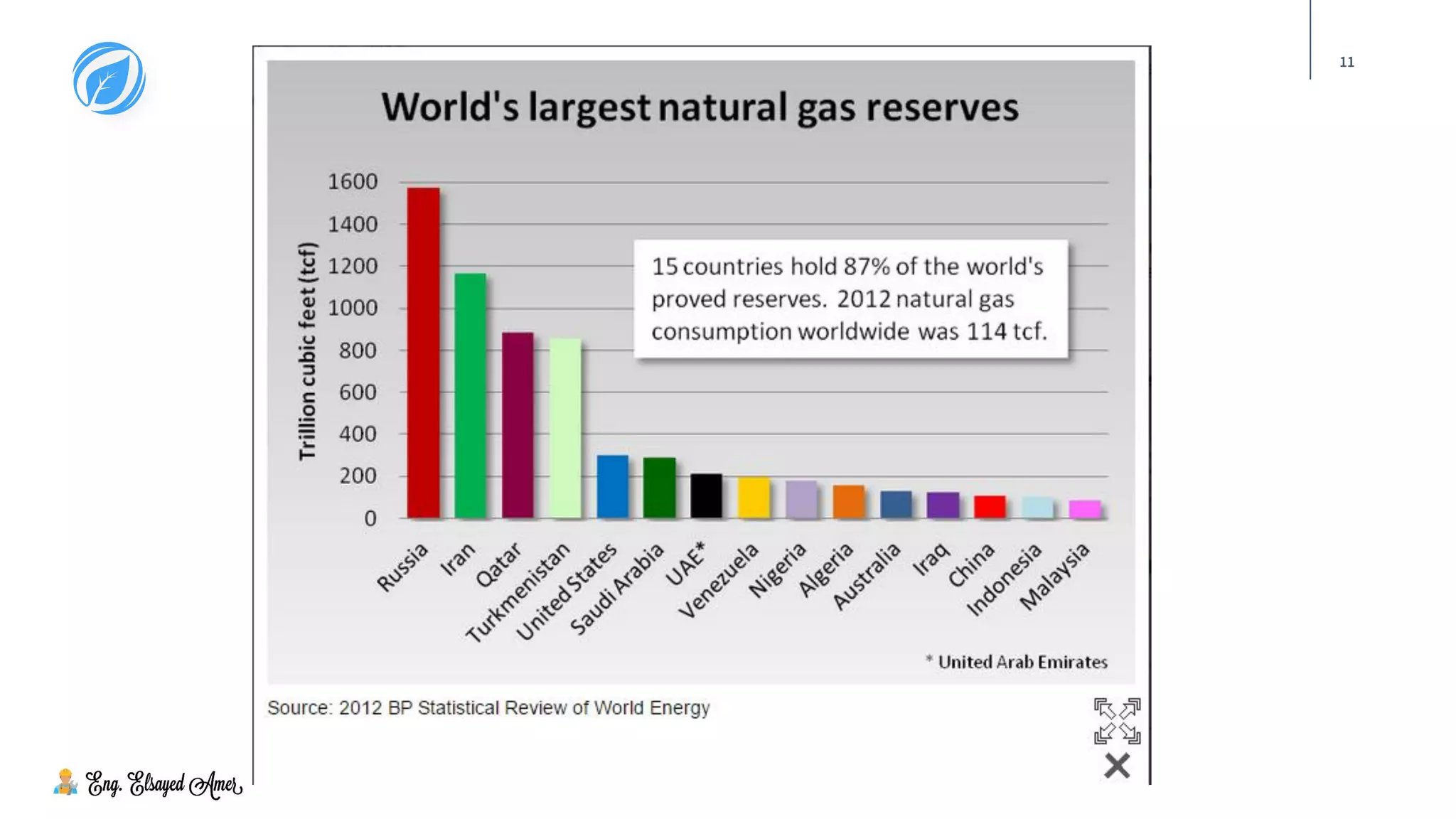
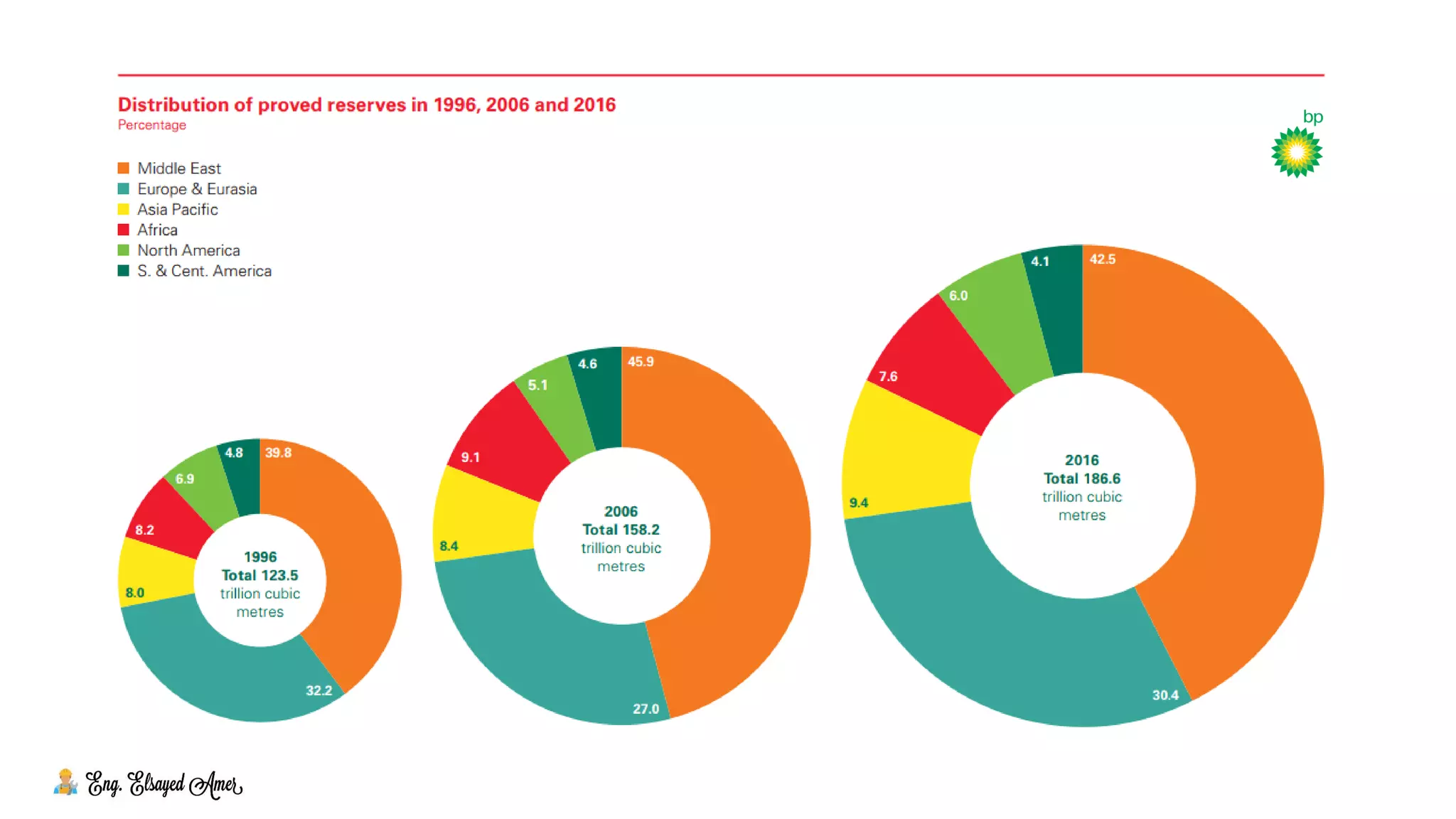
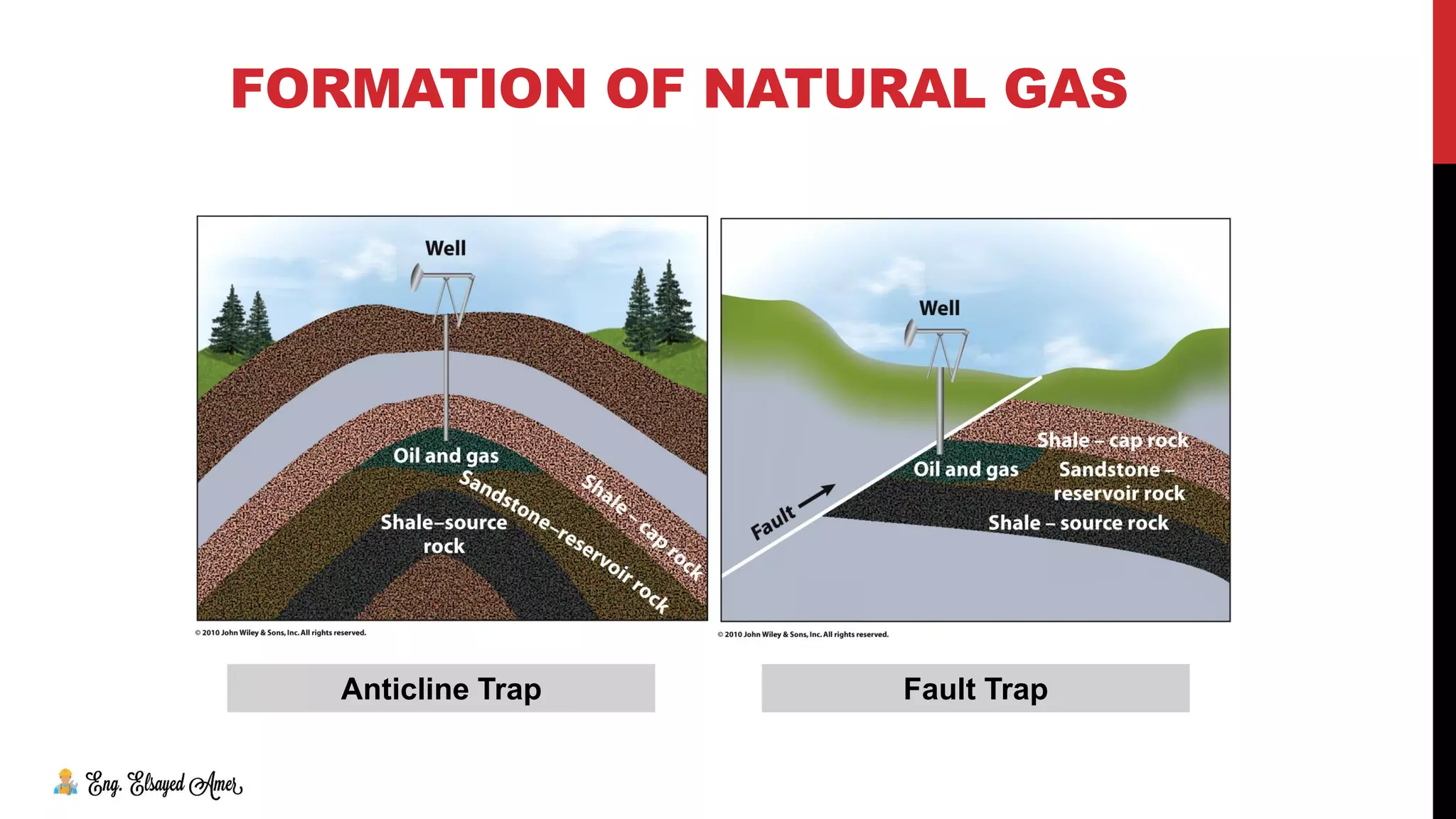
