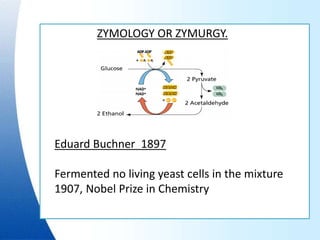
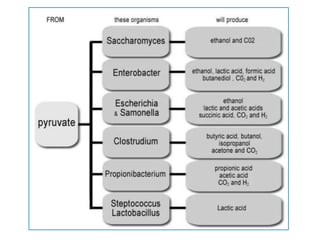
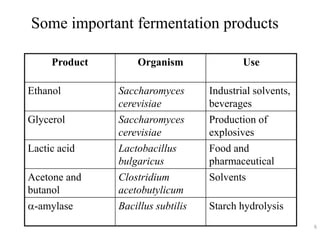
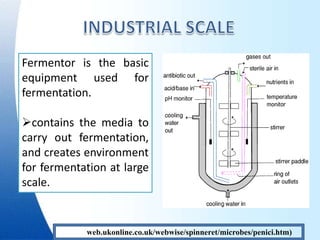
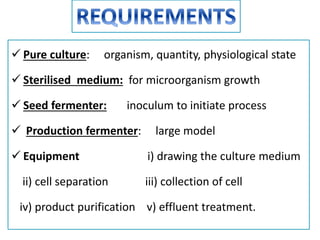
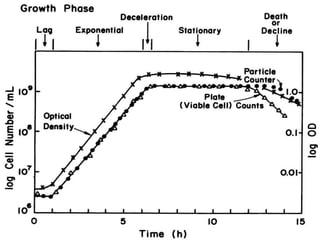
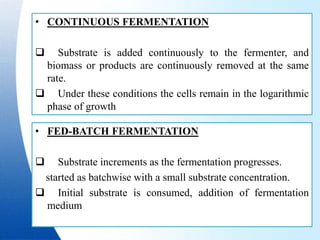
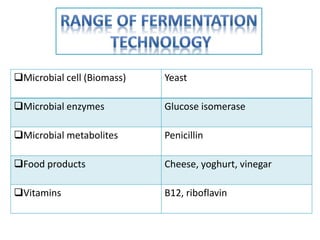
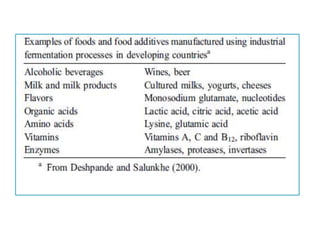
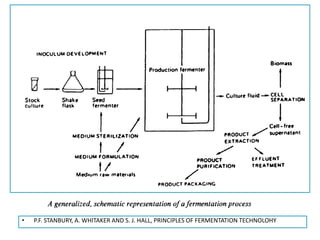
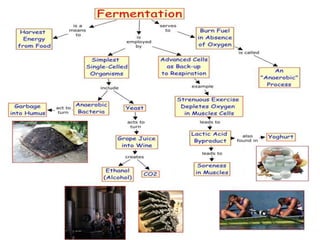
Fermentation is a process where microorganisms are grown on an industrial scale to produce commercial products through metabolic processes. Important fermentation products include ethanol, glycerol, lactic acid, acetone, butanol, and enzymes. Fermentations can occur via submerged or solid-state processes and are carried out using equipment like fermentors. The three main types of fermentation processes are batch, continuous, and fed-batch. Fermentation has advantages like food preservation and production of health and industrial products, though it also has disadvantages like potential microbial contamination issues.