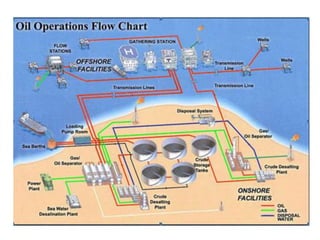
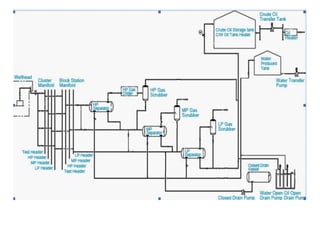
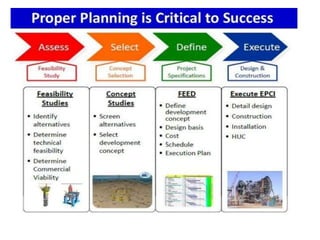
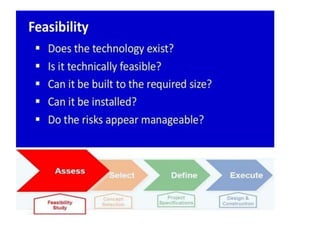
An oil field is an area containing hydrocarbon reservoirs located below the earth's surface that can extend for multiple miles. Field development planning evaluates multiple development options for a field to select the best approach based on factors like recovery rates, costs, risks and net present value. Key components of oil and gas infrastructure include wells, flowlines to connect wells to manifolds, gathering lines to transport from manifolds, and flow stations to separate hydrocarbons before pipelines transport to terminals for storage.