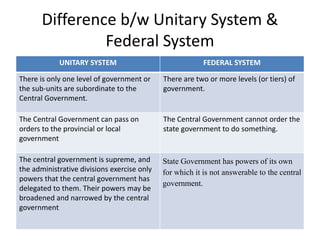
The document summarizes the key differences between a unitary system and federal system of government. In a unitary system, subnational governments are subordinate to the central government, whereas in a federal system there are multiple autonomous levels of government. The document then provides details on features of federalism like division of powers between levels of government and an independent judiciary. It also discusses examples of federalism in India including its three lists of powers and special status for some states.