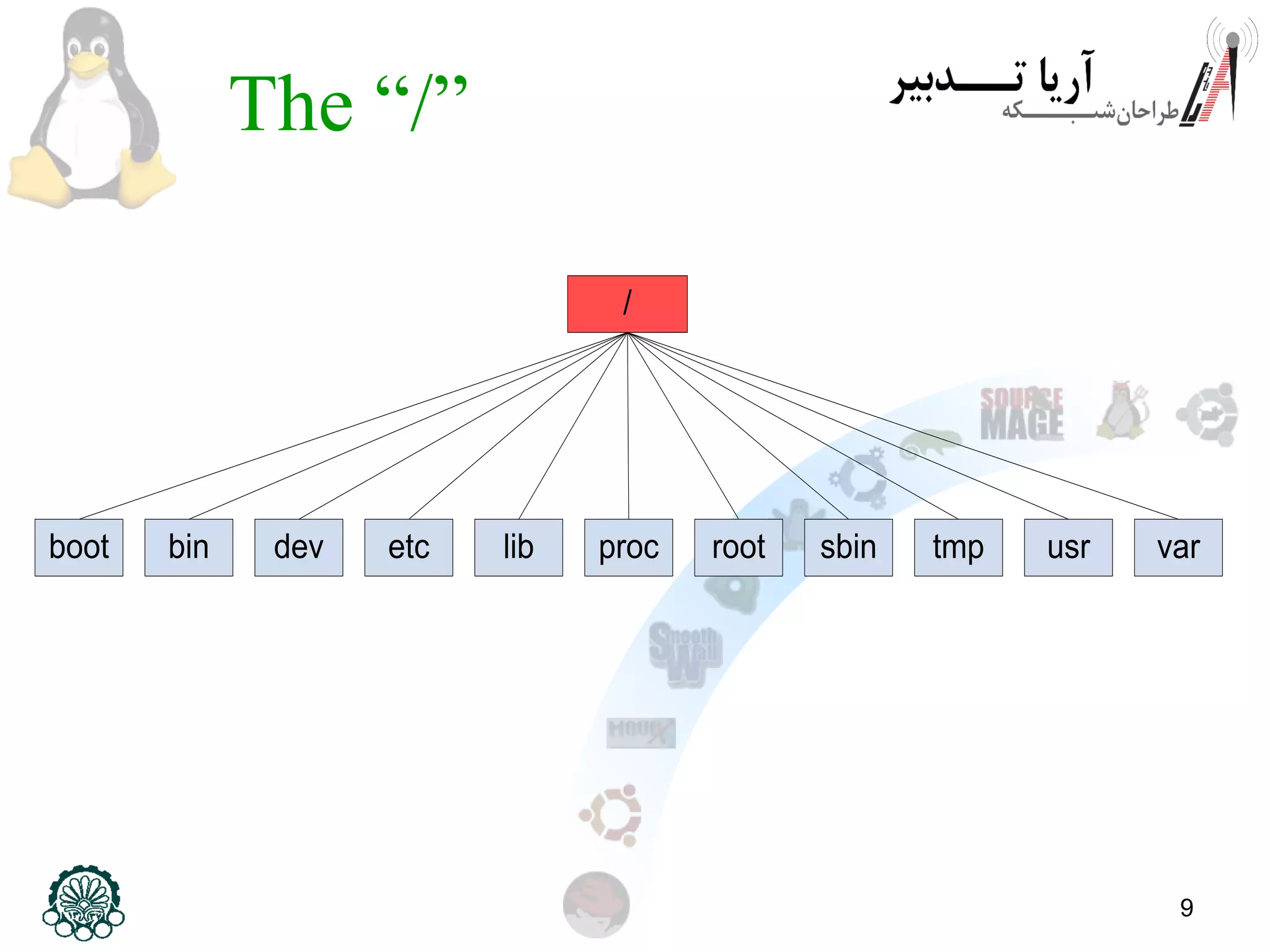
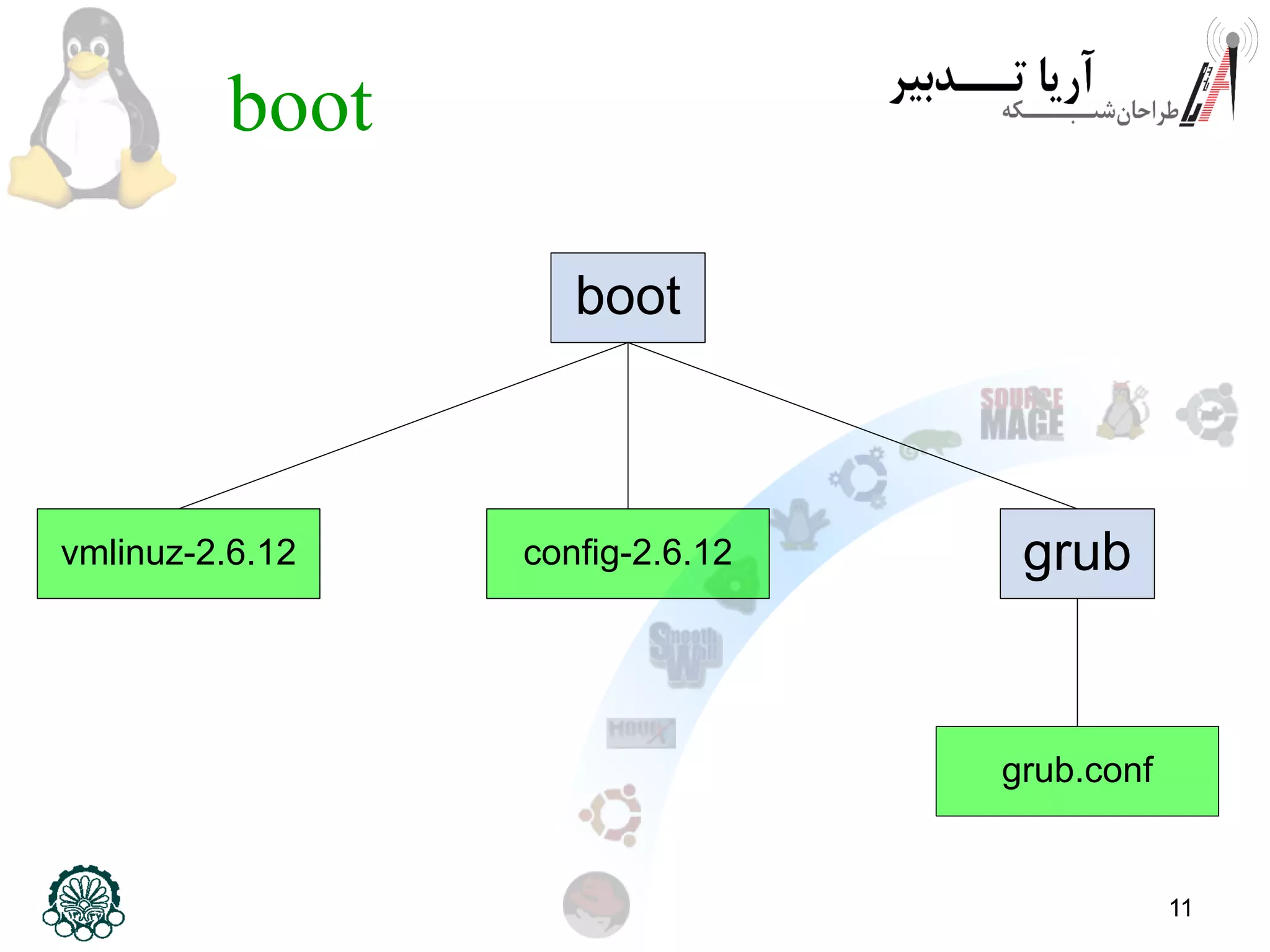
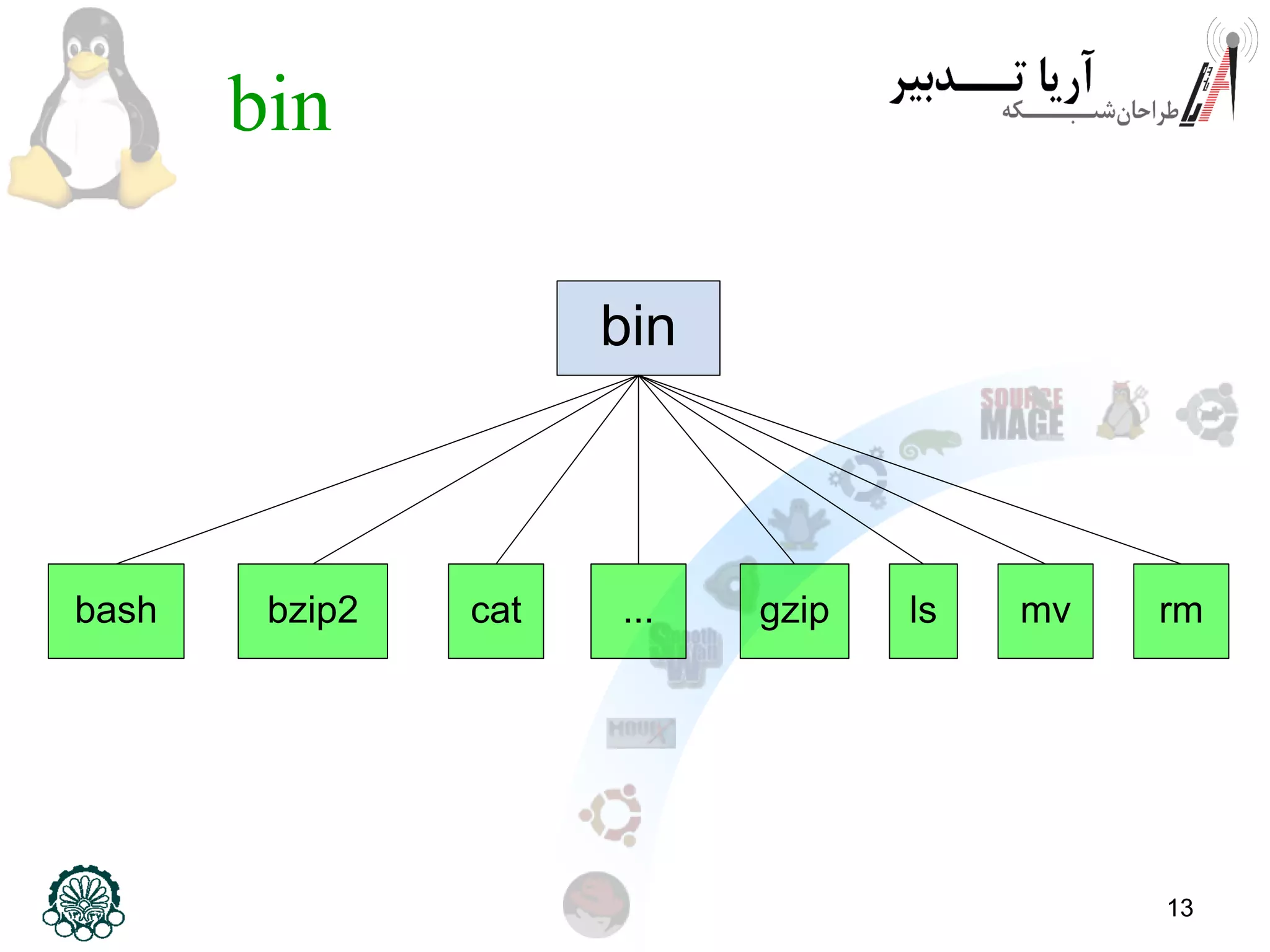