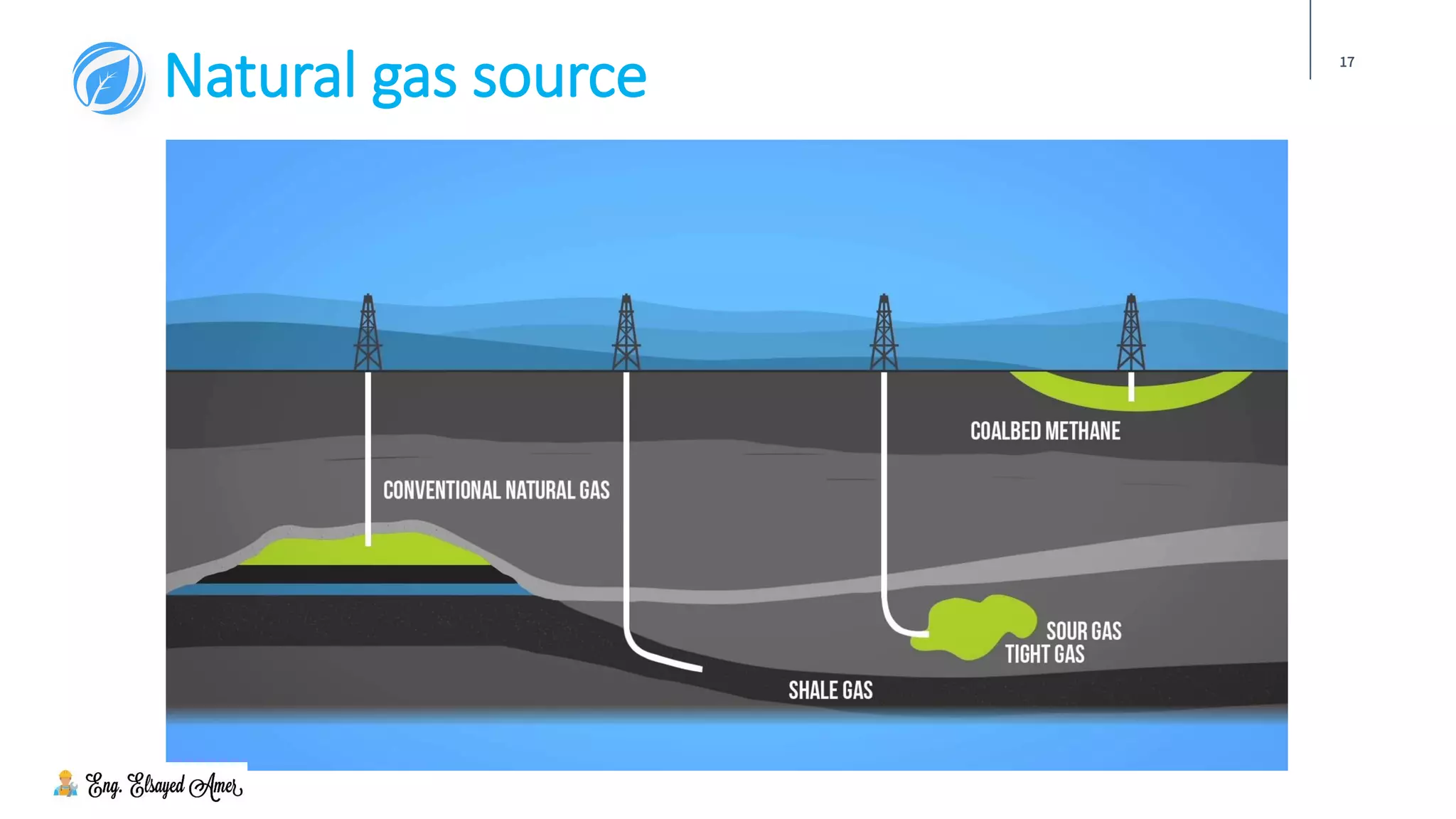
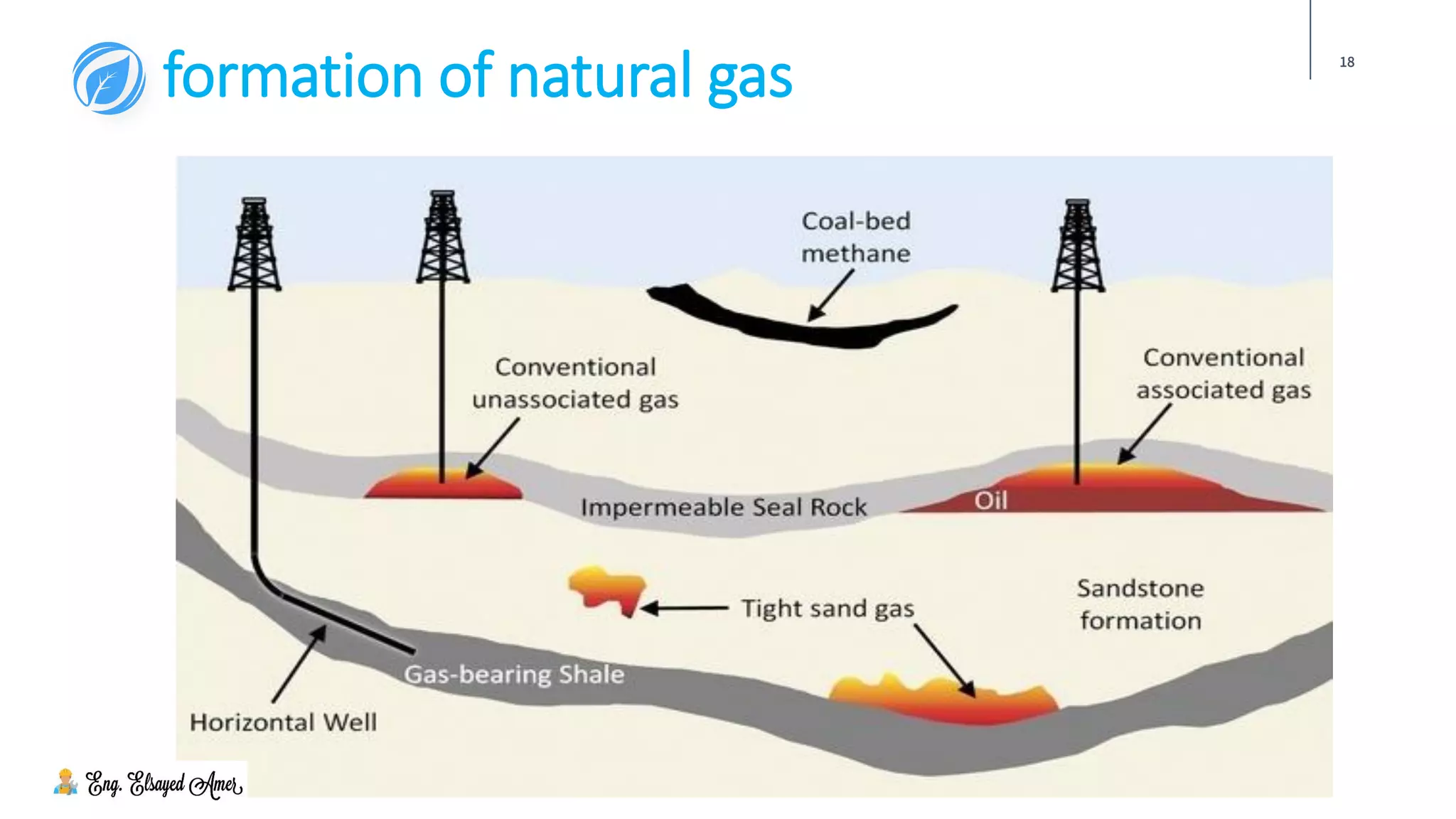
The document provides an overview of natural gas, highlighting its significance as a clean and essential energy source. It details the composition of natural gas, its global reserves, and various formations from which it is extracted, including gas wells and condensate wells. The document also includes comparative energy values and considerations regarding the pressure of gas production and the associated infrastructure.