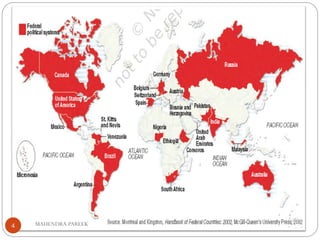
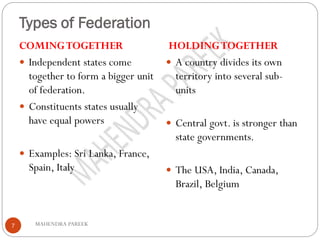
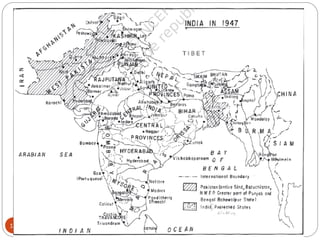
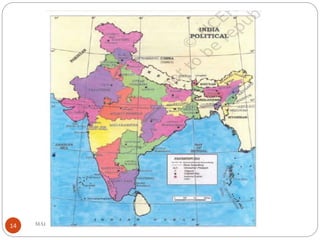
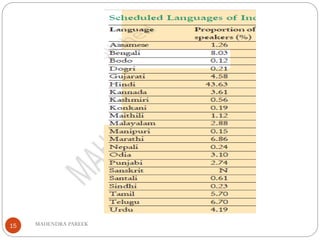
This document provides an overview of federalism and decentralization in India. It defines federalism and describes key features, including division of powers between central and state governments. India is characterized as a federal country based on its constitutional division of legislative powers into union, state and concurrent lists. The document also discusses the creation of states along linguistic lines, the role of the Supreme Court in disputes, and decentralization through rural and urban local governments like panchayats and municipalities. In summary, it outlines India's federal system of government with power shared between central, state and local levels according to the constitution.