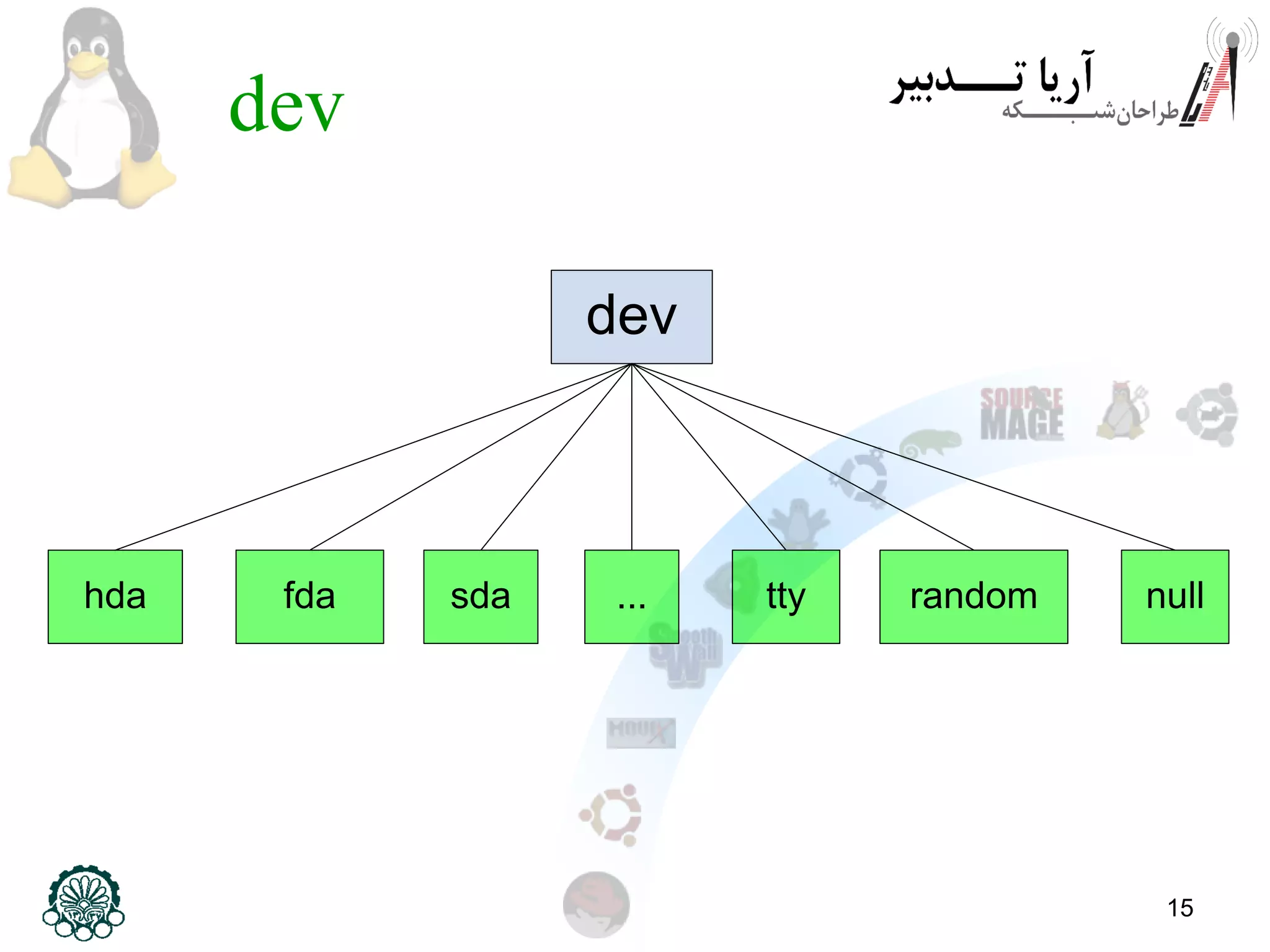
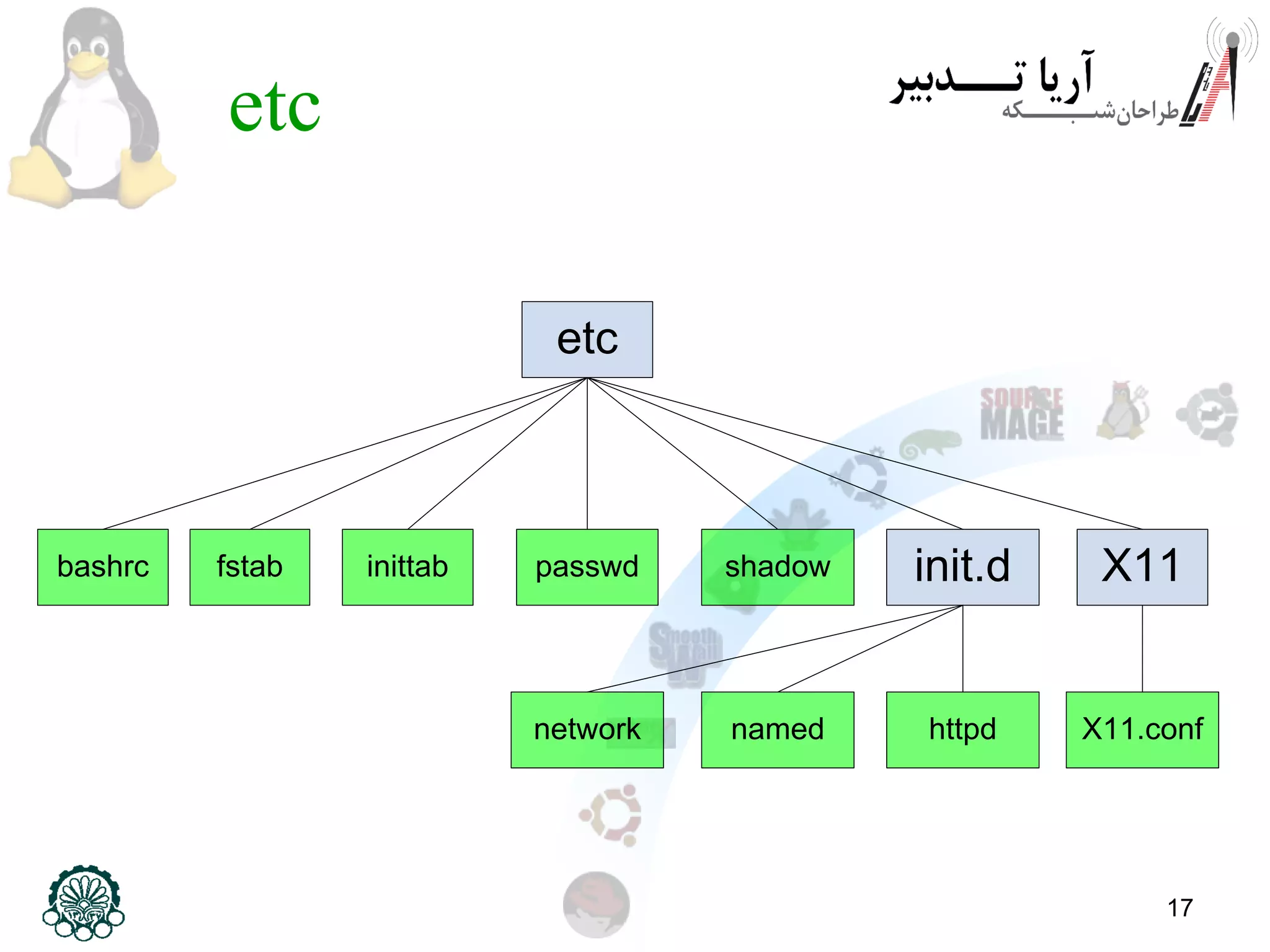
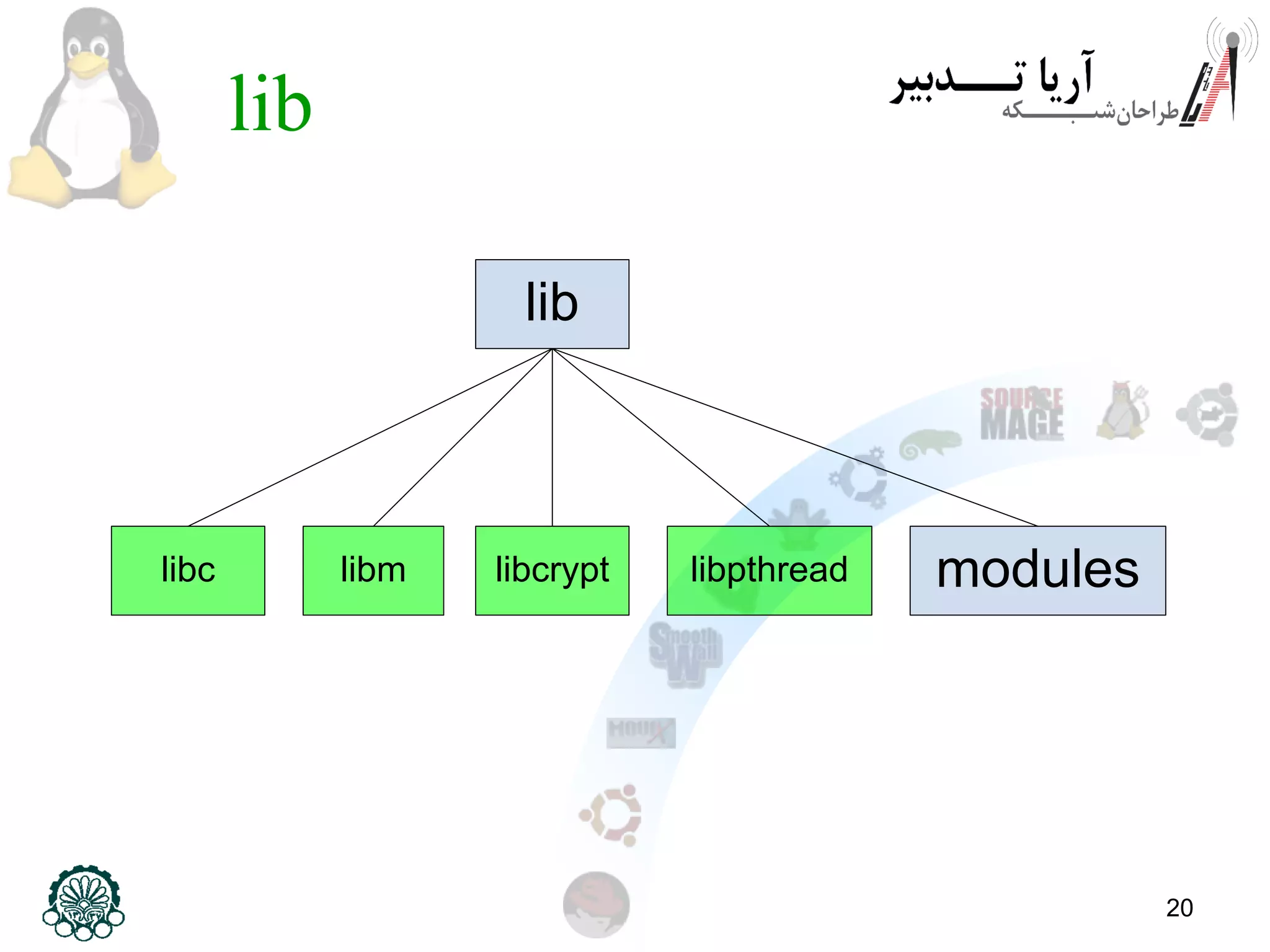
