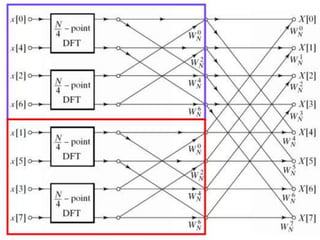
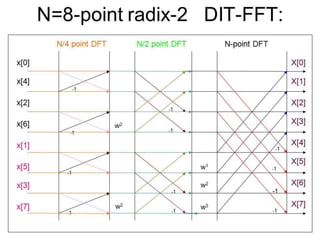
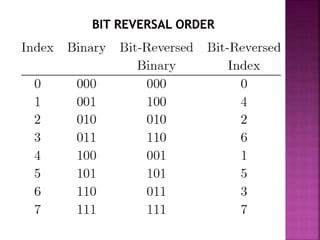
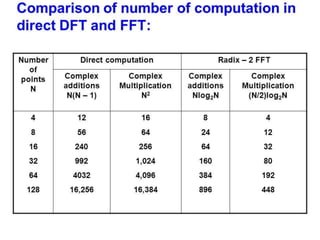
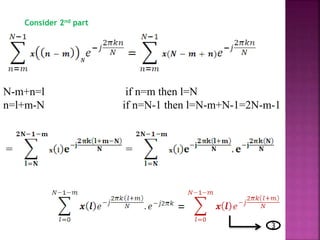
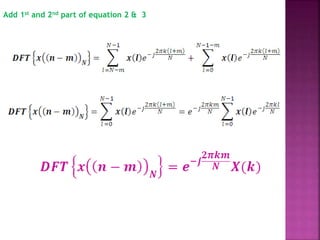
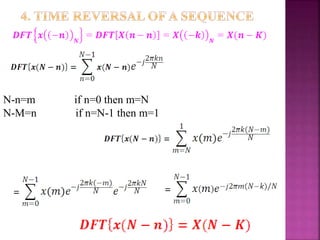
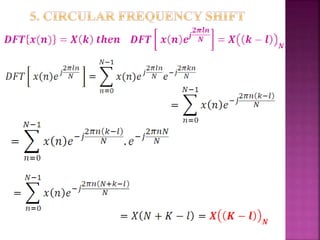
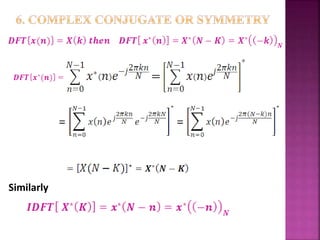
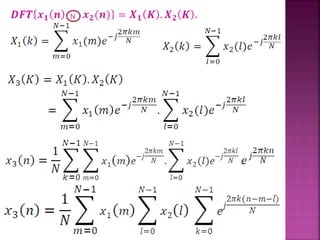
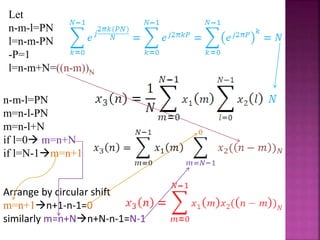
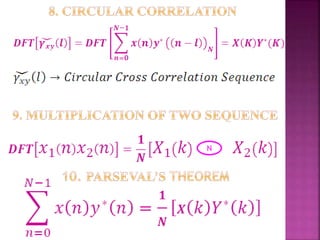
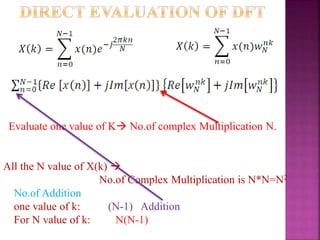
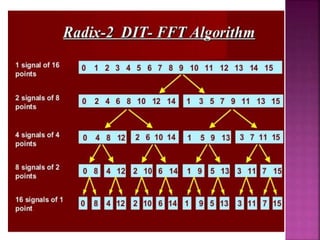
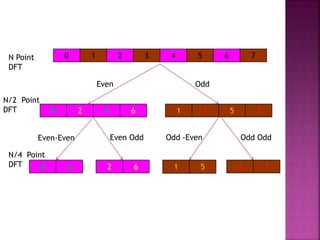
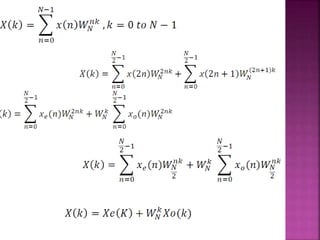
The document discusses the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm. It explains that FFT reduces the number of computations needed to calculate the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of a sequence by decomposing the DFT into successive DFTs of smaller sizes. Specifically, it breaks down the N point DFT into multiple N/2 point DFTs recursively until it reaches DFTs of size 1. This decomposition reduces the complexity from O(N^2) for DFT to O(NlogN) for FFT.






![Fast Fourier Transform
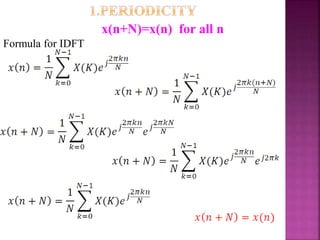
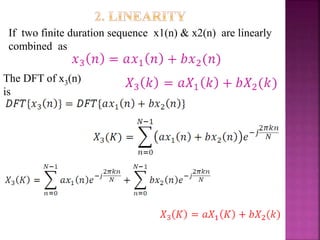
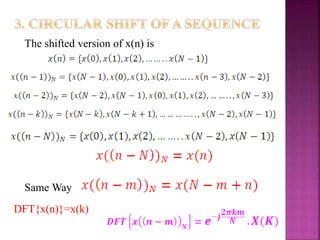
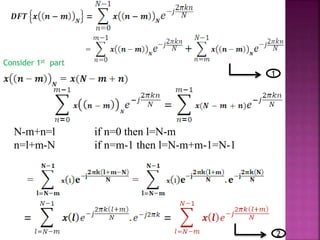
FFT applicable for two basic properties for twiddle
factor
It reduces the no.of complex multiplication
Basic Principle of FFT
Decomposing the computation of Discrete Fourier
transform of sequence of length N into successively smaller
discrete FTs
Types of FFT
1. Decimation in Time [DIT]
2. Decimation Frequency [DIF]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propertiesofdft-190717145448/85/Properties-of-dft-20-320.jpg)


![-1
-1
-1
-1
WN
0
WN
1
WN
2
WN
3
x[7]
x[5]
x[3]
x[1]
x[6]
x[4]
x[2]
x[0]
H[2]
H[3]
H[1]
H[0]
G[3]
G[2]
G[1]
G[0]
X[0]
X[1]
X[2]
X[3]
X[4]
X[5]
X[6]
X[7]
N/2 POINT
DFT
N/2 POINT
DFT
Figure 9.3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/propertiesofdft-190717145448/85/Properties-of-dft-26-320.jpg)