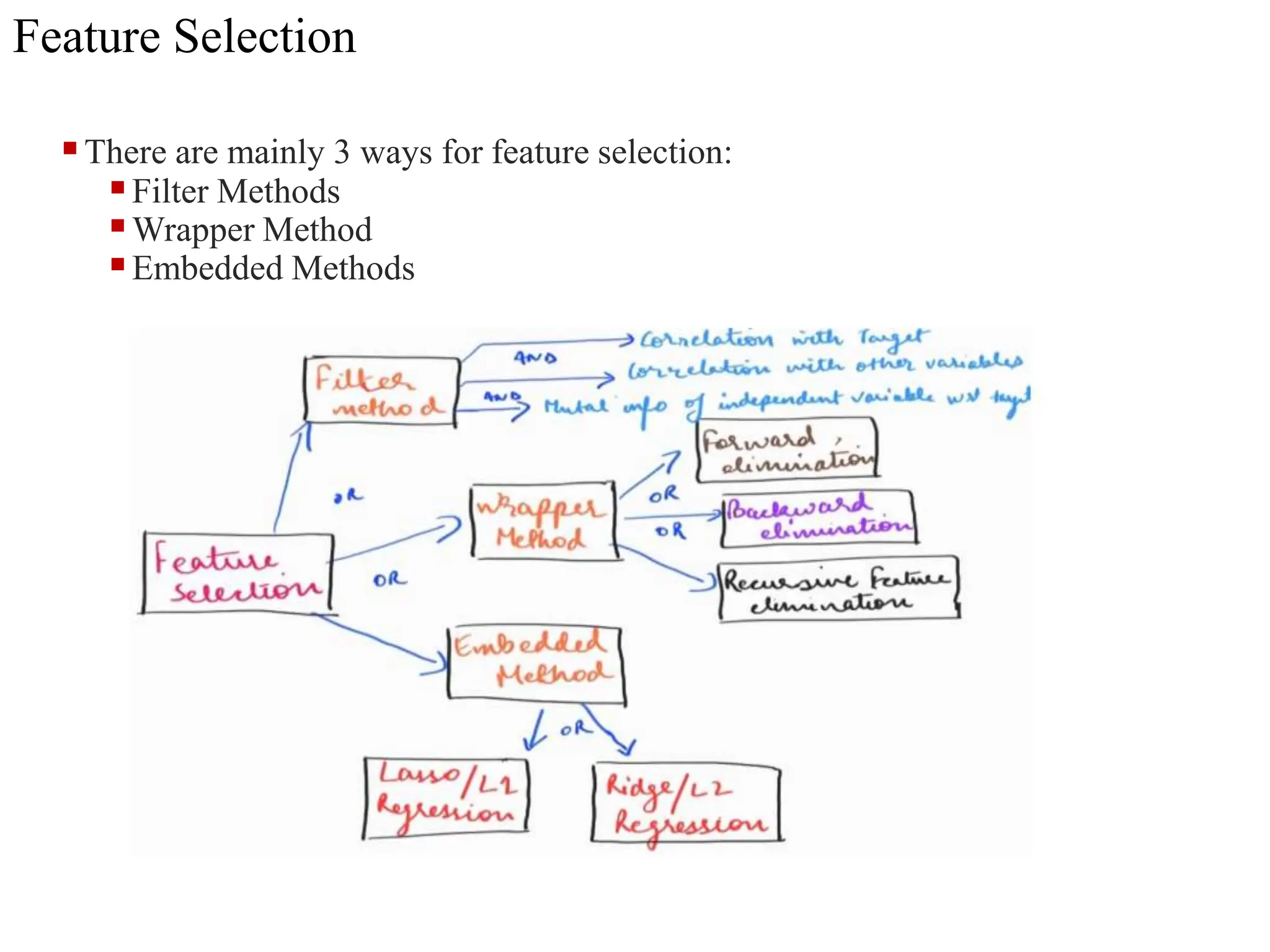
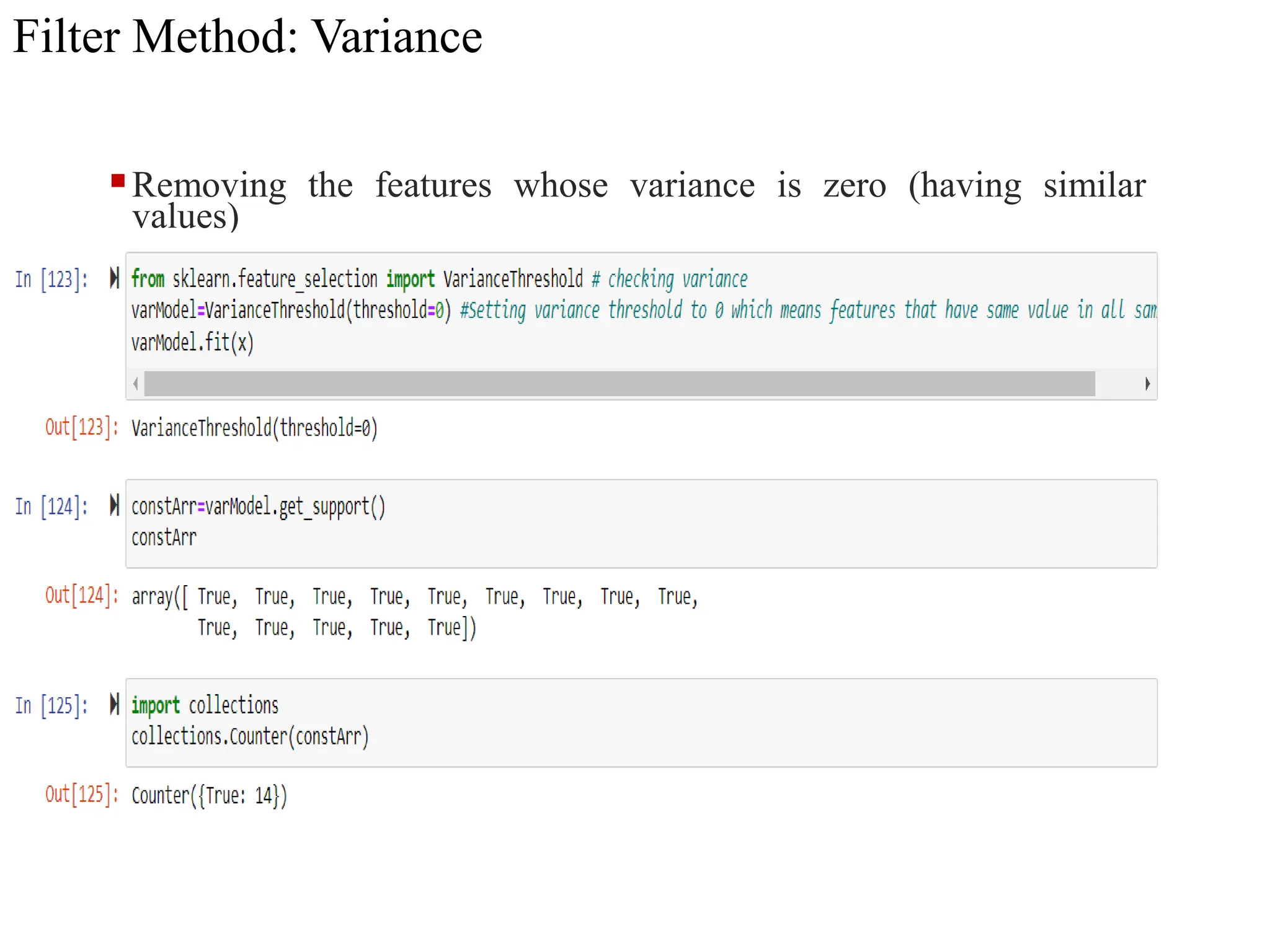
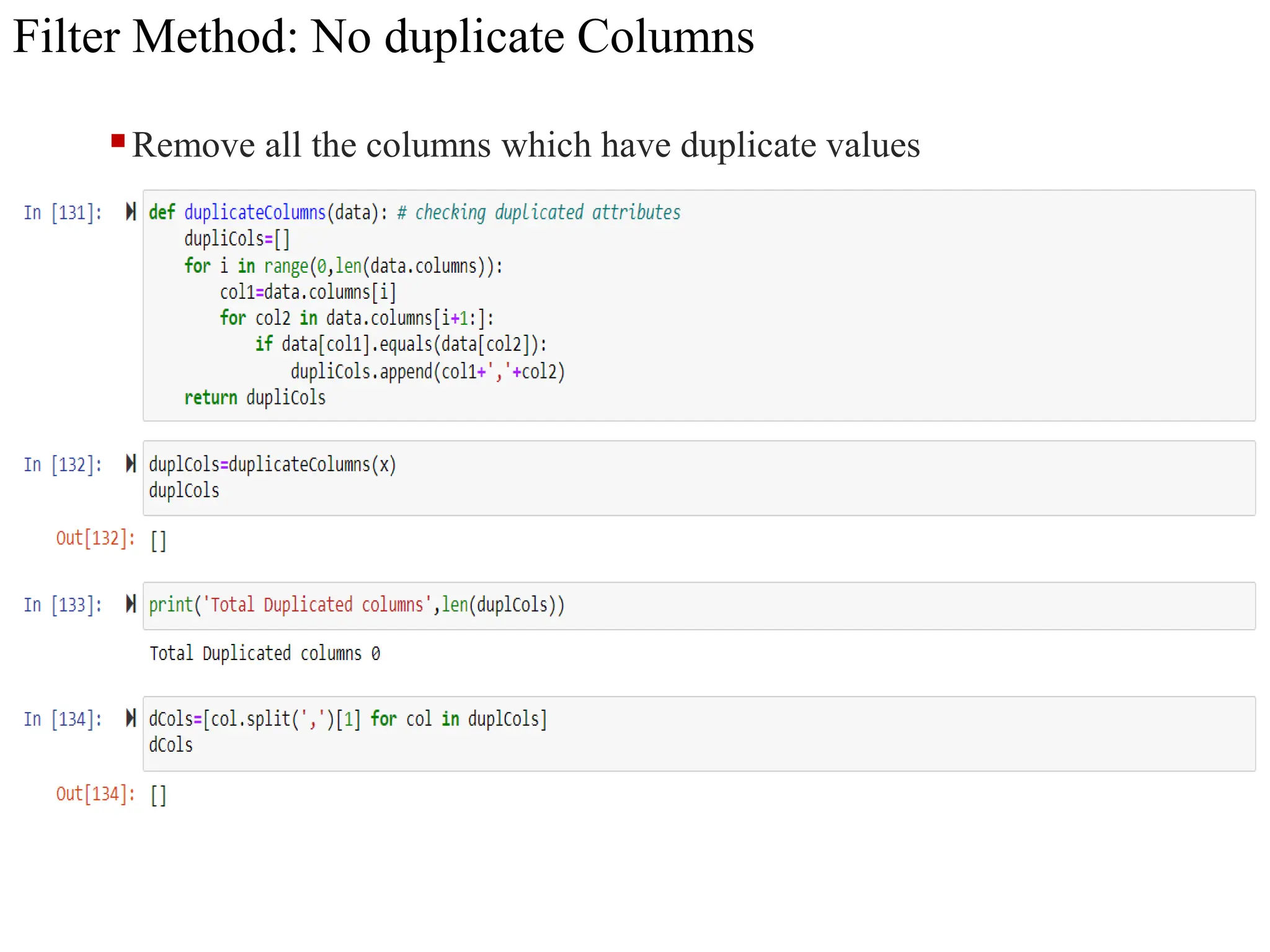