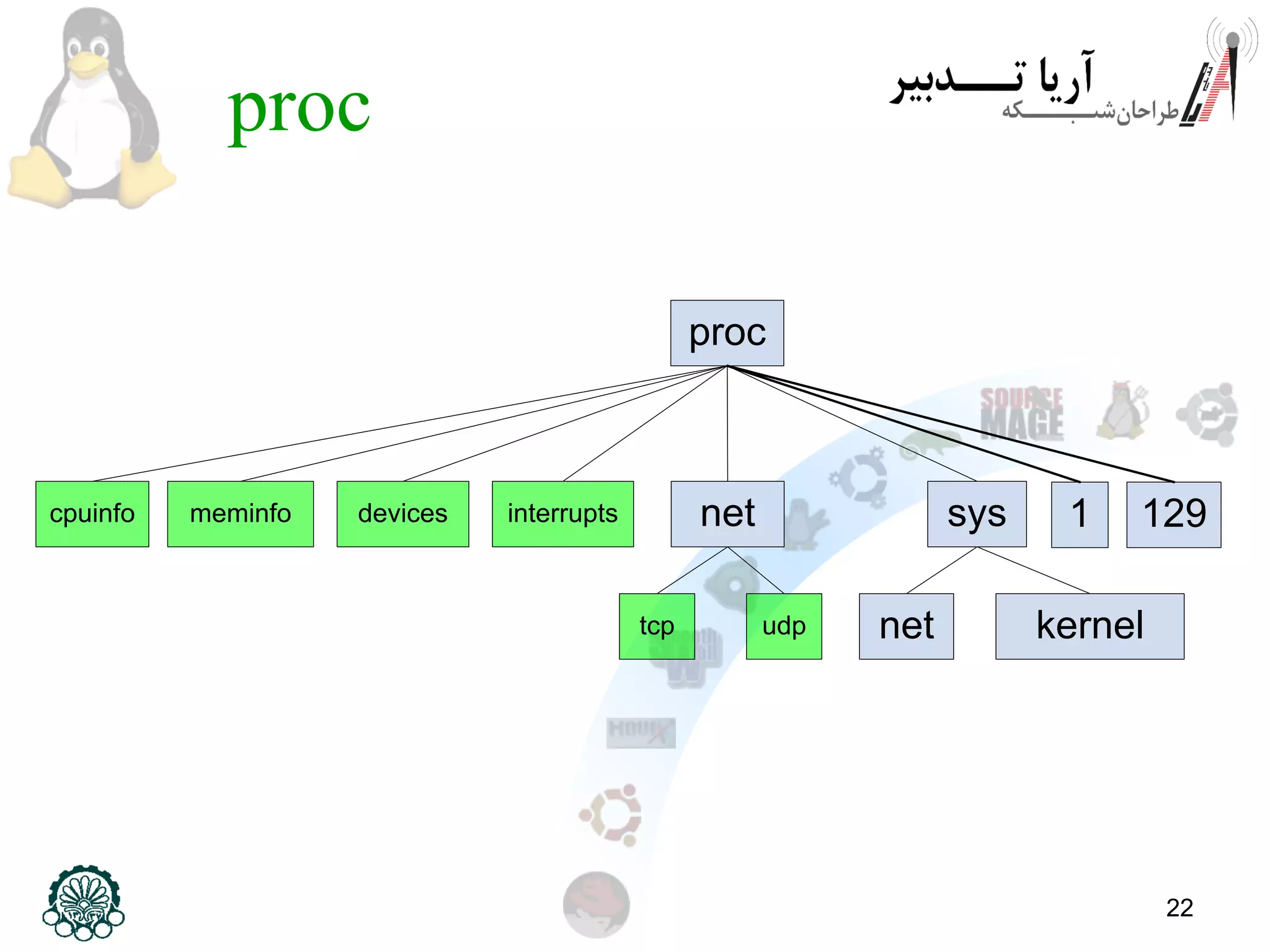
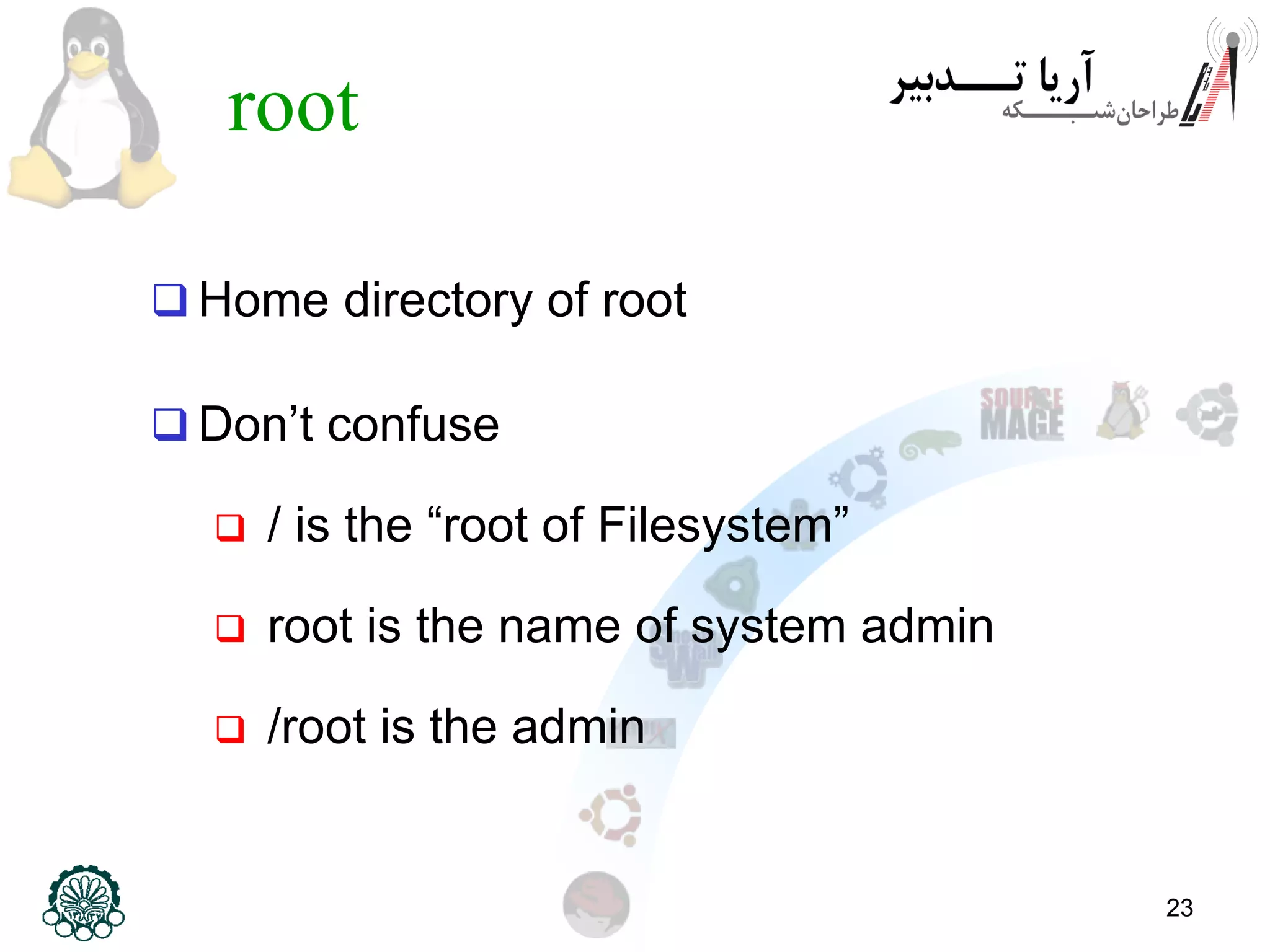
