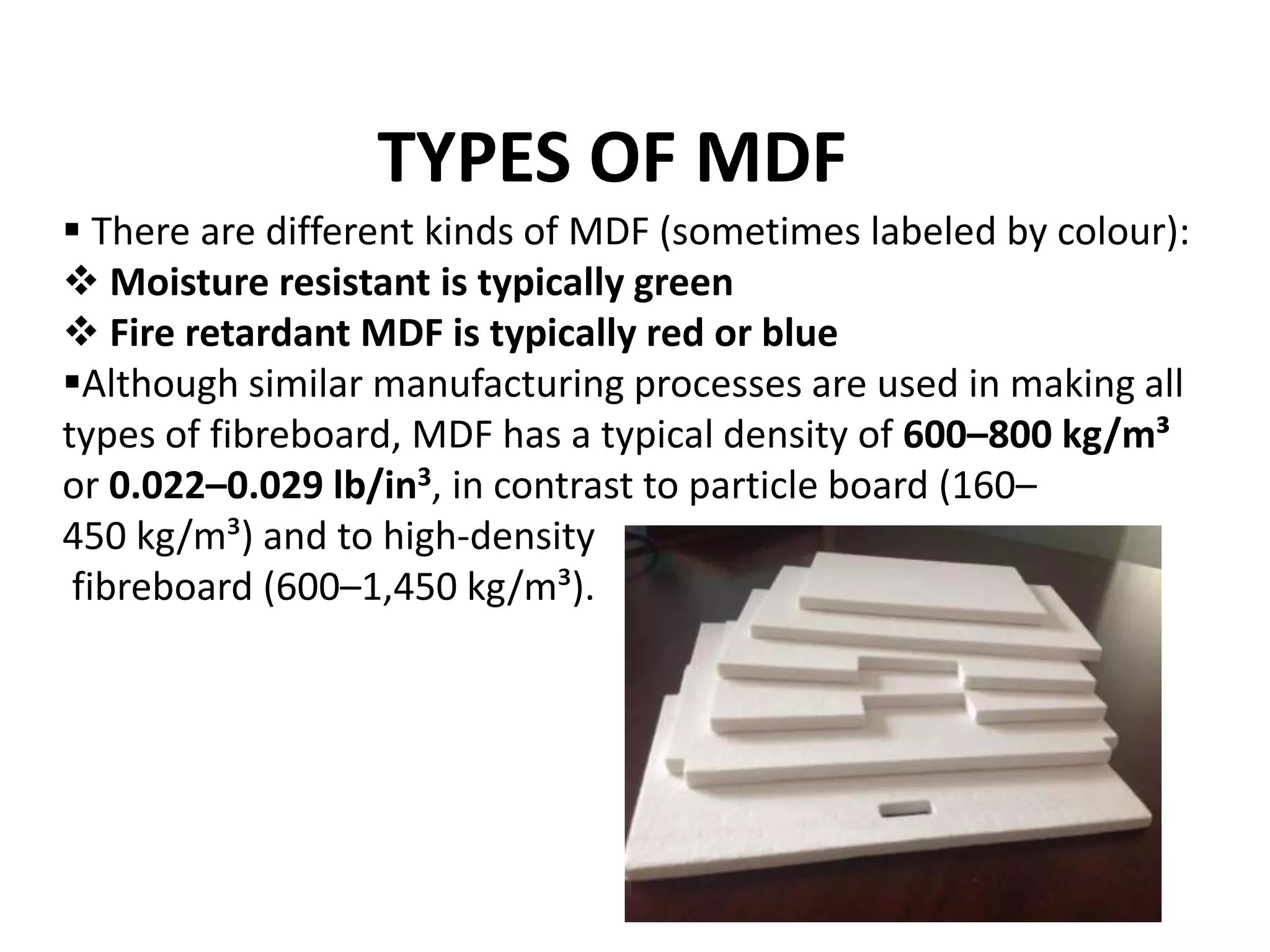
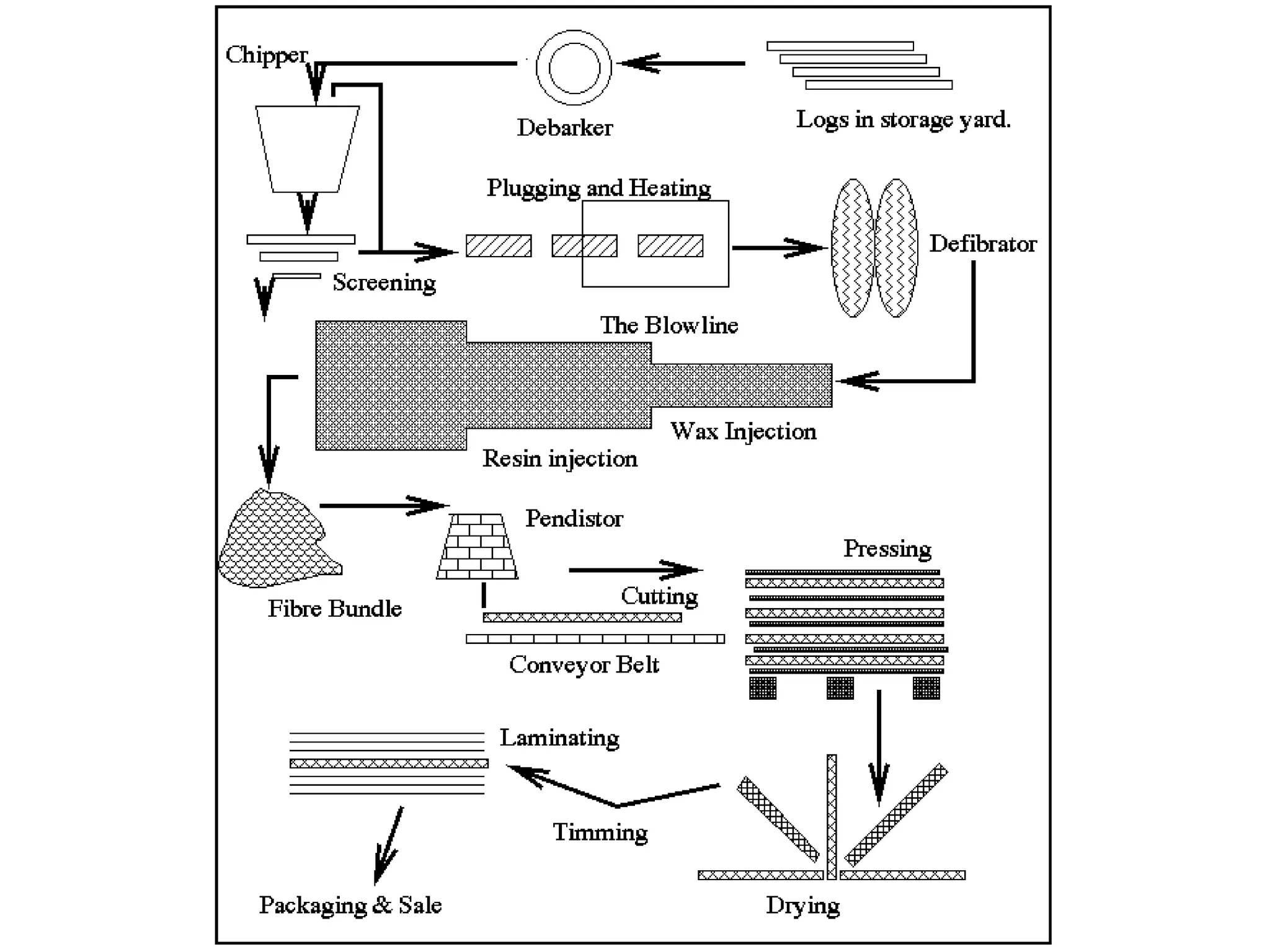
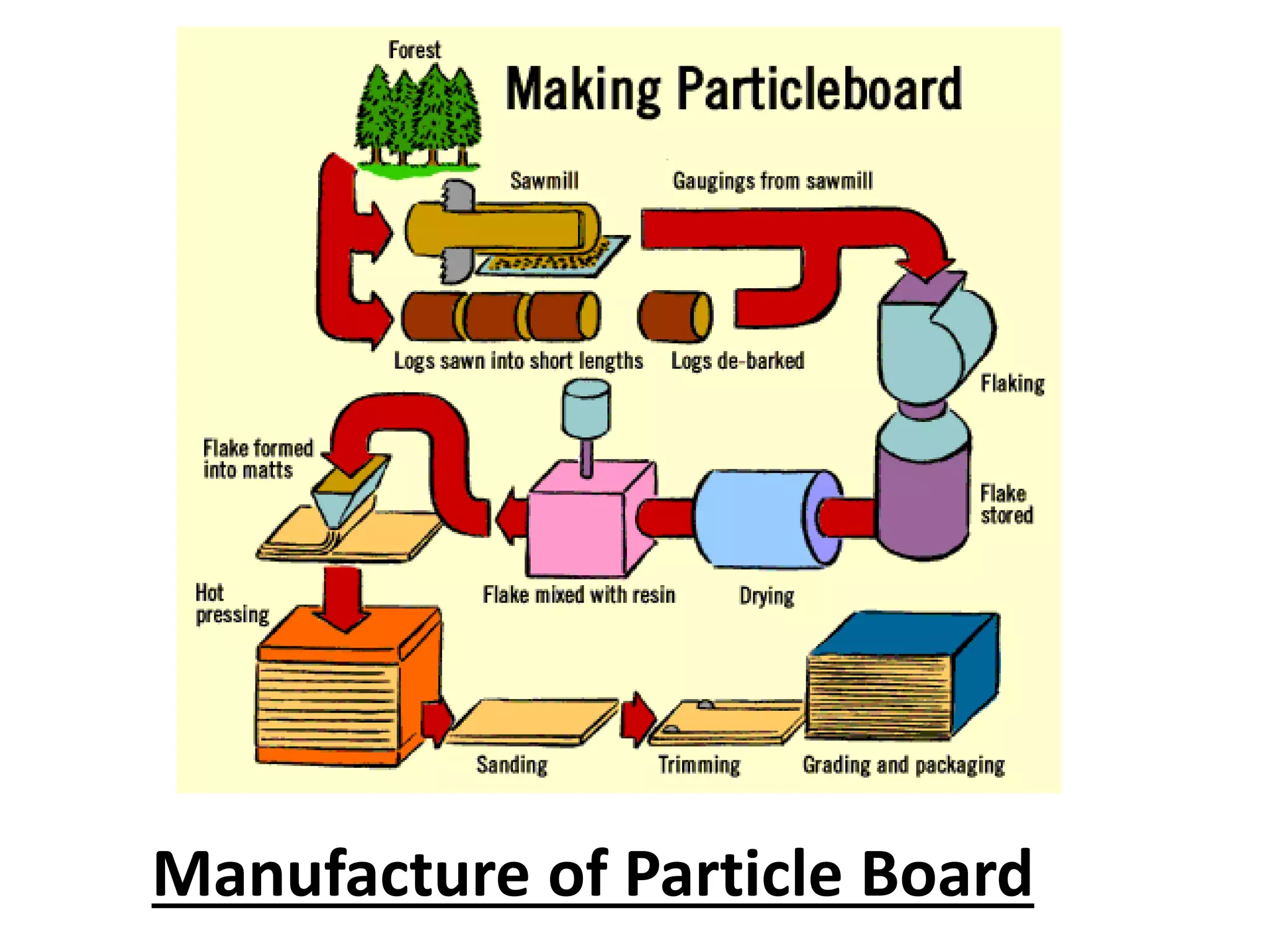
Medium Density Fiber Board (MDF) and particle board are engineered wood products made by breaking down wood fibers or particles, mixing them with adhesives like resin and wax, and forming panels under high temperature and pressure. MDF uses wood fibers while particle board uses wood chips or flakes. Both are cheaper alternatives to plywood and solid wood but are more prone to expansion from moisture. They are commonly used for furniture and interior construction applications.