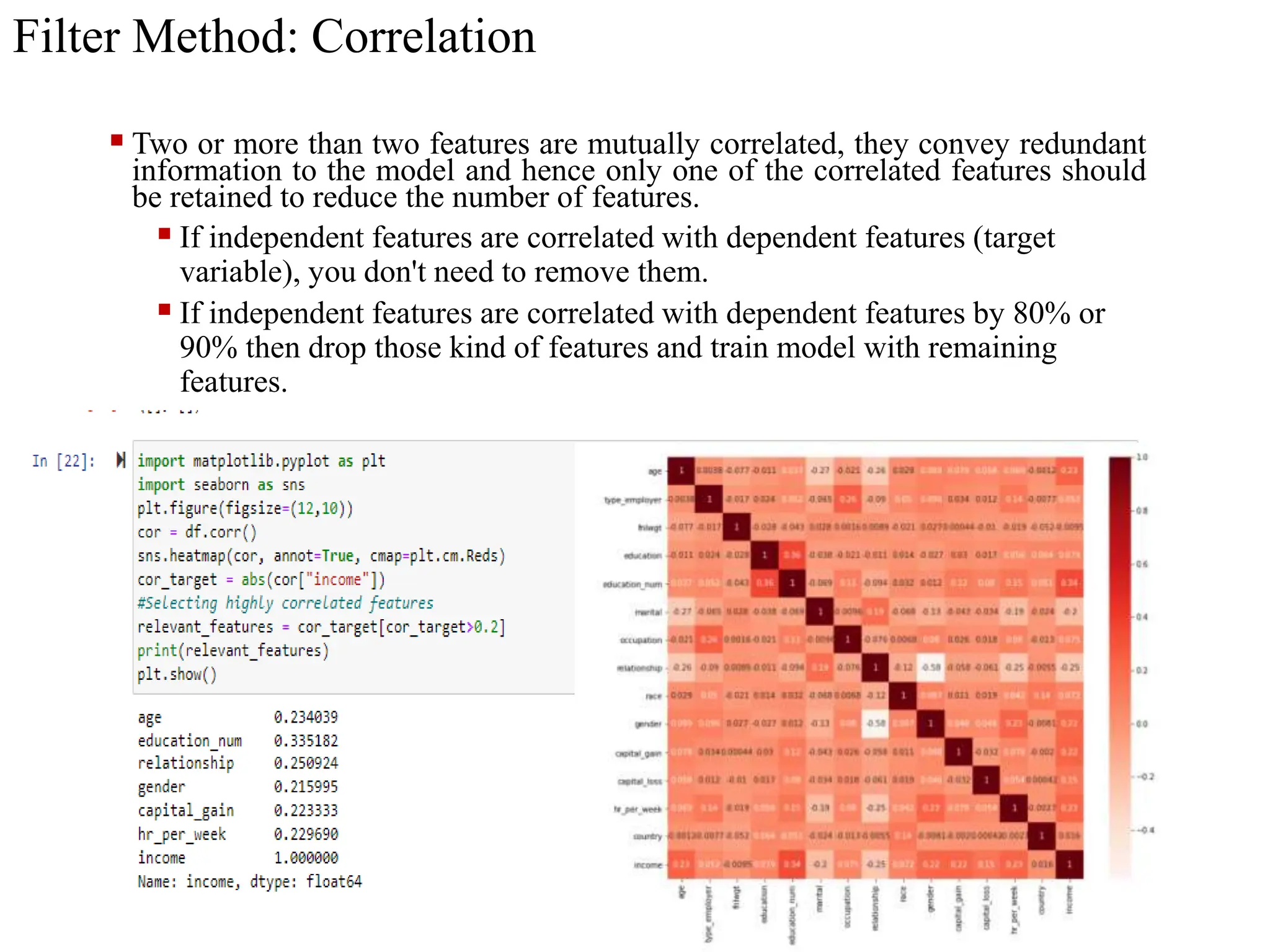
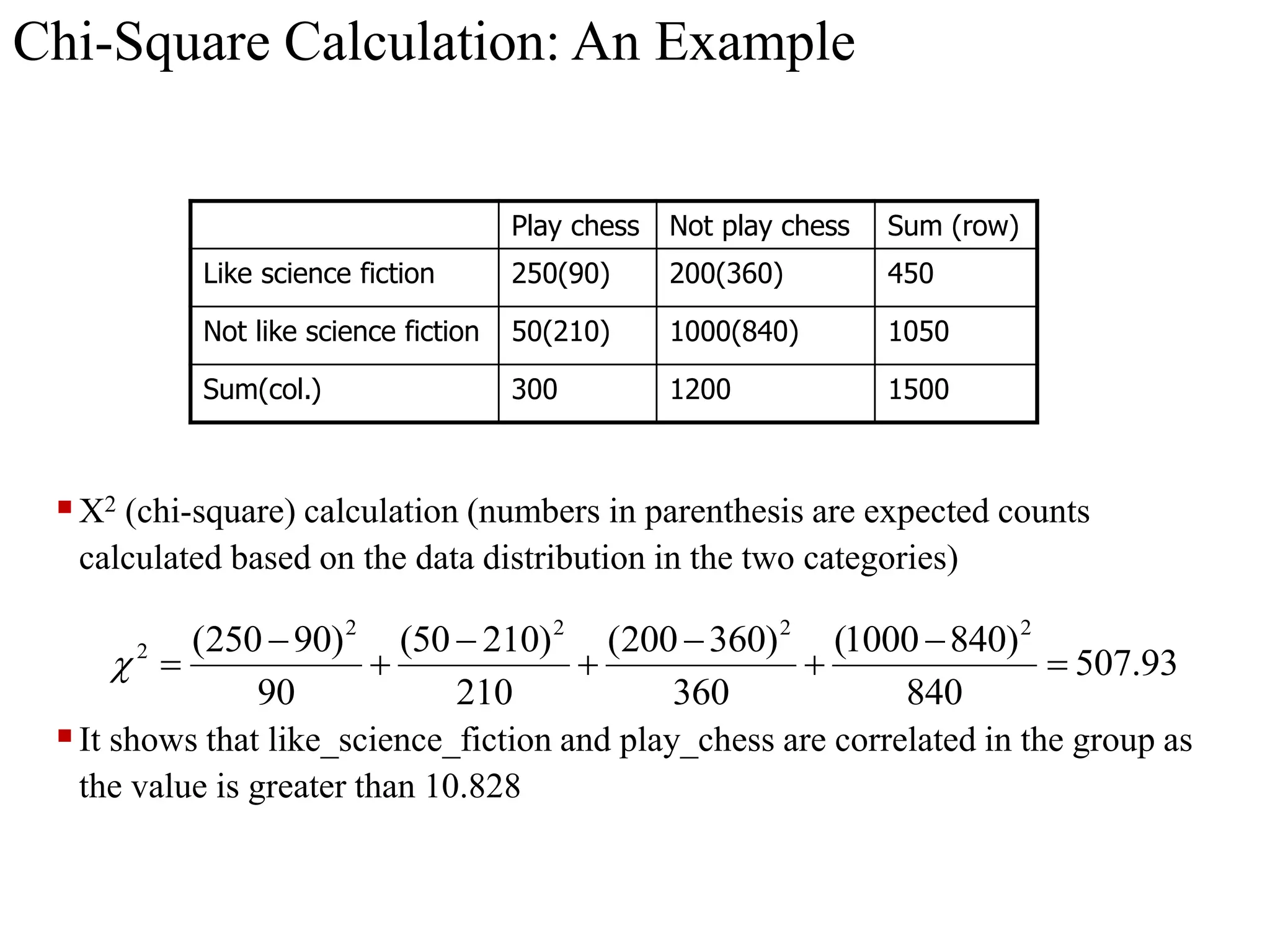
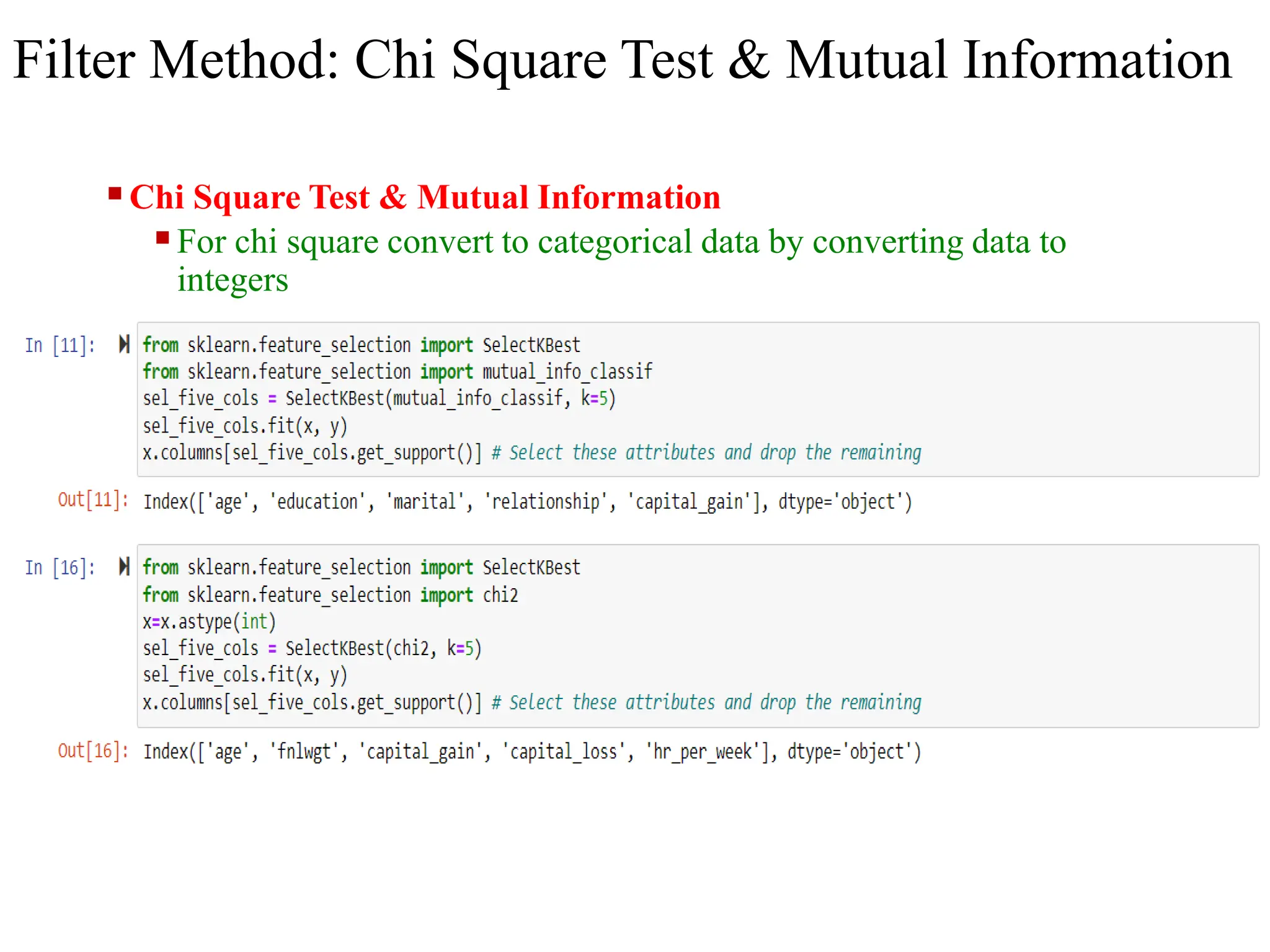
