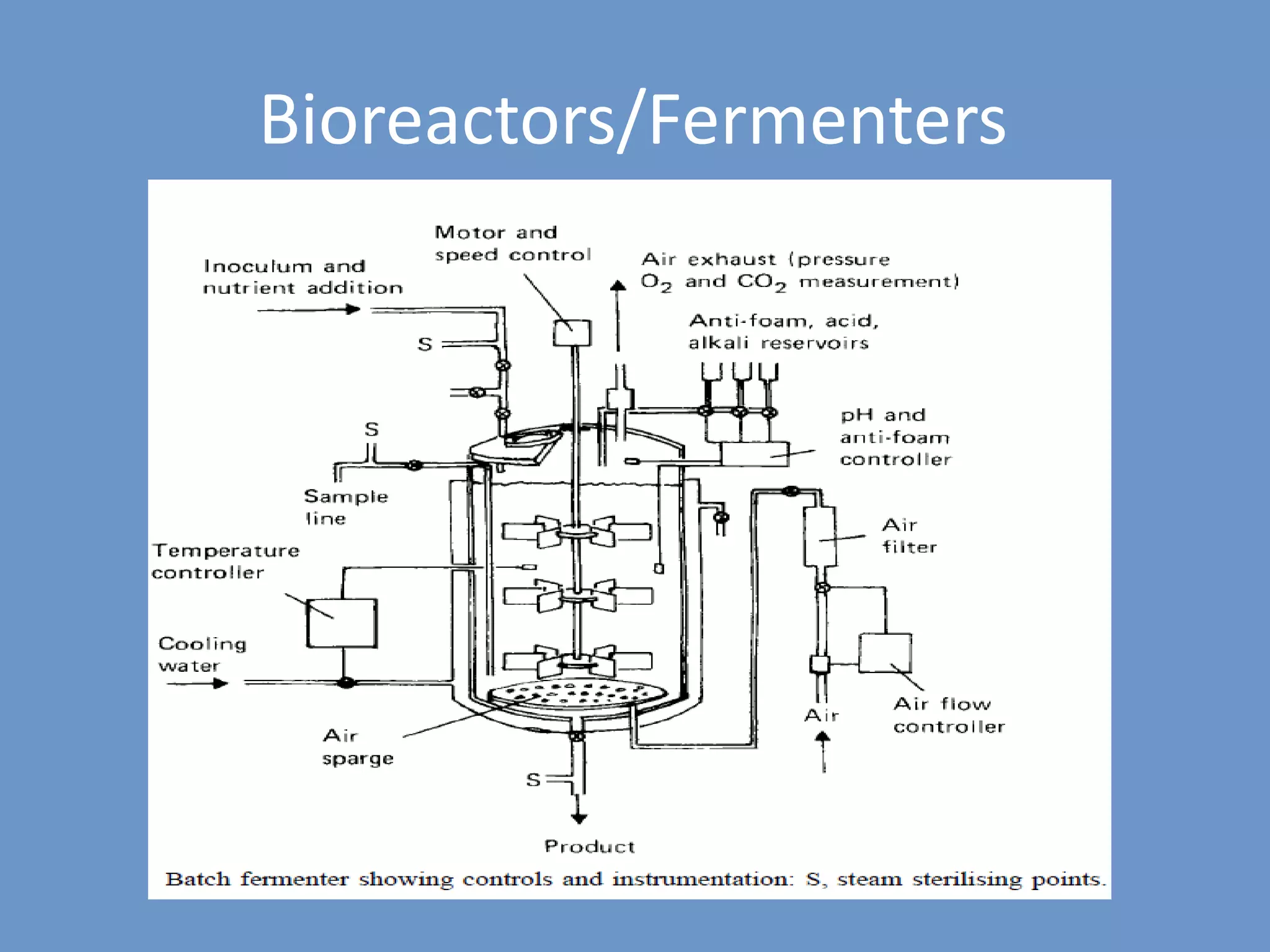
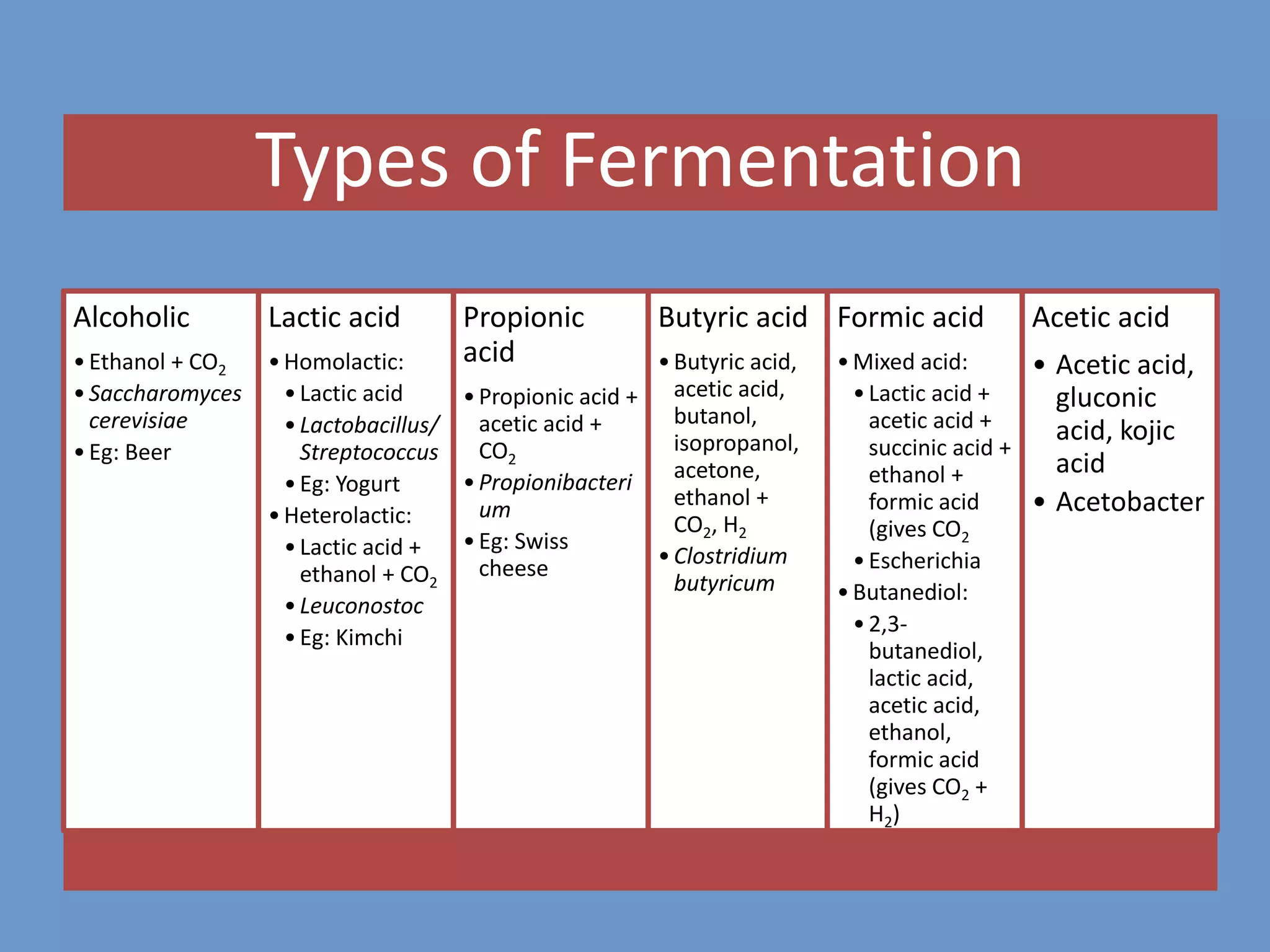
Fermentation is a metabolic process where organic compounds like carbohydrates are broken down by microorganisms to release energy without oxygen. It is used to produce a variety of foods, beverages, industrial products, and more. There are several types of fermentation including alcoholic, lactic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid fermentations. Fermentation can occur via solid state or submerged cultures in different types of bioreactors. Key factors that control microbial growth during fermentation include nutrients, pH, temperature, water activity, and presence of other microorganisms. Proper isolation techniques are required to culture pure microbial strains.