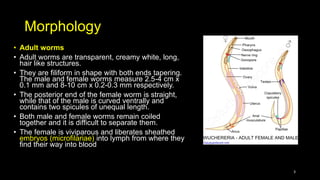
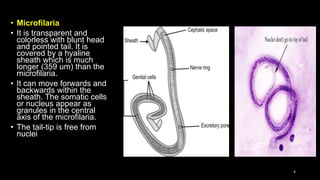
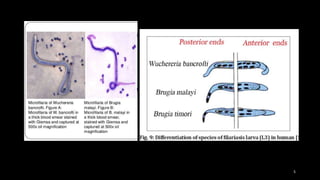
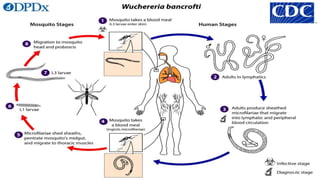
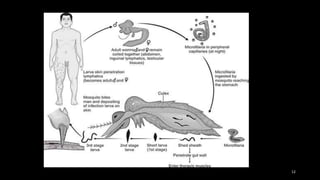
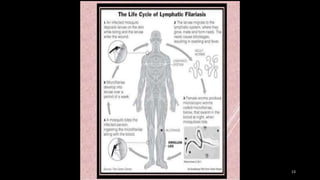
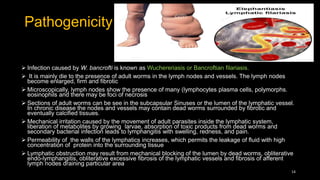
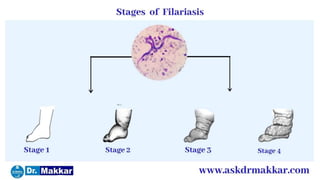
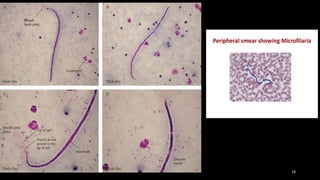
Wuchereria bancrofti causes lymphatic filariasis in humans. It resides in the lymph nodes and vessels. Mosquitoes transmit the infective larvae which develop into adults over a year. The adult female releases microfilariae that show nocturnal periodicity in blood. This allows transmission to mosquitoes whose bites can lead to lymphadenitis, lymphangitis and elephantiasis over time due to lymphatic damage and blockage. Diagnosis involves blood smears to detect microfilariae. Treatment is diethylcarbamazine for 12 days.