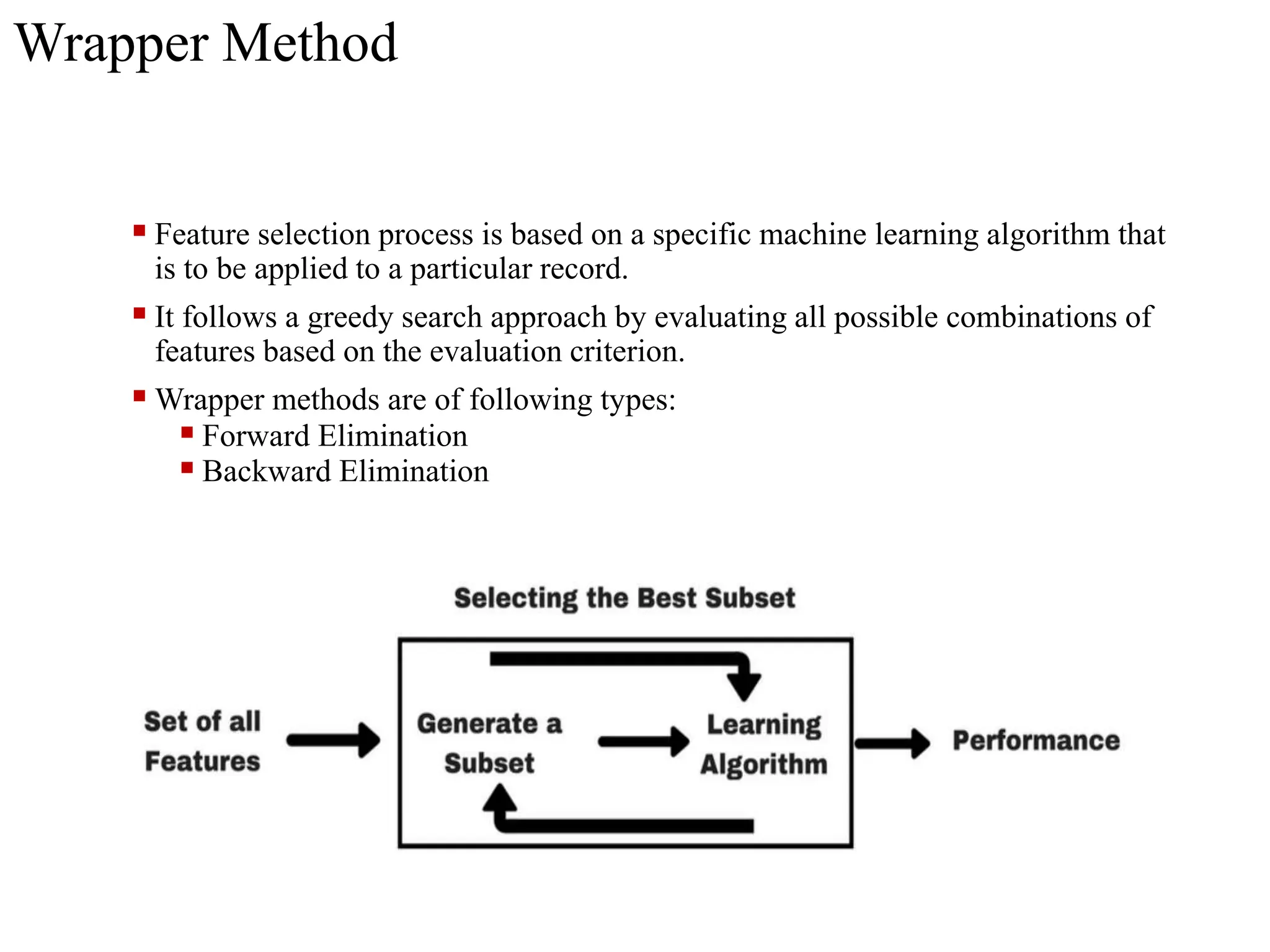
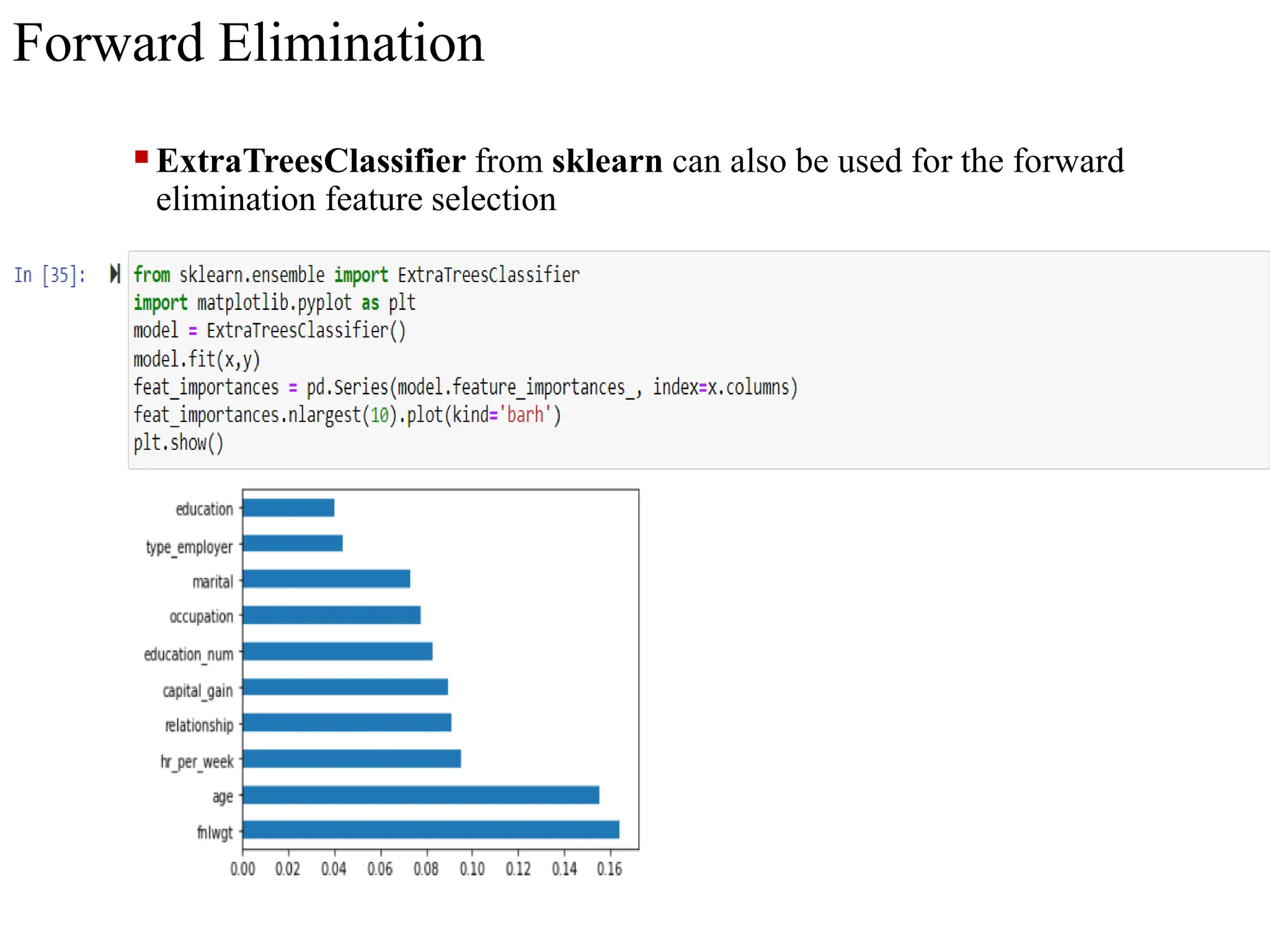
The document discusses feature selection methods in data science, highlighting three main approaches: filter methods, wrapper methods, and embedded methods. It details various filter techniques including univariate selection, variance checks, and chi-square calculations, as well as the greedy search approach of wrapper methods like forward and backward elimination. The text emphasizes the trade-offs between speed and accuracy in using these methods, noting that while filter methods are faster, wrapper methods can provide a more optimal subset of features despite potential overfitting.