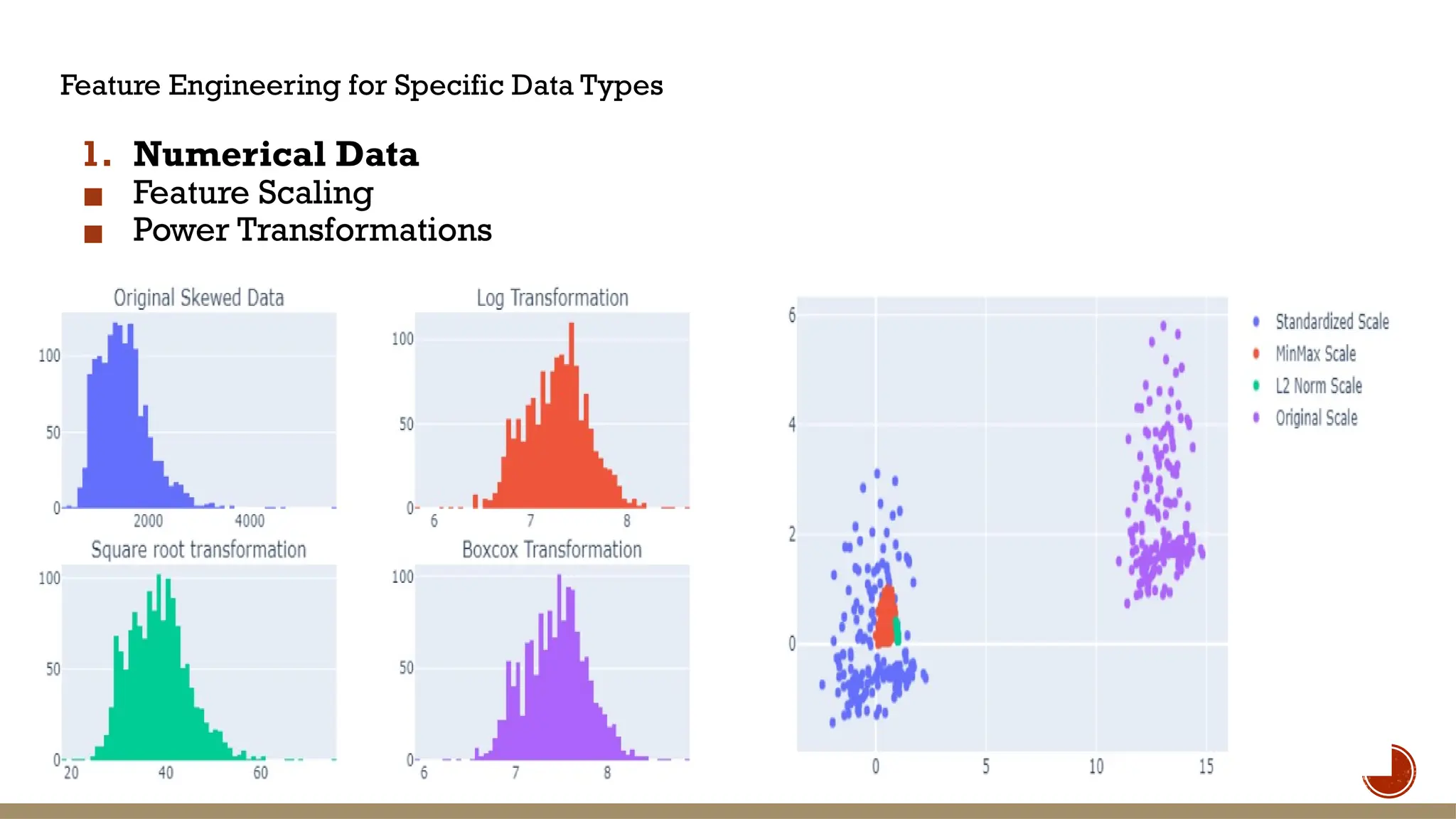
The document covers advanced feature engineering and selection techniques in machine learning, emphasizing the importance of transforming raw data into predictive features for improved model accuracy. It discusses feature transformation methods, scaling techniques, and various feature selection methods such as filter methods, wrapper methods, and embedded methods aimed at enhancing model performance. Additionally, the document introduces automated feature engineering and specific techniques for different data types, highlighting the use of tools like the EvalML library to streamline feature engineering processes.