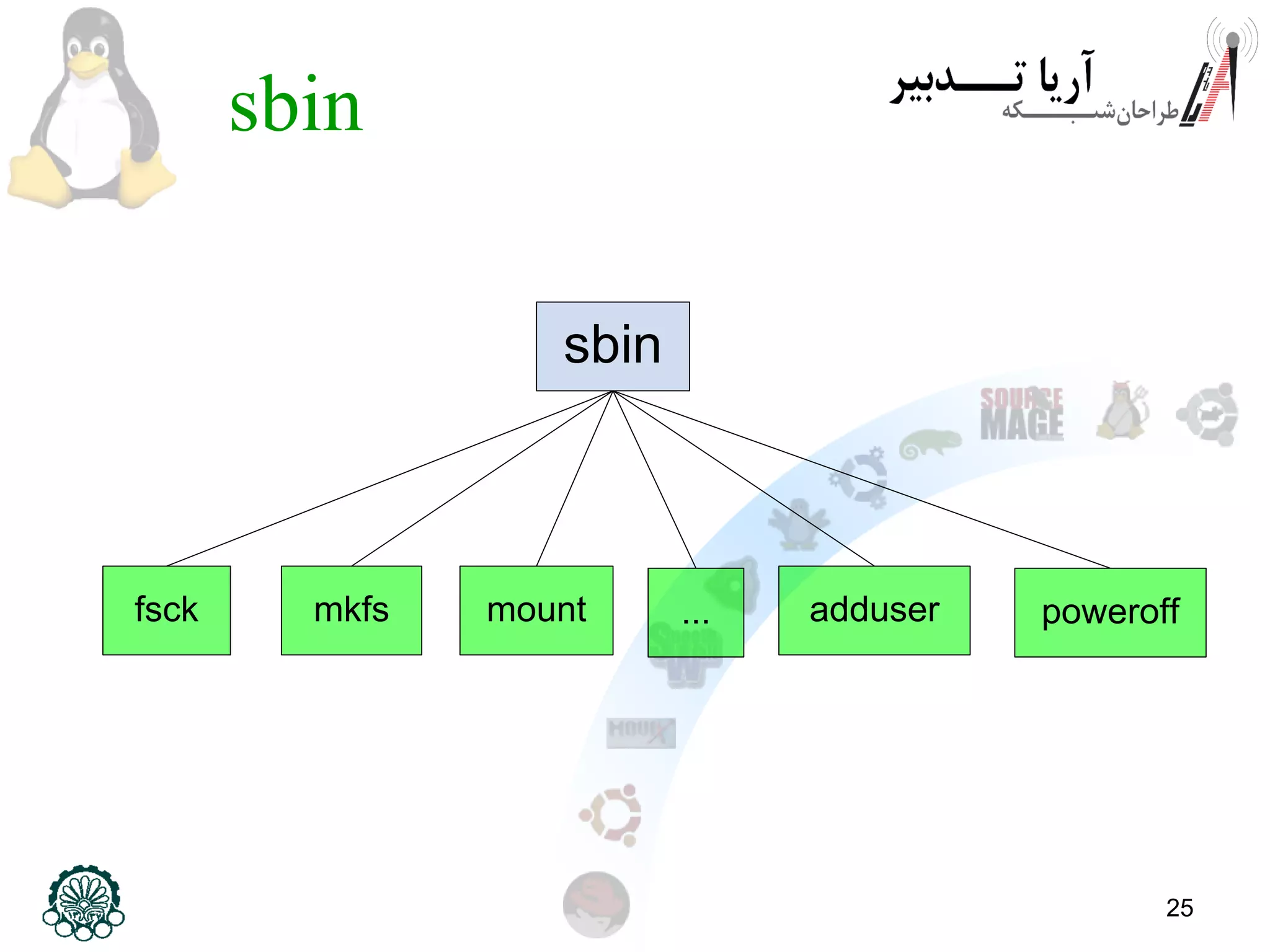
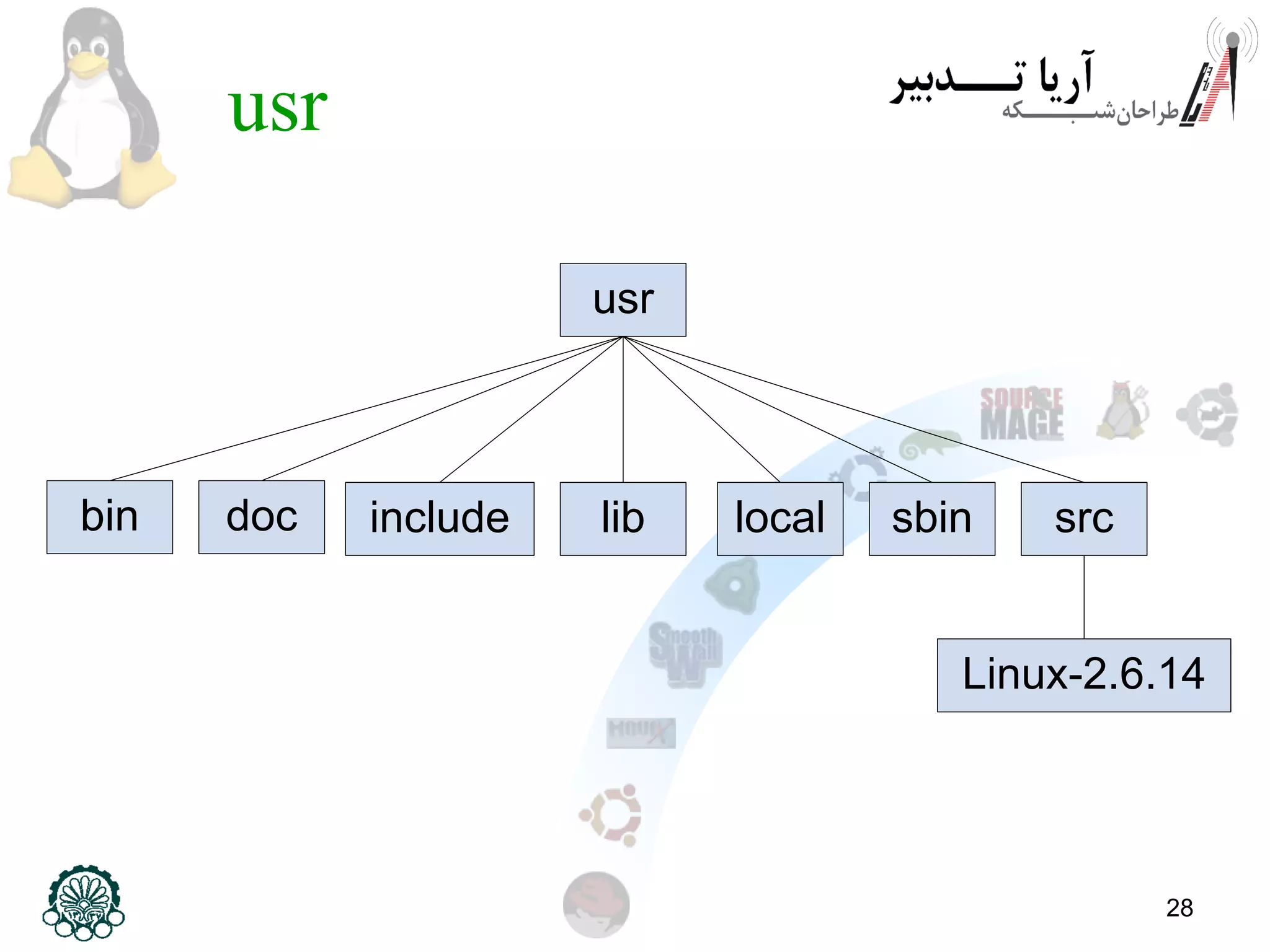
This document provides an overview of the Linux filesystem, including its structure, key directories, and concepts like mounting. It describes the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard which defines the main directories and their contents. Key points covered include that everything in Linux is treated as a file, the top-level root directory is "/", essential directories like /bin, /dev, /etc, /home, /lib, /proc, /sbin, /usr, /var are explained, and mounting additional filesystems is described.